
《JUnit in Action》全新第3版封面截图
写在前面
这一章重点关注表现层测试(presentation-layer testing)即网页测试。主要带领大家通过两款常用的测试工具,了解表现层测试的具体方法和基本流程。上篇梳理 HtmlUnit,下篇梳理 Selenium。
第十五章:表现层测试(上)
本章概要
HtmlUnit测试用例的写法Selenium测试用例的写法HtmlUnit与Selenium对比
If debugging is the process of removing software bugs, then programming must be the process of putting them in.
如果说调试是消除软件缺陷的过程,那么编程必定是植入缺陷的过程。—— Edsger Dijkstra
15.1 表现层测试概述
简言之,表现层测试(presentation-layer testing) 就是在用户图形界面(GUI)中发现应用程序的缺陷的过程。它和其他阶段的测试同等重要,毕竟糟糕的用户体验不仅会让应用的功能异常,更会流失客户、流失订单。
本章重点探讨如何基于 Java 代码对 GUI 中的内容进行断言测试的方法,不涉及字体样式、颜色、布局等主观元素的测试。
表现层测试的难点在于 网站内容的稳定性无法长期保证:网站内容甚至页面结构都会随着时间不断变化。本章介绍的测试方法主要针对短期内相对稳定的网页来设计测试用例。
表现层的测试内容包括:
- 网页内容的任意细节(包括单词拼写等)
- 应用的结构或导航设计(能否链接到预期目标)
- 能否通过验收测试,验证用户叙事逻辑(user stories)
注意
用户叙事逻辑(User stories) 也叫 用户故事,是对软件系统一个或多个功能特性的非正式自然语言描述。
根据 Web 应用是否独立于操作系统的具体特性、以及是否独立于浏览器对 JavaScript、DOM、CSS 等技术标准的特定实现,本章主要对 HtmlUnit、Selenium 两款开源工具的用法进行演示。
15.2 HtmlUnit 简介
HtmlUnit(https://htmlunit.sourceforge.io/)是一款基于 Java 语言开发的开源无头浏览器(headless browser)框架。无头浏览器即没有 GUI 界面的浏览器。它能以编程的方式模拟用户在浏览器上对 Web 应用进行的各种操作,测试全程不显示任何用户界面。
由于实测时随书源码版本过低,因此更新了 pom.xml 中的 HtmlUnit 依赖(更新到最新版 v4.18.0):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.htmlunit</groupId>
<artifactId>htmlunit</artifactId>
<version>4.18.0</version>
</dependency>版本升级后需要逐一更新导入语句,将旧包路 com.gargoylesoftware.htmlunit 一并改为 org.htmlunit。
本章实测代码旨在熟悉 HtmlUnit 具备的基本设置、基础功能,并在最新版的语法下完成各项测试目标。
15.3 HtmlUnit 用法演示
HtmlUnit 执行测试的基本流程:
- 调用
getPage()方法; - 定位某个元素;
- 执行某个操作(如单击元素等);
- 断言结果;
15.3.1 示例1:基础设置及页面元素基础测试
HtmlUnit 部分的所有测试用例几乎都需要继承一个新建的抽象类 ManagedWebClient,目的是为了统一配置 @BeforeEach 和 @AfterEach 方法,让核心测试逻辑更加突出。新版抽象类定义如下:
package com.manning.junitbook.ch15.htmlunit;
import org.htmlunit.BrowserVersion;
import org.htmlunit.SilentCssErrorHandler;
import org.htmlunit.WebClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import java.util.logging.Level;
/**
* Manages an HtmlUnit WebClient on behalf of subclasses. The class makes sure
* the close() method is called when a test is done with a WebClient instance.
*/
public abstract class ManagedWebClient {
protected WebClient webClient;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
webClient = new WebClient(BrowserVersion.BEST_SUPPORTED);
// 抑制无关警告日志
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger("org.htmlunit.IncorrectnessListenerImpl").setLevel(Level.OFF);
// 忽略脚本错误,防止因外部脚本问题导致测试失败
webClient.getOptions().setThrowExceptionOnScriptError(false);
// 默认启用 JavaScript 脚本
webClient.getOptions().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
// 忽略 CSS 错误
webClient.setCssErrorHandler(new SilentCssErrorHandler());
}
@AfterEach
public void tearDown() {
webClient.close();
}
}上述设置中,webClient 用于模拟浏览器客户端;L22 至 L32 为升级后添加的配置项,旨在消除实测过程中因解析 CSS 和 JS 造成的超时和报错。
接着,就可以进行一些基础性测试了,例如测试页面的 title 值、是否包含某个节点元素、是否包含某段文本等:
public class HtmlUnitPageTest extends ManagedWebClient {
@Test
public void homePage() throws IOException {
webClient.getOptions().setJavaScriptEnabled(false);
HtmlPage page = webClient.getPage("https://htmlunit.sourceforge.io/");
assertEquals("HtmlUnit – Welcome to HtmlUnit", page.getTitleText());
String pageAsXml = page.asXml();
assertTrue(pageAsXml.contains("<div class=\"container-fluid\">"));
String pageAsText = page.asNormalizedText();
assertTrue(pageAsText.contains("Support for the HTTP and HTTPS protocols"));
}
@Test
public void testClassNav() throws IOException {
HtmlPage mainPage = webClient.getPage("https://htmlunit.sourceforge.io/apidocs/index.html");
HtmlPage packagePage = (HtmlPage) mainPage.getFrameByName("packageFrame").getEnclosedPage();
HtmlListItem htmlListItem = (HtmlListItem) packagePage.getElementsByTagName("li").item(0);
assertEquals("AbortController", htmlListItem.getTextContent());
}
}实测结果:

15.3.2 示例2:利用参数化测试提效 HtmlUnit 用例
将浏览器版本作为参数化测试的动态参数,可对同一页面快速生成一组等效的用例。新版示例代码如下:
package com.manning.junitbook.ch15.htmlunit;
import org.htmlunit.BrowserVersion;
import org.htmlunit.WebAssert;
import org.htmlunit.WebClient;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlListItem;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlPage;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.MethodSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
/**
* Tests navigating the HtmlUnit SourceForge site.
*/
public class JavadocPageAllBrowserTest {
private static Collection<BrowserVersion[]> getBrowserVersions() {
return Arrays.asList(new BrowserVersion[][]{
{BrowserVersion.FIREFOX},
{BrowserVersion.EDGE},
{BrowserVersion.CHROME},
{BrowserVersion.BEST_SUPPORTED}
});
}
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource("getBrowserVersions")
public void testClassNav(BrowserVersion browserVersion) throws IOException {
WebClient webClient = new WebClient(browserVersion);
webClient.getOptions().setJavaScriptEnabled(false);
HtmlPage mainPage = (HtmlPage) webClient.getPage("https://htmlunit.sourceforge.io/apidocs/index.html");
WebAssert.notNull("Missing main page", mainPage);
HtmlPage packagePage = (HtmlPage) mainPage.getFrameByName("packageFrame").getEnclosedPage();
WebAssert.notNull("Missing package page", packagePage);
HtmlListItem htmlListItem = (HtmlListItem) packagePage.getElementsByTagName("li").item(0);
assertEquals("AbortController", htmlListItem.getTextContent());
}
}实测效果:

15.3.3 示例3:创建页面内容相对固定的测试
这类用例类似第八章介绍的 Mock 对象,需要人为设置模拟的请求和页面响应内容,人为地固化页面内容,以方便测试:
package com.manning.junitbook.ch15.htmlunit;
import org.htmlunit.MockWebConnection;
import org.htmlunit.WebAssert;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlPage;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* Demonstrates using in-line HTML fixtures in test methods.
*/
public class InLineHtmlFixtureTest extends ManagedWebClient {
@Test
public void testInLineHtmlFixture() throws IOException {
final String expectedTitle = "Hello 1!";
String html = "<html><head><title>" + expectedTitle + "</title></head></html>";
MockWebConnection connection = new MockWebConnection();
connection.setDefaultResponse(html);
webClient.setWebConnection(connection);
HtmlPage page = webClient.getPage("http://page");
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(page, expectedTitle);
}
}对于需要模拟多个 URL、响应多个页面内容的情况,也可以通过 MockWebConnection 实例的 setResponse() 方法统一设置。例如:
@Test
public void testInLineHtmlFixtures() throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
final URL page1Url = new URI("http://Page1/").toURL();
final URL page2Url = new URI("http://Page2/").toURL();
final URL page3Url = new URI("http://Page3/").toURL();
MockWebConnection connection = new MockWebConnection();
connection.setResponse(page1Url, "<html><head><title>Hello 1!</title></head></html>");
connection.setResponse(page2Url, "<html><head><title>Hello 2!</title></head></html>");
connection.setResponse(page3Url, "<html><head><title>Hello 3!</title></head></html>");
webClient.setWebConnection(connection);
HtmlPage page1 = webClient.getPage(page1Url);
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(page1, "Hello 1!");
HtmlPage page2 = webClient.getPage(page2Url);
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(page2, "Hello 2!");
HtmlPage page3 = webClient.getPage(page3Url);
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(page3, "Hello 3!");
}实测效果:
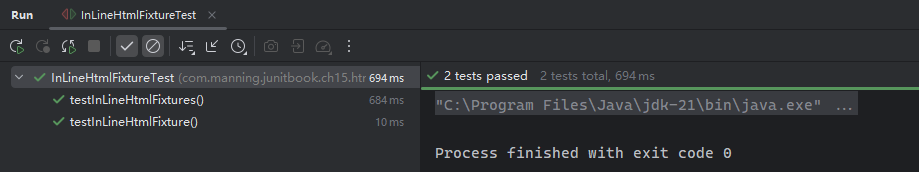
实测备忘录
实测时出现过两个小问题:
- 手动指定响应页面时,
URL一定要以斜杆/结尾,否则解析失败;但设置默认响应时则无需考虑;JDK版本改为21后,URL对象直接通过new关键字实例化的做法已经被淘汰了。推荐写法是通过uri.toURL(),然后抛一个异常URISyntaxException。
15.3.4 示例4:页面表单测试
准备两个 HTML 示例文件,一个是表单页,另一个表单正常提交后的页面:
<!-- formtest.html -->
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script>
function validate_form(form) {
if (form.in_text.value=="") {
alert("Please enter a value.");
form.in_text.focus();
return false;
}
}
</script>
<title>Form Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="validated_form" action="submit.html" onsubmit="return validate_form(this);" method="post">
Value:
<input type="text" name="in_text" id="in_text" size="30"/>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" id="submit" name="submit"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<!-- submit.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"/>
<title>Result</title>
</head>
<body>Result</body></html>然后分三种情况进行演示:
- 文本框正常输入一些内容,模拟表单提交,页面正常跳转到新页面;
- 文本框不输入任何内容,触发校验逻辑
JS脚本,测试弹出的警告框是否符合预期; - 文本框正常输入,提交后正常跳转,测试是否不弹出警告框。
具体实现代码如下:
package com.manning.junitbook.ch15.htmlunit;
import org.htmlunit.CollectingAlertHandler;
import org.htmlunit.WebAssert;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlForm;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlPage;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlSubmitInput;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlTextInput;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
/**
* Demonstrates testing a form.
*/
public class FormTest extends ManagedWebClient {
@Test
public void testForm() throws IOException {
HtmlPage page = webClient.getPage("file:src/main/webapp/formtest.html");
HtmlForm form = page.getFormByName("validated_form");
HtmlTextInput input = form.getInputByName("in_text");
input.setValueAttribute("typing...");
HtmlSubmitInput submitButton = form.getInputByName("submit");
HtmlPage resultPage = submitButton.click();
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(resultPage, "Result");
}
@Test
public void testFormAlert() throws IOException {
CollectingAlertHandler alertHandler = new CollectingAlertHandler();
webClient.setAlertHandler(alertHandler);
//alternative code for the line above:
// webClient.setAlertHandler((page, message) -> fail("JavaScript alert: " + message));
HtmlPage page = webClient.getPage("file:src/main/webapp/formtest.html");
HtmlForm form = page.getFormByName("validated_form");
HtmlSubmitInput submitButton = form.getInputByName("submit");
HtmlPage resultPage = submitButton.click();
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(resultPage, page.getTitleText());
WebAssert.assertTextPresent(resultPage, page.asNormalizedText());
List<String> collectedAlerts = alertHandler.getCollectedAlerts();
List<String> expectedAlerts = Collections.singletonList("Please enter a value.");
assertEquals(expectedAlerts, collectedAlerts);
}
@Test
public void testFormNoAlert() throws IOException {
CollectingAlertHandler alertHandler = new CollectingAlertHandler();
webClient.setAlertHandler(alertHandler);
HtmlPage page = webClient.getPage("file:src/main/webapp/formtest.html");
HtmlForm form = page.getFormByName("validated_form");
HtmlTextInput input = form.getInputByName("in_text");
input.setValueAttribute("typing...");
HtmlSubmitInput submitButton = form.getInputByName("submit");
HtmlPage resultPage = submitButton.click();
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(resultPage, "Result");
assertTrue(alertHandler.getCollectedAlerts().isEmpty(), "No alerts expected");
}
}实测结果:
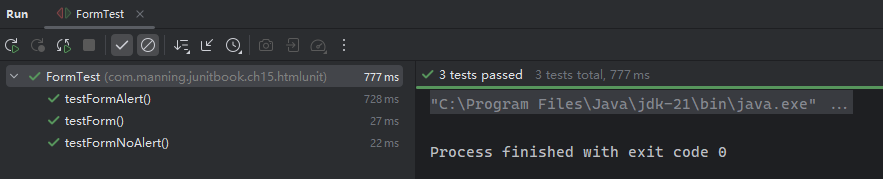
实测备忘录
测试逻辑是否需要启用
JavaScript脚本的解析,是通过webClient的设置开关实现的:webClient.getOptions().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); // true 启用,false 关闭此外,新版
HtmlUnit已经没有专门控制JS超时的写法了:webClient.setJavaScriptTimeout(timeout);。新版只保留了webClient.setTimeout(timeout);的写法,参数类型为int,表示毫秒数。
15.3.5 示例5:测试页面 confirm 弹框内容
与 alert 弹窗类似,HtmlUnit 也支持 confirm 确认对话框内容的测试,并且可以自定义确认对话框的处理逻辑,通过 webClient.setConfirmHandler(handler) 实现(对 alert 调用的是 webClient.setAlertHandler(handler)):
package com.manning.junitbook.ch15.htmlunit;
import org.htmlunit.CollectingAlertHandler;
import org.htmlunit.FailingHttpStatusCodeException;
import org.htmlunit.MockWebConnection;
import org.htmlunit.WebAssert;
import org.htmlunit.html.HtmlPage;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertArrayEquals;
/**
* Demonstrates testing a confirmation handler.
*/
public class WindowConfirmTest extends ManagedWebClient {
@Test
public void testWindowConfirm() throws FailingHttpStatusCodeException, IOException, URISyntaxException {
String html = "<html><head><title>Hello</title></head><body onload='confirm(\"Confirm Message\")'></body></html>";
URL testUrl = new URI("http://Page1/").toURL();
MockWebConnection mockConnection = new MockWebConnection();
final List<String> confirmMessages = new ArrayList<>();
// set up
webClient.setConfirmHandler((page, message) -> {
confirmMessages.add(message);
return true;
});
mockConnection.setResponse(testUrl, html);
webClient.setWebConnection(mockConnection);
// go
HtmlPage firstPage = webClient.getPage(testUrl);
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(firstPage, "Hello");
assertArrayEquals(new String[]{"Confirm Message"}, confirmMessages.toArray());
}
@Test
public void testWindowConfirmAndAlert() throws FailingHttpStatusCodeException, IOException, URISyntaxException {
String html = "<html><head><title>Hello</title>" +
"<script>function go(){" +
"alert(confirm('Confirm Message'))" +
"}</script>\n"
+ "</head><body onload='go()'></body></html>";
URL testUrl = new URI("http://Page1/").toURL();
MockWebConnection mockConnection = new MockWebConnection();
final List<String> confirmMessages = new ArrayList<>();
// set up
webClient.setAlertHandler(new CollectingAlertHandler());
webClient.setConfirmHandler((page, message) -> {
confirmMessages.add(message);
return true;
});
mockConnection.setResponse(testUrl, html);
webClient.setWebConnection(mockConnection);
// go
HtmlPage firstPage = webClient.getPage(testUrl);
WebAssert.assertTitleEquals(firstPage, "Hello");
assertArrayEquals(new String[]{"Confirm Message"}, confirmMessages.toArray());
assertArrayEquals(new String[]{"true"}, ((CollectingAlertHandler) webClient.getAlertHandler()).getCollectedAlerts().toArray());
}
}实测效果:
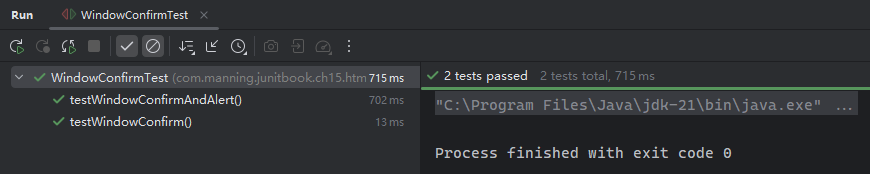
可以通过查看 ConfirmHandler 和 AlertHandler 接口的源码了解更多传参细节:
/**
* A handler for the JavaScript function <code>window.confirm()</code>. Confirms
* are triggered when the JavaScript function <code>window.confirm()</code> is invoked.
*
* @author Mike Bowler
* @author Ronald Brill
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ConfirmHandler extends Serializable {
/**
* Handles a confirm for the specified page.
* @param page the page on which the confirm occurred
* @param message the message in the confirm
* @return {@code true} if we are simulating clicking the OK button,
* {@code false} if we are simulating clicking the Cancel button
*/
boolean handleConfirm(Page page, String message);
}
/**
* A handler for JavaScript alerts. Alerts are triggered when the JavaScript method Window.alert()
* is called.
*
* @author Mike Bowler
* @author Ronald Brill
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface AlertHandler extends Serializable {
/**
* Handle an alert for the given page.
* @param page the page on which the alert occurred
* @param message the message in the alert
*/
void handleAlert(Page page, String message);
}这也是为什么自定义处理逻辑可以直接传入 Lambda 表达式的原因。
(上篇完)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号