C++实现的一些功能代码
将当前时间输出到txt中:
调用c++中的fstream流文件,用tm结构获取日期和时间,其在time.h中定义
用ofstream的时候,ofstream out(txtpath,ios::app); //追加的方式写入 ofstream out(txtpath) //打开文件,从零开始写入
#include <iostream> #include <time.h> #include <fstream> using namespace std; void writeTimeToTxt(string txtname) { ofstream fid(txtname); time_t tt = time(NULL); struct tm local_time; localtime_s(&local_time, &tt); fid << "***testing date: " << local_time.tm_year + 1900 << "-" << local_time.tm_mon + 1 << "-" << local_time.tm_mday << " " << local_time.tm_hour << ":" << local_time.tm_min << ":" << local_time.tm_sec << endl; fid.close(); return; } int main() { string txtname = "time.txt"; writeTimeToTxt(txtname); return 1; }
输出的结果:
将当前时间以字符串的形式返回:

#include <time.h> string get_time_string() { time_t tt = time(NULL); struct tm local_time; localtime_s(&local_time, &tt); clock_t now_clock = clock(); int msecond = now_clock % CLOCKS_PER_SEC; char text[256]; sprintf(text, "%d%d%d%d%d%d%03d", local_time.tm_year + 1900, local_time.tm_mon + 1, local_time.tm_mday, local_time.tm_hour, local_time.tm_min, local_time.tm_sec, msecond); return text; }
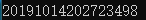
通过argv向程序中输入参数:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { if (4 != argc) { cout << "input params error" << endl; return -1; } string type = argv[1]; string cutmethod = argv[2]; string resolution = argv[3]; cout << type << "_" << cutmethod << "_" << resolution << endl; system("pause"); return 1; }
输出结果: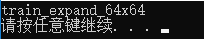
在vs中参数的输入,项目-属性-调试-命令参数-train expand 64x64 输入的字符串,双引号可加可不加
生成的exe调用过程中,.\OutputTimeToTxt.exe "train" expand 64x64 字符串的双引号,可加可不加
linux:
以微秒为单位,返回string类型的时间戳,并以时间戳为名称,建立文件夹

#include <iostream> #include <sys/time.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> std::string get_nowtime_linux() { struct timeval tv; gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); std::string now_time=std::to_string(tv.tv_sec)+"_"+std::to_string(tv.tv_usec); return now_time; } int main(int argc,char** argv) { std::string now_time=get_nowtime_linux(); std::cout<<now_time<<std::endl; int isCreate = mkdir(now_time.c_str(),S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IXUSR | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO); if( !isCreate ) printf("create path:%s\n",now_time.c_str()); else printf("create path failed! error code : %d %s \n",isCreate,now_time.c_str()); return 1; }
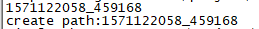
二维数组传引用:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*传二维数组*/
//第1种方式:传数组,第二维必须标明
/*void display(int arr[][4])*/
void display1(int arr[][4], const int irows)
{
for (int i = 0; i<irows; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j<4; ++j)
{
cout << arr[i][j] << " "; //可以采用parr[i][j]
arr[i][j] += 1;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
//第2种方式:一重指针,传数组指针,第二维必须标明
/*void display(int (*parr)[4])*/
void display2(int(*parr)[4], const int irows)
{
for (int i = 0; i<irows; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j<4; ++j)
{
cout << parr[i][j] << " "; //可以采用parr[i][j]
parr[i][j] += 1;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
//注意:parr[i]等价于*(parr+i),一维数组和二维数组都适用
//第3种方式:传指针,不管是几维数组都把他看成是指针
/*void display3(int *arr)*/
void display3(int *arr, const int irows, const int icols)
{
for (int i = 0; i<irows; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j<icols; ++j)
{
cout << *(arr + i*icols + j) << " "; //注意:(arr+i*icols+j),不是(arr+i*irows+j)
*(arr + i*icols + j) += 1;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[][4] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 };
int irows = 3;
int icols = 4;
//display1(arr, irows);
display2(arr, irows);
//注意(int*)强制转换.个人理解:相当于将a拉成了一维数组处理。
//display3((int*)arr, irows, icols);
for (int i = 0; i < irows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < icols; j++)
printf("%d ",arr[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号