Docker:Getting Started
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
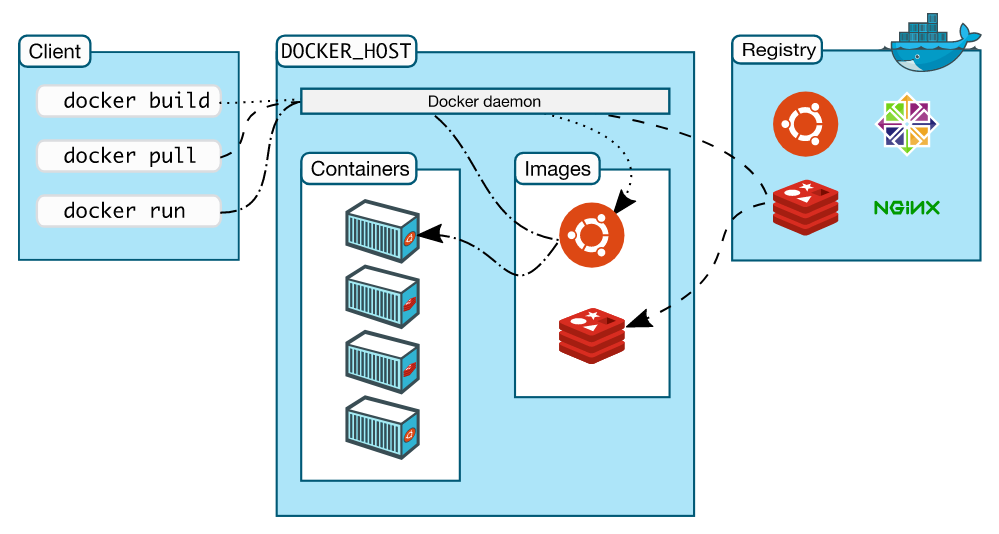
Docker architecture
Docker uses a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks to the Docker daemon, which does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing your Docker containers. The Docker client and daemon can run on the same system, or you can connect a Docker client to a remote Docker daemon. The Docker client and daemon communicate using a REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface. Another Docker client is Docker Compose, that lets you work with applications consisting of a set of containers.
1、Check CentOS version>= 3.10
by uname -r to check your linux version
$ uname -r
2、user root to login Centos。Make sure the packages of yum is the latest one
$ sudo yum update
3、uninstall if the version is too old
$ sudo yum remove docker docker-common docker-selinux docker-engine
4、install packages which is for yum to manage config, and another one is for device mapper
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
5、set the source
$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
6、all the versions of dockers
$ yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r
7、install docker
$ sudo yum install docker-ce 例如:sudo yum install docker-ce-17.12.0.ce
8、start and add in system start up
$ sudo systemctl start docker $ sudo systemctl enable docke
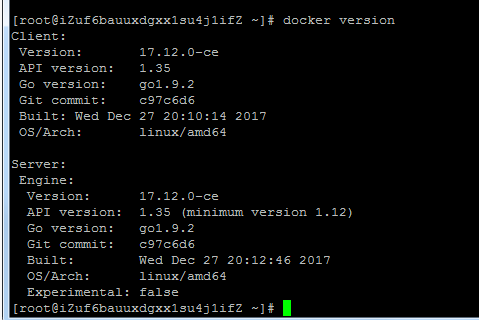
9、verify that the installation wa successfull:Client + Server
$ docker version

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号