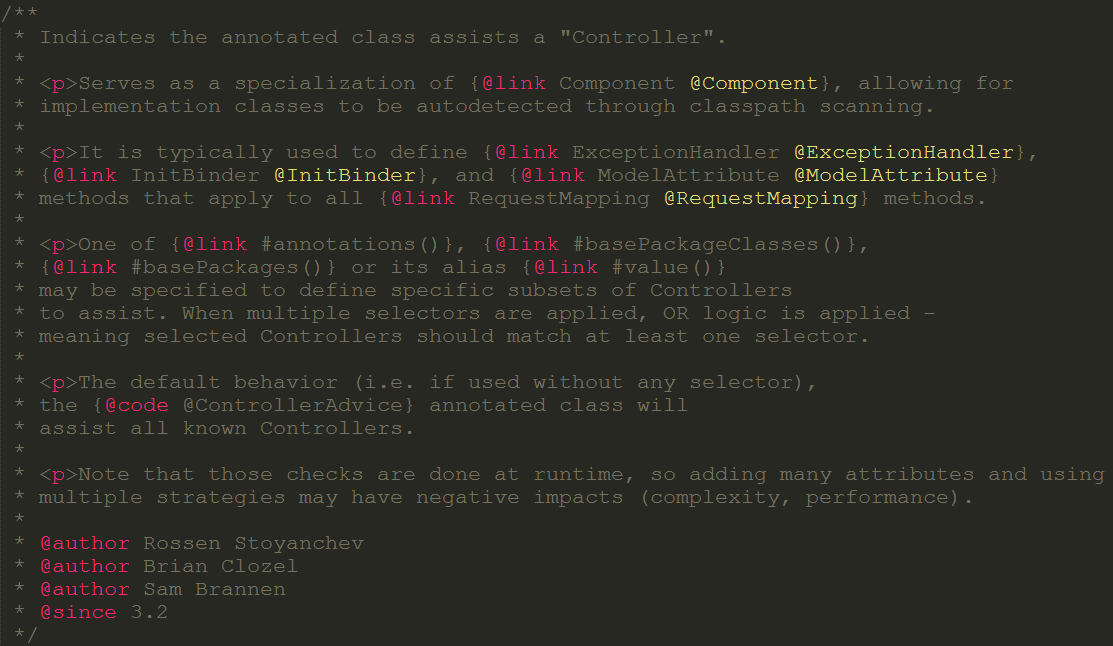
@ControllerAdvice,是Spring3.2提供的新注解,从名字上可以看出大体意思是控制器增强。让我们先看看@ControllerAdvice的实现:
-
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
-
-
-
-
-
-
public
-
-
-
String[] value() default {};
-
-
-
String[] basePackages() default {};
-
-
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
-
-
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
-
-
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
-
}
没什么特别之处,该注解使用@Component注解,这样的话当我们使用<context:component-scan>扫描时也能扫描到。
再一起看看官方提供的comment。
大致意思是:
-
@ControllerAdvice是一个@Component,用于定义@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute方法,适用于所有使用@RequestMapping方法。 -
Spring4之前,
@ControllerAdvice在同一调度的Servlet中协助所有控制器。Spring4已经改变:@ControllerAdvice支持配置控制器的子集,而默认的行为仍然可以利用。 -
在Spring4中,
@ControllerAdvice通过annotations(),basePackageClasses(),basePackages()方法定制用于选择控制器子集。
不过据经验之谈,只有配合@ExceptionHandler最有用,其它两个不常用。
在SpringMVC重要注解(一)@ExceptionHandler和@ResponseStatus我们提到,如果单使用@ExceptionHandler,只能在当前Controller中处理异常。但当配合@ControllerAdvice一起使用的时候,就可以摆脱那个限制了。
-
package com.somnus.advice;
-
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
-
-
-
public class ExceptionAdvice {
-
-
-
-
public String handleArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
return "testArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException";
-
-
-
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
-
-
-
-
public String testExceptionHandle2(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
-
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"a","b","c","d"});
-
return list.get(id-1);
-
}
-
-
}
当我们访问http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/exception/e2/5的时候会抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常,这时候定义在@ControllerAdvice中的@ExceptionHandler就开始发挥作用了。
如果我们想定义一个处理全局的异常
-
-
package com.somnus.advice;
-
-
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
-
-
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
-
-
-
public class ExceptionAdvice {
-
-
-
-
public String handException(HttpServletRequest request ,Exception e) throws Exception {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
-
return e.getMessage();
-
}
-
}
乍一眼看上去毫无问题,但这里有一个纰漏,由于Exception是异常的父类,如果你的项目中出现过在自定义异常中使用@ResponseStatus的情况,你的初衷是碰到那个自定义异常响应对应的状态码,而这个控制器增强处理类,会首先进入,并直接返回,不会再有@ResponseStatus的事情了,这里为了解决这种纰漏,我提供了一种解决方式。
-
package com.somnus.advice;
-
-
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
-
-
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
-
-
-
public class ExceptionAdvice {
-
-
-
-
-
public String handException(HttpServletRequest request ,Exception e) throws Exception {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
//If the exception is annotated with @ResponseStatus rethrow it and let
-
// the framework handle it - like the OrderNotFoundException example
-
// at the start of this post.
-
// AnnotationUtils is a Spring Framework utility class.
-
if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(e.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class) != null){
-
throw e;
-
}
-
// Otherwise setup and send the user to a default error-view.
-
/*ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
-
mav.addObject("exception", e);
-
mav.addObject("url", request.getRequestURL());
-
mav.setViewName(DEFAULT_ERROR_VIEW);
-
return mav;*/
-
return e.getMessage();
-
}
-
-
}
如果碰到了某个自定义异常加上了@ResponseStatus,就继续抛出,这样就不会让自定义异常失去加上@ResponseStatus的初衷
原文出处https://blog.csdn.net/w372426096/article/details/78429141





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号