实验5 支持向量机分类实验
作者: 康慎吾
一、实验要求
在计算机上验证和测试莺尾花数据的支持向量机分类实验,sklearn的支持向量机分类算法。
二、实验目的
1、掌握支持向量机的原理;
2、能够理解支持向量机分类算法;
3、掌握sklearn的支持向量机分类算法。
三、实验内容
👉1、请参考LinearSVC.pdf文档,将莺尾花的数据替换为make_blobs自动生成两个测试数据集(一个是两个类别数据完全分离,另一个是两个类别数据有很少部分的交叉),对比KNN,贝叶斯,决策树,随机森林还有LinearSVC的分界边界线的区别。
(1)数据完全分离
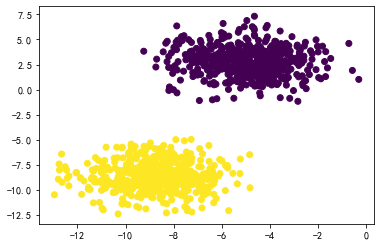
数据:
X,y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=2, cluster_std=1.5)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show()
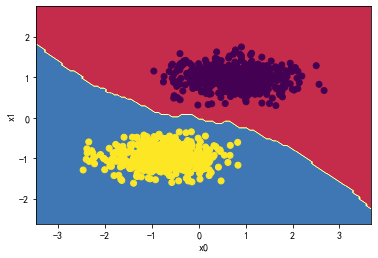
KNN:
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_classifier,X_standard,y)
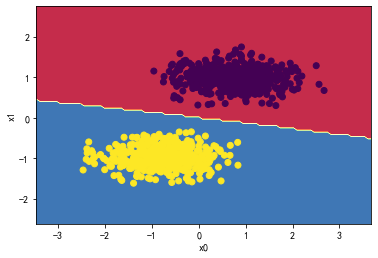
贝叶斯:
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
Gaussian_classifier = GaussianNB()
Gaussian_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(Gaussian_classifier,X_standard, y)
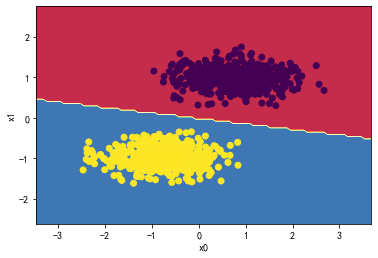
决策树:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
DTree_classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3)
DTree_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(DTree_classifier,X_standard, y)

随机森林:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500)
random_forest.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(random_forest,X_standard, y)

LinearSVC:
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
svc = LinearSVC()
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc = LinearSVC(C=0.01)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_

svc = LinearSVC(C=30)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
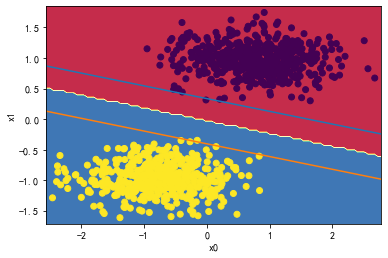
svc = LinearSVC(C=1000)
svc.fit(X_standard1, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard1, y)
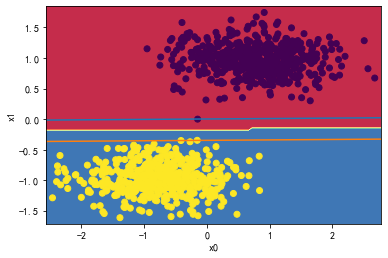
(2)数据部分交叉:
数据:
X,y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=2, cluster_std=1.5)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show()

KNN:
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_classifier,X_standard,y)
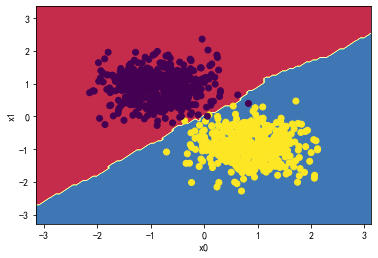
贝叶斯:
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
Gaussian_classifier = GaussianNB()
Gaussian_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(Gaussian_classifier,X_standard, y)
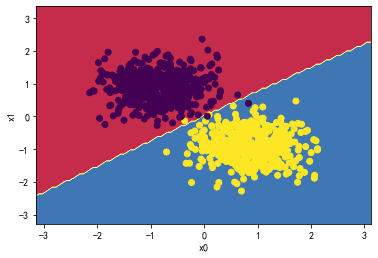
决策树:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
DTree_classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3)
DTree_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(DTree_classifier,X_standard, y)

随机森林:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500)
random_forest.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(random_forest,X_standard, y)

LinearSVC:
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
svc = LinearSVC()
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
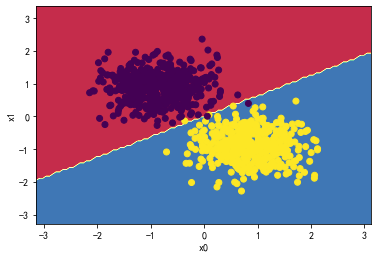
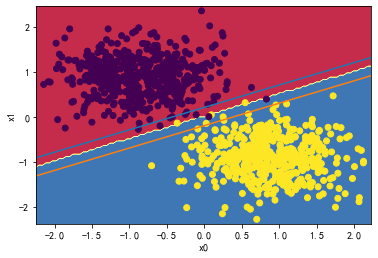
svc = LinearSVC(C=0.01)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_

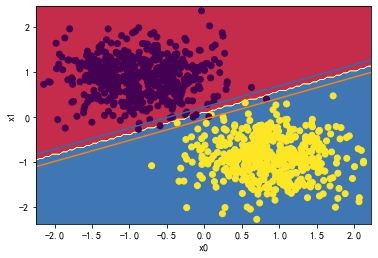
svc = LinearSVC(C=30)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
svc = LinearSVC(C=1000)
svc.fit(X_standard1, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard1, y)
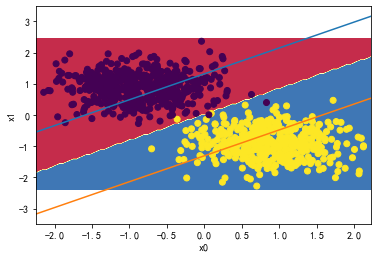
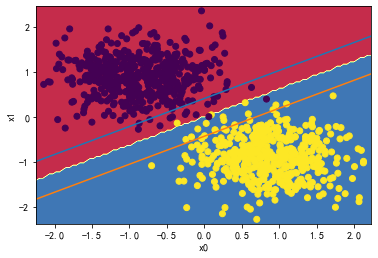
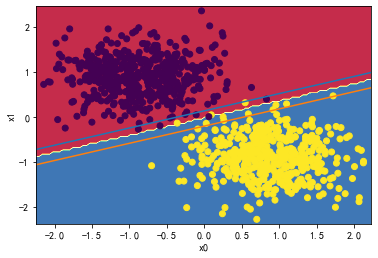
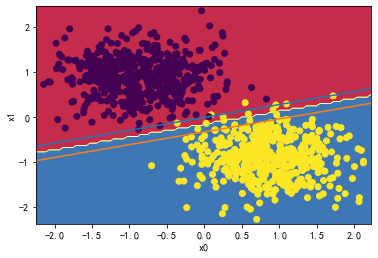
👉2、请详细测试LinearSVC中的C超参数对分类分界边界线的影响。
for i in [0.01,1,1000,10000000]:
svc = LinearSVC(C=i)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
👉3、请同时对比,LinearSVC,NuSVC和SVC,三者在莺尾花数据集,make_blobs生成的数据集,还有makemoons生成的数据集,还有makecircles生成的数据集,对比差异。
(1)生成数据对比:
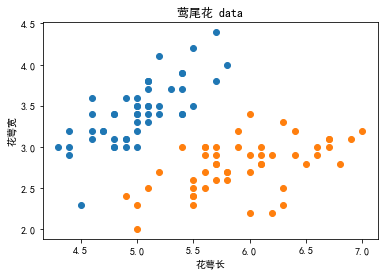
#↓莺尾花的数据集↓#
iris = datasets.load_iris()
#采用花瓣长宽
X = iris.data[0:100,:2]
y = iris.target[0:100]
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1])
plt.title('莺尾花 data')
plt.xlabel('花萼长')
plt.ylabel('花萼宽')
plt.show()
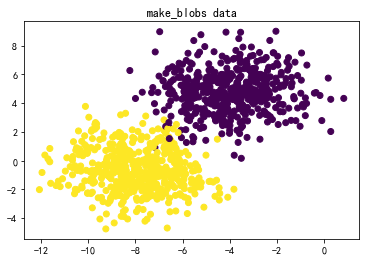
#↓make_blobs的数据集↓#
X,y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=2, cluster_std=1.5)
plt.title('make_blobs data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show()
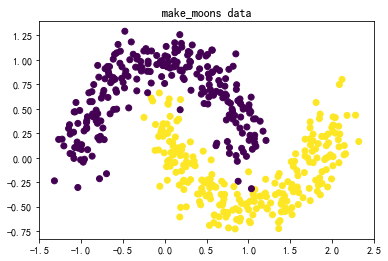
#↓makemoons的数据集↓#
X,y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.15)
plt.title('make_moons data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],marker='o',c=y)
plt.show()
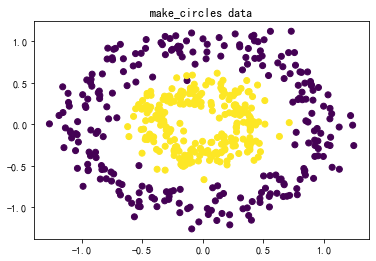
#↓makecircles的数据集↓#
X,y = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=500,factor=0.4,noise=0.12)
plt.title('make_circles data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],marker='o',c=y)
plt.show()
(2)三种SVM分类方法和四组数据综合对比:
备注:三种分类方法纵向对比,四组数组横向对比
数据:图3-1 莺尾花数据、图3-2 make_blobs生成的数据、图3-3 makemoons生成的数据、图3-4 makecircles生成的数据。
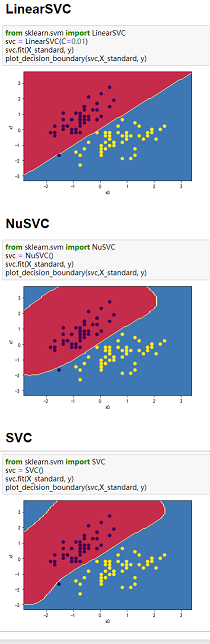
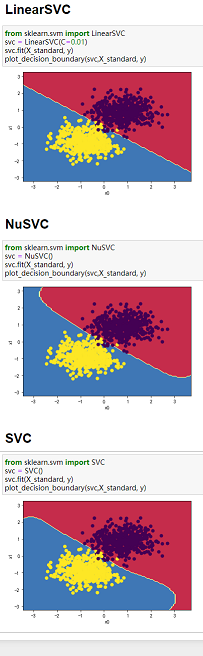
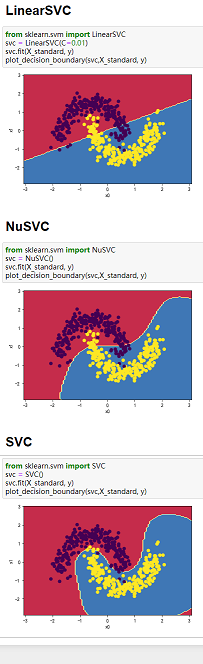
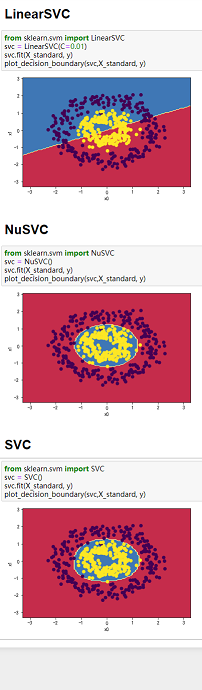
图3-1 图3-2 图3-3 图3-4
四、实验总结
1、掌握了支持向量机的原理
2、理解了支持向量机分类算法;
3、掌握了sklearn的支持向量机分类算法;
4、当数据分类界限明显且能用直线分割时,可以用LinearSVC;当数据类别分界线呈包围或者半包围状态时,用SVC最好。综上,SVC处理数据综合性最好。
五、附录
1、源码(注:空一行即jupyter notebook里一个可执行代码块):
- SVC实验5-1、2.ipynb
from sklearn import datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from warnings import simplefilter
simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 用来正常显示负号
X,y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=2, cluster_std=1.5)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show()
#X只有2个特征
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
x0_min, x0_max = X[:,0].min()-1, X[:,0].max()+1
x1_min, x1_max = X[:,1].min()-1, X[:,1].max()+1
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x0_min, x0_max, 100), np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, 100))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(x0.shape)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.ylabel('x1')
plt.xlabel('x0')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=np.squeeze(y))
plt.show()
#SVM数归一化,因为要算距离
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X)
X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)
knn_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_classifier,X_standard,y)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
Gaussian_classifier = GaussianNB()
Gaussian_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(Gaussian_classifier,X_standard, y)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
DTree_classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3)
DTree_classifier.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(DTree_classifier,X_standard, y)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500)
random_forest.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(random_forest,X_standard, y)
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
svc = LinearSVC()
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc = LinearSVC(C=0.01)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
svc.intercept_
#svc上下边界图绘制,X只有2个特征
def plot_svc_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
x0_min, x0_max = X[:,0].min()-0.1, X[:,0].max()+0.1
x1_min, x1_max = X[:,1].min()-0.1, X[:,1].max()+0.1
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x0_min, x0_max, 100), np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, 100))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(x0.shape)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.ylabel('x1')
plt.xlabel('x0')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=np.squeeze(y))
w = model.coef_[0]
b = model.intercept_[0]
#w0*x0 + w1*x1 +b =0
# x1 = -w0/w1*x0 - (b+1)/w1
plot_x = np.linspace(x0_min,x0_max,200)
up_y = -w[0]/w[1]*plot_x - (b+1)/w[1]
dn_y = -w[0]/w[1]*plot_x - (b-1)/w[1]
plt.plot(plot_x,up_y)
plt.plot(plot_x,dn_y)
plt.show()
svc = LinearSVC(C=i)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
np.sum(X_standard*svc.coef_+svc.intercept_,axis=1)
svc = LinearSVC(C=30)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
svc.coef_
X_standard1= X_standard.copy()
X_standard1[1,:]=np.array([-0.15,0])
svc = LinearSVC(C=1000)
svc.fit(X_standard1, y)
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard1, y)
- SVC实验5-3.ipynb
from sklearn import datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from warnings import simplefilter
simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 用来正常显示负号
iris = datasets.load_iris()
##采用花瓣长宽
X = iris.data[0:100,:2]
y = iris.target[0:100]
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1])
plt.title('莺尾花 data')
plt.xlabel('花萼长')
plt.ylabel('花萼宽')
plt.show()
X,y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=2, cluster_std=1.5)
plt.title('make_blobs data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show()
X,y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500,noise=0.15)
plt.title('make_moons data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],marker='o',c=y)
plt.show()
X,y = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=500,factor=0.4,noise=0.12)
plt.title('make_circles data')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],marker='o',c=y)
plt.show()
#X只有2个特征
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
x0_min, x0_max = X[:,0].min()-1, X[:,0].max()+1
x1_min, x1_max = X[:,1].min()-1, X[:,1].max()+1
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x0_min, x0_max, 100), np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, 100))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(x0.shape)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.ylabel('x1')
plt.xlabel('x0')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=np.squeeze(y))
plt.show()
#SVM数归一化,因为要算距离
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X)
X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
svc = LinearSVC(C=0.01)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
from sklearn.svm import NuSVC
svc = NuSVC()
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC()
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc,X_standard, y)
鄙人第一次写博客,(写着玩玩记录一下)
end



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号