java学习day28---(序列化/Properties集合/复制文件/lambda)
流的分类
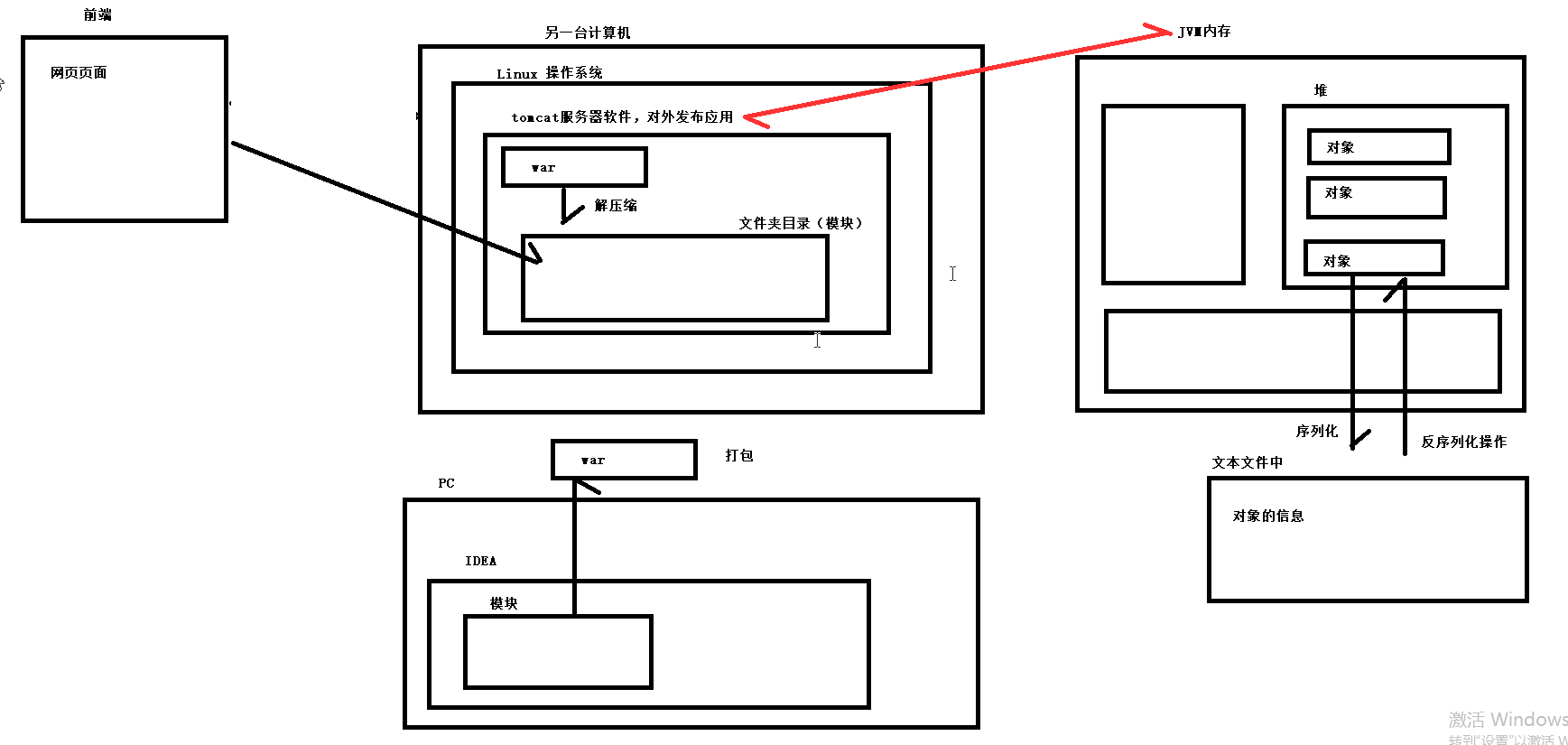
序列化流
概念:将JVM中内存的对象记录在文本中
反序列化:将文本中记录的对象,重现在JVM内存中
Serializable接口 只是作为一个标记的存在
序列化:
ObjectOutputStream类
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\abc.txt")) //创建一个序列化流对象,将对象存放在abc.txt文件中
oos.writeObject(对象名); 存储对象
序列化之后的文本是看不懂的!不是编码乱了!
反序列化:
ObjectInputSream类
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\abc.txt")) //创建一个反序列化流对象,将存放在abc.txt文件中的对象读入内存中
ois.readObject(对象名); 将对象读到内存中
返回值是 Object类型的对象,需要instanceof判断一下
反序列化循环
while (true)
取消校验机制
在对象所在的类中添加属性
private static final long seriaVersionUID = 30L; //值可以随意改,必定是固定的
Properties集合(Map集合)
将配置文件快速读取到Properties集合中
key一定是String,value一定是String
集合用于读取配置文件的,key和value都是固定类型的,因此Ptroperties不使用泛型
.load(传入一个输入字符流)
配置文件后缀.properties 可以读取中文,使用字节流
可以读取txt文件,但txt文件中有中文会乱码,在读取txt文件要用字符流
拷贝整个文件夹
String getName() 返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称。
boolean mkdir() 创建此抽象路径名指定的目录。
File[] listFiles() 返回一个抽象路径名数组,这些路径名表示此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件。
复制有多级目录的文件夹
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.描述数据源文件夹File对象
File srcFolder = new File("D:\\iofile");
//2.获取数据源文件夹的名称
String srcFolderName = srcFolder.getName();
//3.构造目的地文件夹File对象
File destFolder = new File("day10", srcFolderName);
//4.判断不存在则创建该文件夹
if (!destFolder.exists()){
destFolder.mkdir();
}
copyFolder(srcFolder,destFolder);
}
public static void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
public static void copyFolder(File srcFolder,File destFolder) throws IOException{
//5.遍历数据源文件夹,拿到下面的第一级的内容的File对象
File[] files = srcFolder.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()){
String srcZiFolderName = file.getName();
File destZiFolder = new File(destFolder, srcZiFolderName);
destZiFolder.mkdir();
copyFolder(file,destZiFolder);//递归
}else {
String srcFileName = file.getName();
File destFile = new File(destFolder, srcFileName);
copyFile(file,destFile);
}
}
}
lambda
可推导,可省略思想
一个接口中有且仅有一个抽象方法
lambda语法
() 参数个数
->参数传递
{}方法内容




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号