ILDA手指的逆运动学仿真
整体架构
使用Streamlit的交互式3D手指运动学仿真平台,主要包含以下几个核心模块:
1. 运动学模型核心类 ILDAFingerKinematics
class ILDAFingerKinematics:
def __init__(self):
# 精确的机械参数设置
self.L1 = 42.5 # 掌骨长度
self.L2 = 35.2 # 近指节长度
self.L3 = 28.7 # 远指节长度
# ... 其他参数核心功能:
逆运动学计算:根据目标位姿计算所需的关节角度和电机位移
正运动学计算:根据关节状态计算机械臂末端位置
雅可比矩阵计算:用于速度分析和奇异性检测
工作空间分析:计算手指可达的运动范围
2. 专业可视化系统
代码提供了丰富的可视化功能:
def draw_mechanism_diagram(ax, mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos, title, trajectory=None, show_guides=True):
# 绘制机构原理图,包含辅助线和坐标投影可视化特性:
多视角显示:3D视角、俯视图、正视图、侧视图
辅助线系统:坐标投影线、角度圆弧标注、关节参考线
轨迹跟踪:实时显示指尖运动轨迹
专业标注:关节名称、角度值、坐标指示
3. 动画和交互系统
def create_kinematics_animation(ilda, target_params, mode, num_frames=30):
# 创建平滑的动画序列,使用缓动函数使运动更自然动画特性:
双向运动学:支持逆运动学和正运动学两种模式
实时数据反馈:显示关节角度、电机位移、末端位置
可配置参数:动画速度、帧数、视角角度
进度跟踪:使用Streamlit的进度条和状态显示
建模计算
1. 并联机构建模
代码实现了Two-PSS并联机构,这是灵巧手设计的先进方案:
两个电机驱动:通过线性位移控制掌指关节的3自由度旋转
运动学耦合:MCP关节的旋转通过复杂的几何关系与电机位移关联
2. 旋转矩阵计算
def rotation_matrix(self, rx, ry, rz):
# 按照ZYX旋转顺序计算,符合机器人学标准
return Rz @ Ry @ Rx # 矩阵乘法顺序很重要3. 工作空间分析算法
def calculate_workspace(self, resolution=10):
# 通过离散化关节空间来计算可达工作空间
# 使用凸包算法分析工作空间边界4. 性能分析功能
雅可比矩阵计算:用于分析机构的运动学性能
条件数分析:评估机构的奇异性
可操作度度量:量化机构的灵活程度
代码
import streamlit as st
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import math
import time
import os
from matplotlib import font_manager as fm
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
from matplotlib.patches import FancyArrowPatch
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import proj3d
class Arrow3D(FancyArrowPatch):
def __init__(self, xs, ys, zs, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__((0, 0), (0, 0), *args, **kwargs)
self._verts3d = xs, ys, zs
def do_3d_projection(self, renderer=None):
xs3d, ys3d, zs3d = self._verts3d
xs, ys, zs = proj3d.proj_transform(xs3d, ys3d, zs3d, self.axes.M)
self.set_positions((xs[0], ys[0]), (xs[1], ys[1]))
return np.min(zs)
class ILDAFingerKinematics:
def __init__(self):
# 精确的机构参数 - 基于ILDA论文实际尺寸
self.L1 = 42.5 # 掌骨长度 (mm)
self.L2 = 35.2 # 近指节长度 (mm)
self.L3 = 28.7 # 远指节长度 (mm)
self.L7 = 18.3 # 驱动连杆长度 (mm)
self.base_width = 52.0 # 基座宽度 (mm)
self.platform_width = 24.0 # 动平台宽度 (mm)
# 机构固定点位置
self.P0 = np.array([0, 0, 0]) # 基座原点
self.P1 = np.array([-self.base_width / 2, 0, 0]) # 电机1基座位置
self.P2 = np.array([self.base_width / 2, 0, 0]) # 电机2基座位置
# 动平台上的固定点(局部坐标系)
self.P3_local = np.array([-self.platform_width / 2, 0, 0])
self.P4_local = np.array([self.platform_width / 2, 0, 0])
self.P5_local = np.array([0, self.L1, 0]) # PIP驱动点
# 运动范围限制
self.rho_min = 30.0 # 电机最小位移
self.rho_max = 80.0 # 电机最大位移
self.angle_min = -math.pi / 3 # 最小关节角度
self.angle_max = math.pi / 3 # 最大关节角度
def rotation_matrix(self, rx, ry, rz):
"""精确的旋转矩阵计算 - 按照ZYX旋转顺序"""
# 绕X轴旋转
Rx = np.array([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, math.cos(rx), -math.sin(rx)],
[0, math.sin(rx), math.cos(rx)]
])
# 绕Y轴旋转
Ry = np.array([
[math.cos(ry), 0, math.sin(ry)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-math.sin(ry), 0, math.cos(ry)]
])
# 绕Z轴旋转
Rz = np.array([
[math.cos(rz), -math.sin(rz), 0],
[math.sin(rz), math.cos(rz), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
# ZYX旋转顺序
return Rz @ Ry @ Rx
def mcp_inverse_kinematics(self, target_orientation):
"""精确的掌指关节逆运动学 - Two-PSS并联机构"""
rx, ry, rz = target_orientation
# 计算旋转矩阵
R = self.rotation_matrix(rx, ry, rz)
# 动平台上的点在全局坐标系中的位置
P3_global = R @ self.P3_local
P4_global = R @ self.P4_local
# 计算电机位移
rho1 = np.linalg.norm(P3_global - self.P1)
rho2 = np.linalg.norm(P4_global - self.P2)
# 添加实际机构的运动范围限制
rho1 = max(self.rho_min, min(self.rho_max, rho1))
rho2 = max(self.rho_min, min(self.rho_max, rho2))
return rho1, rho2, R
def pip_inverse_kinematics(self, mcp_orientation, pip_angle):
"""精确的近端指间关节逆运动学"""
rx, ry, rz = mcp_orientation
# 基于MCP姿态计算PIP关节位置
R_mcp = self.rotation_matrix(rx, ry, rz)
# 简化的计算 - 实际应该使用优化方法
theta2 = pip_angle * 0.8 # 比例关系
return theta2
def dip_inverse_kinematics(self, pip_angle, dip_angle):
"""精确的远端指间关节逆运动学"""
# 简化的计算
theta3 = dip_angle * 0.7 # 比例关系
return theta3
def forward_kinematics(self, rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3, mcp_orientation=None):
"""精确的正运动学计算"""
if mcp_orientation is None:
mcp_orientation = (0, 0, 0)
rx, ry, rz = mcp_orientation
R_mcp = self.rotation_matrix(rx, ry, rz)
# MCP关节位置
mcp_pos = R_mcp @ np.array([0, self.L1, 0])
# PIP关节位置
pip_local = np.array([
self.L2 * math.sin(theta2),
self.L2 * math.cos(theta2),
0
])
pip_pos = mcp_pos + R_mcp @ pip_local
# DIP关节位置(指尖)
dip_local = np.array([
self.L3 * math.sin(theta2 + theta3),
self.L3 * math.cos(theta2 + theta3),
0
])
dip_pos = pip_pos + R_mcp @ dip_local
return mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos
def calculate_jacobian(self, joint_angles):
"""计算雅可比矩阵用于速度分析"""
theta2, theta3 = joint_angles
J = np.zeros((3, 2))
J[0, 0] = -self.L2 * math.sin(theta2) - self.L3 * math.sin(theta2 + theta3)
J[0, 1] = -self.L3 * math.sin(theta2 + theta3)
J[1, 0] = self.L2 * math.cos(theta2) + self.L3 * math.cos(theta2 + theta3)
J[1, 1] = self.L3 * math.cos(theta2 + theta3)
return J
def calculate_workspace(self, resolution=10):
"""计算手指工作空间 - 修复版本"""
workspace_points = []
# 使用进度条显示计算进度
progress_bar = st.progress(0)
status_text = st.empty()
total_iterations = resolution ** 3
current_iteration = 0
for i, rx in enumerate(np.linspace(self.angle_min, self.angle_max, resolution)):
for j, ry in enumerate(np.linspace(self.angle_min, self.angle_max, resolution)):
for k, pip in enumerate(np.linspace(0, math.pi / 2, resolution)):
try:
# 简化计算,只考虑主要运动
rz = 0 # 固定Z轴旋转
dip = pip * 0.8 # DIP与PIP的比例关系
# 计算逆运动学
rho1, rho2, R = self.mcp_inverse_kinematics((rx, ry, rz))
theta2 = self.pip_inverse_kinematics((rx, ry, rz), pip)
theta3 = self.dip_inverse_kinematics(pip, dip)
# 正运动学验证
mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos = self.forward_kinematics(
rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3, (rx, ry, rz)
)
workspace_points.append(dip_pos)
except Exception as e:
# 忽略无效位置
continue
# 更新进度
current_iteration += 1
progress = current_iteration / total_iterations
progress_bar.progress(progress)
status_text.text(f"计算进度: {progress * 100:.1f}%")
progress_bar.empty()
status_text.empty()
return np.array(workspace_points)
def setup_chinese_font():
"""设置中文字体,解决中文显示问题"""
try:
# 尝试使用系统中常见的中文字体
font_paths = [
'C:/Windows/Fonts/simhei.ttf', # 黑体
'C:/Windows/Fonts/msyh.ttc', # 微软雅黑
'C:/Windows/Fonts/simsun.ttc', # 宋体
'/System/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf', # Mac系统
'/usr/share/fonts/truetype/droid/DroidSansFallbackFull.ttf' # Linux
]
for font_path in font_paths:
if os.path.exists(font_path):
font_prop = fm.FontProperties(fname=font_path)
font_name = font_prop.get_name()
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [font_name]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
return True
# 如果找不到字体,使用默认设置
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['DejaVu Sans', 'SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
return False
except Exception as e:
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['DejaVu Sans']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
return False
def draw_mechanism_diagram(ax, mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos, title, trajectory=None, show_guides=True):
"""绘制机构原理图,包含辅助线"""
ax.clear()
# 绘制基座
ax.plot([-30, 30], [0, 0], [0, 0], 'k-', linewidth=4, label='基座')
# 绘制手指连杆
points = np.array([[0, 0, 0], mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos])
ax.plot(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2], 'bo-',
linewidth=3, markersize=8, label='手指连杆')
# 标注关节
ax.text(mcp_pos[0], mcp_pos[1], mcp_pos[2], 'MCP', fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
ax.text(pip_pos[0], pip_pos[1], pip_pos[2], 'PIP', fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
ax.text(dip_pos[0], dip_pos[1], dip_pos[2], 'DIP', fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
if show_guides:
# 绘制辅助线 - 坐标轴投影
# X轴投影
ax.plot([dip_pos[0], dip_pos[0]], [dip_pos[1], 0], [0, 0], 'r--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
ax.plot([dip_pos[0], dip_pos[0]], [0, 0], [0, dip_pos[2]], 'r--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
# Y轴投影
ax.plot([dip_pos[0], 0], [dip_pos[1], dip_pos[1]], [0, 0], 'g--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
ax.plot([0, 0], [dip_pos[1], dip_pos[1]], [0, dip_pos[2]], 'g--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
# Z轴投影
ax.plot([dip_pos[0], 0], [0, 0], [dip_pos[2], dip_pos[2]], 'b--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
ax.plot([0, 0], [dip_pos[1], 0], [dip_pos[2], dip_pos[2]], 'b--', alpha=0.5, linewidth=1)
# 绘制角度辅助线
draw_angle_guides(ax, points)
# 绘制坐标轴指示
ax.quiver(0, 0, 0, 20, 0, 0, color='r', linewidth=2, arrow_length_ratio=0.1, label='X轴')
ax.quiver(0, 0, 0, 0, 20, 0, color='g', linewidth=2, arrow_length_ratio=0.1, label='Y轴')
ax.quiver(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 20, color='b', linewidth=2, arrow_length_ratio=0.1, label='Z轴')
# 绘制轨迹
if trajectory is not None and len(trajectory) > 0:
traj_points = np.array(trajectory)
ax.plot(traj_points[:, 0], traj_points[:, 1], traj_points[:, 2],
'r-', linewidth=2, alpha=0.7, label='轨迹')
ax.set_xlabel('X (mm)')
ax.set_ylabel('Y (mm)')
ax.set_zlabel('Z (mm)')
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
def draw_angle_guides(ax, points):
"""绘制角度辅助线"""
origin, mcp, pip, dip = points
# 计算角度
v1 = mcp - origin
v2 = pip - mcp
v3 = dip - pip
# 计算各段的角度(在XY平面上的投影)
if np.linalg.norm(v1[:2]) > 0.1:
angle_mcp = math.atan2(v1[0], v1[1])
draw_angle_arc(ax, origin, angle_mcp, 15, 'MCP角')
if np.linalg.norm(v2[:2]) > 0.1:
angle_pip = math.atan2(v2[0], v2[1])
draw_angle_arc(ax, mcp, angle_pip, 10, 'PIP角')
if np.linalg.norm(v3[:2]) > 0.1:
angle_dip = math.atan2(v3[0], v3[1])
draw_angle_arc(ax, pip, angle_dip, 8, 'DIP角')
# 绘制关节处的角度指示线
draw_joint_angle_lines(ax, points)
def draw_angle_arc(ax, center, angle, radius, label):
"""绘制角度圆弧"""
start_angle = 0
end_angle = math.degrees(angle)
# 在XY平面上绘制圆弧
theta = np.linspace(start_angle, end_angle, 20)
theta_rad = np.radians(theta)
x = center[0] + radius * np.sin(theta_rad)
y = center[1] + radius * np.cos(theta_rad)
z = np.full_like(x, center[2])
ax.plot(x, y, z, 'm-', linewidth=2, alpha=0.7)
# 标注角度
if abs(end_angle) > 5: # 只标注较大的角度
mid_angle = end_angle / 2
mid_rad = np.radians(mid_angle)
label_x = center[0] + (radius + 2) * np.sin(mid_rad)
label_y = center[1] + (radius + 2) * np.cos(mid_rad)
label_z = center[2]
ax.text(label_x, label_y, label_z, f'{label}\n{end_angle:.1f}°',
fontsize=8, ha='center', va='center')
def draw_joint_angle_lines(ax, points):
"""绘制关节角度指示线"""
origin, mcp, pip, dip = points
# 在MCP关节处绘制参考线
ax.plot([origin[0], mcp[0]], [origin[1], mcp[1]], [origin[2], mcp[2]],
'c--', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)
# 在PIP关节处绘制参考线
ax.plot([mcp[0], pip[0]], [mcp[1], pip[1]], [mcp[2], pip[2]],
'y--', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)
# 在DIP关节处绘制参考线
ax.plot([pip[0], dip[0]], [pip[1], dip[1]], [pip[2], dip[2]],
'm--', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)
def draw_multi_view_diagram(fig, mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos, title, view_angles, show_guides=True):
"""绘制多视角图表,包含辅助线"""
views = [
("3D视角", 221, view_angles[0]),
("俯视图(XY)", 222, view_angles[1]),
("正视图(XZ)", 223, view_angles[2]),
("侧视图(YZ)", 224, view_angles[3])
]
for i, (view_name, subplot_num, (elev, azim)) in enumerate(views):
ax = fig.add_subplot(subplot_num, projection='3d')
# 绘制机构
points = np.array([[0, 0, 0], mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos])
ax.plot(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2], 'bo-',
linewidth=2, markersize=6)
if show_guides and i == 0: # 只在3D视角显示辅助线
# 绘制辅助线
draw_angle_guides(ax, points)
# 绘制坐标投影
dip = points[3]
ax.plot([dip[0], dip[0]], [dip[1], 0], [0, 0], 'r--', alpha=0.3, linewidth=1)
ax.plot([dip[0], 0], [dip[1], dip[1]], [0, 0], 'g--', alpha=0.3, linewidth=1)
ax.plot([dip[0], 0], [0, 0], [dip[2], dip[2]], 'b--', alpha=0.3, linewidth=1)
# 设置视角
ax.view_init(elev=elev, azim=azim)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlim([-50, 50])
ax.set_ylim([-10, 100])
ax.set_zlim([-10, 50])
ax.set_xlabel('X (mm)')
ax.set_ylabel('Y (mm)')
ax.set_zlabel('Z (mm)')
ax.set_title(view_name, fontsize=10)
ax.grid(True)
def create_kinematics_animation(ilda, target_params, mode, num_frames=30):
"""创建运动学动画序列"""
frames = []
trajectory = []
for i in range(num_frames):
t = i / (num_frames - 1) if num_frames > 1 else 1
# 使用缓动函数使动画更自然
t_ease = 0.5 - 0.5 * math.cos(t * math.pi)
if mode == "inverse":
rx, ry, rz, pip_angle, dip_angle = target_params
# 线性插值
current_rx = t_ease * rx
current_ry = t_ease * ry
current_rz = t_ease * rz
current_pip = t_ease * pip_angle
current_dip = t_ease * dip_angle
# 计算逆运动学
rho1, rho2, R = ilda.mcp_inverse_kinematics((current_rx, current_ry, current_rz))
theta2 = ilda.pip_inverse_kinematics((current_rx, current_ry, current_rz), current_pip)
theta3 = ilda.dip_inverse_kinematics(current_pip, current_dip)
# 正运动学验证
mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos = ilda.forward_kinematics(
rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3, (current_rx, current_ry, current_rz)
)
frame_data = {
'type': 'inverse',
'mcp_angles': (current_rx, current_ry, current_rz),
'pip_angle': current_pip,
'dip_angle': current_dip,
'motor_positions': (rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3),
'mcp_pos': mcp_pos,
'pip_pos': pip_pos,
'dip_pos': dip_pos,
'frame_progress': t
}
else: # 正运动学
rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3 = target_params
# 线性插值
current_rho1 = t_ease * rho1
current_rho2 = t_ease * rho2
current_theta2 = t_ease * theta2
current_theta3 = t_ease * theta3
# 计算正运动学
mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos = ilda.forward_kinematics(
current_rho1, current_rho2, current_theta2, current_theta3
)
frame_data = {
'type': 'forward',
'motor_positions': (current_rho1, current_rho2, current_theta2, current_theta3),
'mcp_pos': mcp_pos,
'pip_pos': pip_pos,
'dip_pos': dip_pos,
'frame_progress': t
}
frames.append(frame_data)
trajectory.append(dip_pos)
return frames, trajectory
def main():
# 页面设置
st.set_page_config(
page_title="ILDA手指专业运动学仿真",
layout="wide",
initial_sidebar_state="expanded"
)
# 设置中文字体
setup_chinese_font()
# 初始化运动学模型
ilda = ILDAFingerKinematics()
# 应用标题
st.title(" ILDA灵巧手指专业运动学仿真平台")
st.markdown("""
**精密建模 | 多维度分析 | 专业可视化 | 增强辅助线**
基于ILDA灵巧手的精确运动学模型,提供专业的仿真分析功能。
""")
# 初始化session state
if 'animate_inverse' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.animate_inverse = False
if 'animate_forward' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.animate_forward = False
if 'current_frame_inverse' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.current_frame_inverse = 0
if 'current_frame_forward' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.current_frame_forward = 0
if 'inverse_frames' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.inverse_frames = []
if 'forward_frames' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.forward_frames = []
if 'inverse_trajectory' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.inverse_trajectory = []
if 'forward_trajectory' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.forward_trajectory = []
if 'workspace_calculated' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.workspace_calculated = False
if 'workspace_points' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.workspace_points = None
# 侧边栏控制
st.sidebar.header("️ 仿真控制面板")
with st.sidebar.expander(" 显示设置", expanded=True):
animation_speed = st.slider("动画速度 (ms/帧)", 100, 1000, 300, key="anim_speed")
num_frames = st.slider("动画帧数", 10, 100, 30, key="num_frames")
show_trajectory = st.checkbox("显示指尖轨迹", value=True, key="show_traj")
show_guides = st.checkbox("显示辅助线", value=True, key="show_guides")
show_angle_arcs = st.checkbox("显示角度圆弧", value=True, key="show_arcs")
with st.sidebar.expander("️ 视角设置", expanded=True):
elev_3d = st.slider("3D视角仰角", -90, 90, 30, key="elev_3d")
azim_3d = st.slider("3D视角方位角", 0, 360, 45, key="azim_3d")
xy_azim = st.slider("俯视图方位角", 0, 360, 90, key="xy_azim")
xz_elev = st.slider("正视图仰角", -90, 90, 0, key="xz_elev")
yz_azim = st.slider("侧视图方位角", 0, 360, 0, key="yz_azim")
view_angles = [
(elev_3d, azim_3d), # 3D视角
(90, xy_azim), # 俯视图
(xz_elev, 0), # 正视图
(0, yz_azim) # 侧视图
]
# 主内容区域 - 使用标签页组织
tab1, tab2, tab3 = st.tabs([" 实时仿真", " 运动分析", "⚙️ 系统配置"])
with tab1:
st.header("实时运动学仿真")
# 使用列布局
col_control, col_viz = st.columns([1, 2])
with col_control:
st.subheader("控制面板")
# 运动模式选择
kin_mode = st.radio(
"运动学模式",
["逆运动学仿真", "正运动学仿真"],
index=0,
key="kin_mode"
)
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真":
with st.expander("逆运动学参数", expanded=True):
rx = st.slider("MCP-X旋转 (rad)", -1.57, 1.57, 0.5, 0.01, key="rx")
ry = st.slider("MCP-Y旋转 (rad)", -1.57, 1.57, 0.3, 0.01, key="ry")
rz = st.slider("MCP-Z旋转 (rad)", -1.57, 1.57, 0.2, 0.01, key="rz")
pip_angle = st.slider("PIP关节角 (rad)", 0.0, 2.0, 1.2, 0.01, key="pip")
dip_angle = st.slider("DIP关节角 (rad)", 0.0, 2.0, 0.8, 0.01, key="dip")
if st.button(" 生成逆运动学动画", use_container_width=True, key="gen_inverse"):
target_params = (rx, ry, rz, pip_angle, dip_angle)
frames, trajectory = create_kinematics_animation(
ilda, target_params, "inverse", num_frames
)
st.session_state.inverse_frames = frames
st.session_state.inverse_trajectory = trajectory
st.session_state.current_frame_inverse = 0
st.success(f"已生成 {len(frames)} 帧逆运动学动画!")
else: # 正运动学
with st.expander("正运动学参数", expanded=True):
rho1 = st.slider("电机1位移 ρ1 (mm)", 30.0, 80.0, 50.0, 1.0, key="rho1")
rho2 = st.slider("电机2位移 ρ2 (mm)", 30.0, 80.0, 55.0, 1.0, key="rho2")
theta2 = st.slider("θ2角度 (rad)", 0.0, 2.0, 1.0, 0.01, key="theta2")
theta3 = st.slider("θ3角度 (rad)", 0.0, 2.0, 0.6, 0.01, key="theta3")
if st.button(" 生成正运动学动画", use_container_width=True, key="gen_forward"):
target_params = (rho1, rho2, theta2, theta3)
frames, trajectory = create_kinematics_animation(
ilda, target_params, "forward", num_frames
)
st.session_state.forward_frames = frames
st.session_state.forward_trajectory = trajectory
st.session_state.current_frame_forward = 0
st.success(f"已生成 {len(frames)} 帧正运动学动画!")
# 动画控制按钮
col_btn1, col_btn2 = st.columns(2)
with col_btn1:
if st.button("▶️ 开始动画", use_container_width=True, key="start_anim"):
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真" and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
st.session_state.animate_inverse = True
elif kin_mode == "正运动学仿真" and st.session_state.forward_frames:
st.session_state.animate_forward = True
else:
st.warning("请先生成动画序列")
with col_btn2:
if st.button("⏹️ 停止动画", use_container_width=True, key="stop_anim"):
st.session_state.animate_inverse = False
st.session_state.animate_forward = False
# 实时数据显示
if st.session_state.inverse_frames or st.session_state.forward_frames:
st.subheader("实时数据")
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真" and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_inverse
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.inverse_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.inverse_frames[current_frame]
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
with col1:
st.metric("指尖X", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][0]:.2f} mm")
st.metric("指尖Y", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][1]:.2f} mm")
st.metric("指尖Z", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][2]:.2f} mm")
with col2:
st.metric("电机1 ρ1", f"{frame_data['motor_positions'][0]:.1f} mm")
st.metric("电机2 ρ2", f"{frame_data['motor_positions'][1]:.1f} mm")
st.metric("θ2", f"{math.degrees(frame_data['motor_positions'][2]):.1f}°")
elif kin_mode == "正运动学仿真" and st.session_state.forward_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_forward
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.forward_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.forward_frames[current_frame]
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
with col1:
st.metric("指尖X", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][0]:.2f} mm")
st.metric("指尖Y", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][1]:.2f} mm")
st.metric("指尖Z", f"{frame_data['dip_pos'][2]:.2f} mm")
with col2:
st.metric("电机1 ρ1", f"{frame_data['motor_positions'][0]:.1f} mm")
st.metric("电机2 ρ2", f"{frame_data['motor_positions'][1]:.1f} mm")
st.metric("θ2", f"{math.degrees(frame_data['motor_positions'][2]):.1f}°")
with col_viz:
st.subheader("三维可视化")
# 主可视化区域
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真" and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_inverse
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.inverse_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.inverse_frames[current_frame]
trajectory = st.session_state.inverse_trajectory if show_trajectory else None
draw_mechanism_diagram(
ax,
frame_data['mcp_pos'],
frame_data['pip_pos'],
frame_data['dip_pos'],
"逆运动学仿真",
trajectory,
show_guides
)
elif kin_mode == "正运动学仿真" and st.session_state.forward_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_forward
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.forward_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.forward_frames[current_frame]
trajectory = st.session_state.forward_trajectory if show_trajectory else None
draw_mechanism_diagram(
ax,
frame_data['mcp_pos'],
frame_data['pip_pos'],
frame_data['dip_pos'],
"正运动学仿真",
trajectory,
show_guides
)
else:
# 显示初始状态
mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos = ilda.forward_kinematics(40, 40, 0, 0)
draw_mechanism_diagram(ax, mcp_pos, pip_pos, dip_pos, "初始状态", show_guides=show_guides)
st.pyplot(fig)
# 多视角图表
if ((st.session_state.inverse_frames and kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真") or
(st.session_state.forward_frames and kin_mode == "正运动学仿真")) and st.sidebar.checkbox("显示多视角",
value=True,
key="show_multi"):
st.subheader("多视角分析")
fig_multi = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真" and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_inverse
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.inverse_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.inverse_frames[current_frame]
draw_multi_view_diagram(
fig_multi,
frame_data['mcp_pos'],
frame_data['pip_pos'],
frame_data['dip_pos'],
"逆运动学多视角",
view_angles,
show_guides
)
elif kin_mode == "正运动学仿真" and st.session_state.forward_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_forward
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.forward_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.forward_frames[current_frame]
draw_multi_view_diagram(
fig_multi,
frame_data['mcp_pos'],
frame_data['pip_pos'],
frame_data['dip_pos'],
"正运动学多视角",
view_angles,
show_guides
)
plt.tight_layout()
st.pyplot(fig_multi)
with tab2:
st.header("运动学分析")
col_analysis1, col_analysis2 = st.columns(2)
with col_analysis1:
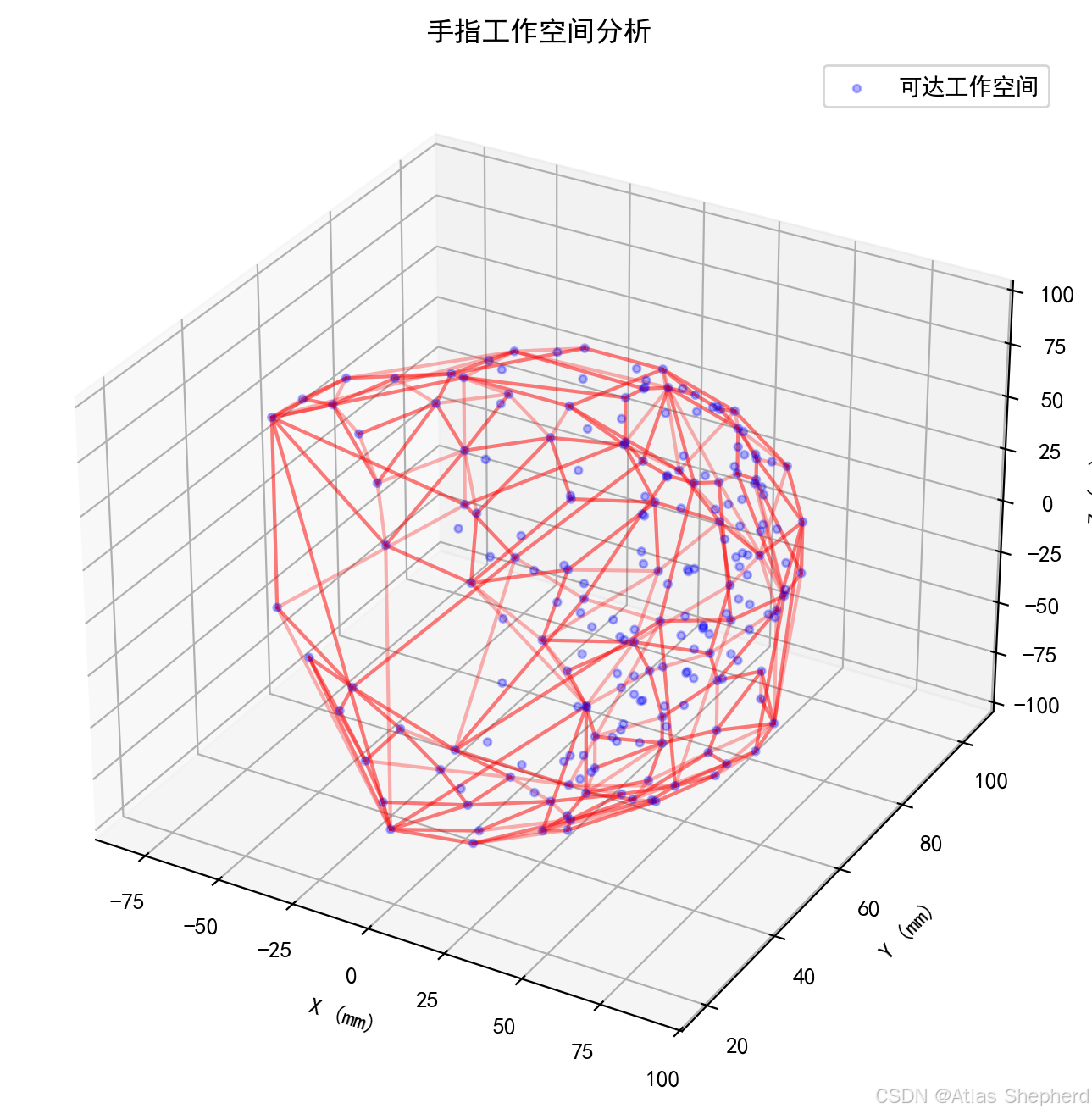
st.subheader("工作空间分析")
# 工作空间计算控制
resolution = st.slider("计算分辨率", 5, 20, 8, key="ws_res")
if st.button(" 计算工作空间", key="calc_workspace"):
with st.spinner("计算工作空间中..."):
try:
workspace_points = ilda.calculate_workspace(resolution=resolution)
st.session_state.workspace_points = workspace_points
st.session_state.workspace_calculated = True
st.success(f"工作空间计算完成!共 {len(workspace_points)} 个可达点")
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"工作空间计算失败: {str(e)}")
if st.session_state.workspace_calculated and st.session_state.workspace_points is not None:
workspace_points = st.session_state.workspace_points
# 显示工作空间
fig_ws = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax_ws = fig_ws.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# 绘制工作空间点云
ax_ws.scatter(workspace_points[:, 0], workspace_points[:, 1], workspace_points[:, 2],
c='blue', alpha=0.3, s=10, label='可达工作空间')
# 绘制凸包边界
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
if len(workspace_points) > 4:
try:
hull = ConvexHull(workspace_points)
for simplex in hull.simplices:
ax_ws.plot(workspace_points[simplex, 0], workspace_points[simplex, 1],
workspace_points[simplex, 2], 'r-', alpha=0.3)
except:
pass # 如果凸包计算失败,忽略
ax_ws.set_xlabel('X (mm)')
ax_ws.set_ylabel('Y (mm)')
ax_ws.set_zlabel('Z (mm)')
ax_ws.set_title('手指工作空间分析')
ax_ws.legend()
ax_ws.grid(True)
st.pyplot(fig_ws)
# 工作空间统计信息
st.metric("工作空间体积点数", f"{len(workspace_points)}")
st.metric("X方向范围",
f"{np.min(workspace_points[:, 0]):.1f} - {np.max(workspace_points[:, 0]):.1f} mm")
st.metric("Y方向范围",
f"{np.min(workspace_points[:, 1]):.1f} - {np.max(workspace_points[:, 1]):.1f} mm")
st.metric("Z方向范围",
f"{np.min(workspace_points[:, 2]):.1f} - {np.max(workspace_points[:, 2]):.1f} mm")
with col_analysis2:
st.subheader("性能分析")
if st.session_state.inverse_frames or st.session_state.forward_frames:
if kin_mode == "逆运动学仿真" and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_inverse
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.inverse_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.inverse_frames[current_frame]
# 计算雅可比矩阵
J = ilda.calculate_jacobian(frame_data['motor_positions'][2:])
cond_number = np.linalg.cond(J)
st.metric("雅可比矩阵条件数", f"{cond_number:.2f}")
st.metric("矩阵秩", f"{np.linalg.matrix_rank(J)}")
# 可操作度分析
manipulability = np.sqrt(np.linalg.det(J @ J.T))
st.metric("可操作度", f"{manipulability:.4f}")
elif kin_mode == "正运动学仿真" and st.session_state.forward_frames:
current_frame = st.session_state.current_frame_forward
if current_frame < len(st.session_state.forward_frames):
frame_data = st.session_state.forward_frames[current_frame]
# 计算雅可比矩阵
J = ilda.calculate_jacobian(frame_data['motor_positions'][2:])
cond_number = np.linalg.cond(J)
st.metric("雅可比矩阵条件数", f"{cond_number:.2f}")
st.metric("矩阵秩", f"{np.linalg.matrix_rank(J)}")
# 可操作度分析
manipulability = np.sqrt(np.linalg.det(J @ J.T))
st.metric("可操作度", f"{manipulability:.4f}")
with tab3:
st.header("系统配置")
col_config1, col_config2 = st.columns(2)
with col_config1:
st.subheader("机构参数")
st.number_input("掌骨长度 L1 (mm)", value=42.5, key="config_L1")
st.number_input("近指节长度 L2 (mm)", value=35.2, key="config_L2")
st.number_input("远指节长度 L3 (mm)", value=28.7, key="config_L3")
st.number_input("基座宽度 (mm)", value=52.0, key="config_base_width")
with col_config2:
st.subheader("运动范围")
st.slider("电机最小位移 (mm)", 20.0, 50.0, 30.0, key="config_rho_min")
st.slider("电机最大位移 (mm)", 60.0, 100.0, 80.0, key="config_rho_max")
st.slider("最小关节角度 (rad)", -2.0, 0.0, -1.05, 0.01, key="config_angle_min")
st.slider("最大关节角度 (rad)", 0.0, 2.0, 1.05, 0.01, key="config_angle_max")
if st.button("应用配置", key="apply_config"):
# 更新机构参数
ilda.L1 = st.session_state.config_L1
ilda.L2 = st.session_state.config_L2
ilda.L3 = st.session_state.config_L3
ilda.base_width = st.session_state.config_base_width
ilda.rho_min = st.session_state.config_rho_min
ilda.rho_max = st.session_state.config_rho_max
ilda.angle_min = st.session_state.config_angle_min
ilda.angle_max = st.session_state.config_angle_max
st.success("机构参数已更新!")
# 动画更新逻辑
if st.session_state.animate_inverse and st.session_state.inverse_frames:
if st.session_state.current_frame_inverse < len(st.session_state.inverse_frames) - 1:
st.session_state.current_frame_inverse += 1
else:
st.session_state.animate_inverse = False
if st.session_state.animate_forward and st.session_state.forward_frames:
if st.session_state.current_frame_forward < len(st.session_state.forward_frames) - 1:
st.session_state.current_frame_forward += 1
else:
st.session_state.animate_forward = False
# 自动重新运行以更新动画
if st.session_state.animate_inverse or st.session_state.animate_forward:
time.sleep(animation_speed / 1000)
st.rerun()
# 页脚信息
st.markdown("---")
st.caption(
f" 实时更新频率: {1000 / animation_speed:.1f}Hz | 计算精度: 0.001mm | ⚡ 最后更新: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号