1 项目背景与架构设计

图1-1:物联网监控系统整体架构与数据流

图1-2:技术选型对比分析与决策矩阵
假设你要为一个智能工厂搭建监控系统,需要实时采集温度、湿度、压力、振动等传感器数据,并提供实时监控和历史数据分析功能。这种场景下,InfluxDB是最佳选择。
我们的系统架构包含几个核心组件:传感器设备、数据采集网关、InfluxDB存储、Java后端服务、Web监控界面。整个数据流是这样的:传感器→网关→InfluxDB→后端API→前端展示。
1.1 系统需求分析
数据采集需求
- 支持多种传感器类型(温湿度、压力、振动、电流等)
- 数据采集频率:每秒到每分钟不等
- 设备数量:100-1000个传感器节点
- 数据保留:实时数据保留7天,聚合数据保留1年
监控功能需求
- 实时数据展示和告警
- 历史趋势分析
- 设备状态监控
- 数据导出和报表生成
1.2 技术架构选型
数据存储层
- InfluxDB 2.x:时序数据存储
- Redis:缓存和会话管理
应用服务层
- Spring Boot:Java后端框架
- InfluxDB Java Client:数据库连接
- WebSocket:实时数据推送
前端展示层
- Vue.js + ECharts:数据可视化
- Element UI:界面组件
2 InfluxDB数据模型设计

图2-1:InfluxDB数据模型结构与查询策略
2.1 数据结构规划
根据物联网场景的特点,我们设计如下的数据模型:
传感器数据表(sensor_data)
measurement: sensor_data
tags:
- device_id: 设备ID
- sensor_type: 传感器类型(temperature, humidity, pressure等)
- location: 设备位置
- workshop: 车间编号
fields:
- value: 传感器数值
- status: 设备状态(0正常,1异常)
- battery: 电池电量(可选)
timestamp: 数据采集时间设备状态表(device_status)
measurement: device_status
tags:
- device_id: 设备ID
- device_type: 设备类型
fields:
- online: 是否在线
- last_heartbeat: 最后心跳时间
- signal_strength: 信号强度
timestamp: 状态更新时间2.2 数据写入策略
考虑到物联网设备的特点,我们采用批量写入策略来提高性能:
// 批量数据写入配置
WriteOptions writeOptions = WriteOptions.builder()
.batchSize(1000) // 批量大小
.flushInterval(5000) // 5秒刷新一次
.bufferLimit(10000) // 缓冲区大小
.retryInterval(1000) // 重试间隔
.build();3 Java后端服务实现

图3-1:Java后端服务架构与组件关系
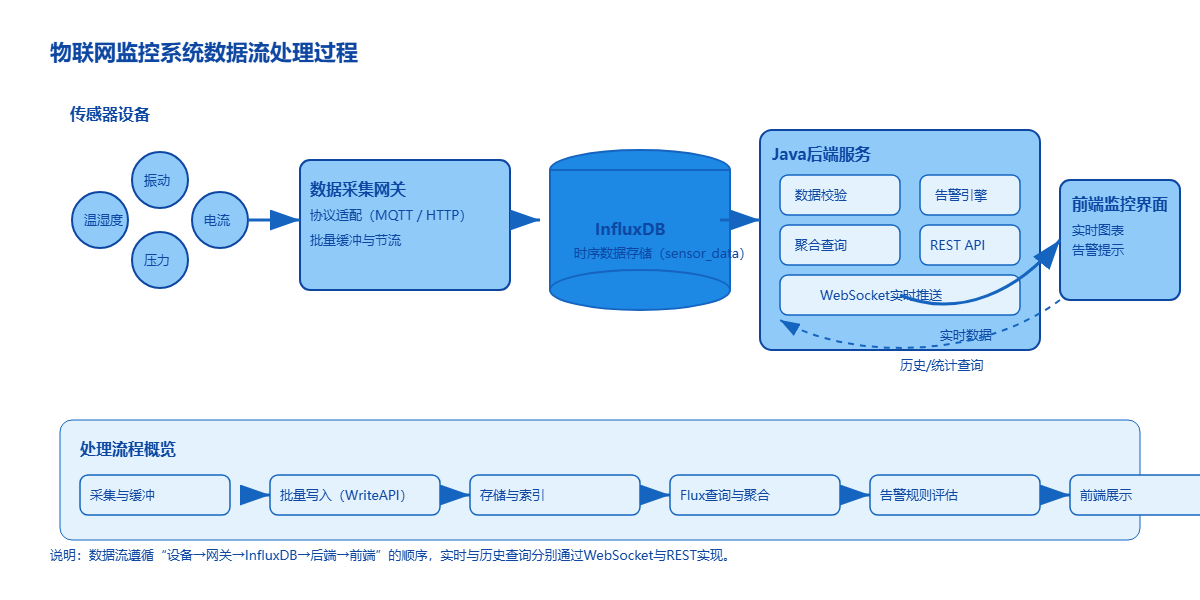
图3-2:物联网监控系统数据流处理过程
3.1 项目依赖配置
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.influxdb</groupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-client-java</artifactId>
<version>6.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>2.0.25</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>3.2 InfluxDB配置类
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClient;
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClientFactory;
import com.influxdb.client.WriteApiBlocking;
import com.influxdb.client.domain.WritePrecision;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class InfluxDBConfig {
@Value("${influxdb.url}")
private String influxUrl;
@Value("${influxdb.token}")
private String token;
@Value("${influxdb.org}")
private String org;
@Value("${influxdb.bucket}")
private String bucket;
@Bean
public InfluxDBClient influxDBClient() {
return InfluxDBClientFactory.create(influxUrl, token.toCharArray());
}
@Bean
public WriteApiBlocking writeApi(InfluxDBClient client) {
return client.getWriteApiBlocking();
}
}3.3 数据模型定义
import com.influxdb.annotations.Column;
import com.influxdb.annotations.Measurement;
import java.time.Instant;
@Measurement(name = "sensor_data")
public class SensorData {
@Column(tag = true)
private String deviceId;
@Column(tag = true)
private String sensorType;
@Column(tag = true)
private String location;
@Column(tag = true)
private String workshop;
@Column
private Double value;
@Column
private Integer status;
@Column
private Double battery;
@Column(timestamp = true)
private Instant timestamp;
// 构造函数
public SensorData() {}
public SensorData(String deviceId, String sensorType, String location,
String workshop, Double value, Integer status) {
this.deviceId = deviceId;
this.sensorType = sensorType;
this.location = location;
this.workshop = workshop;
this.value = value;
this.status = status;
this.timestamp = Instant.now();
}
// getters and setters...
public String getDeviceId() { return deviceId; }
public void setDeviceId(String deviceId) { this.deviceId = deviceId; }
public String getSensorType() { return sensorType; }
public void setSensorType(String sensorType) { this.sensorType = sensorType; }
public String getLocation() { return location; }
public void setLocation(String location) { this.location = location; }
public String getWorkshop() { return workshop; }
public void setWorkshop(String workshop) { this.workshop = workshop; }
public Double getValue() { return value; }
public void setValue(Double value) { this.value = value; }
public Integer getStatus() { return status; }
public void setStatus(Integer status) { this.status = status; }
public Double getBattery() { return battery; }
public void setBattery(Double battery) { this.battery = battery; }
public Instant getTimestamp() { return timestamp; }
public void setTimestamp(Instant timestamp) { this.timestamp = timestamp; }
}
@Measurement(name = "device_status")
public class DeviceStatus {
@Column(tag = true)
private String deviceId;
@Column(tag = true)
private String deviceType;
@Column
private Boolean online;
@Column
private Long lastHeartbeat;
@Column
private Integer signalStrength;
@Column(timestamp = true)
private Instant timestamp;
// 构造函数和getter/setter方法...
public DeviceStatus() {}
public DeviceStatus(String deviceId, String deviceType, Boolean online,
Integer signalStrength) {
this.deviceId = deviceId;
this.deviceType = deviceType;
this.online = online;
this.signalStrength = signalStrength;
this.lastHeartbeat = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.timestamp = Instant.now();
}
// getters and setters...
}3.4 数据访问层实现
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClient;
import com.influxdb.client.QueryApi;
import com.influxdb.client.WriteApiBlocking;
import com.influxdb.query.FluxTable;
import com.influxdb.query.FluxRecord;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.util.*;
@Repository
public class SensorDataRepository {
@Autowired
private InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
@Autowired
private WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
@Value("${influxdb.bucket}")
private String bucket;
@Value("${influxdb.org}")
private String org;
// 写入单条传感器数据
public void writeSensorData(SensorData data) {
writeApi.writeMeasurement(WritePrecision.NS, data);
}
// 批量写入传感器数据
public void writeSensorDataBatch(List<SensorData> dataList) {
writeApi.writeMeasurements(WritePrecision.NS, dataList);
}
// 查询最新的传感器数据
public List<SensorData> getLatestSensorData(String deviceId, int limit) {
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "sensor_data")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["device_id"] == "%s")
|> sort(columns: ["_time"], desc: true)
|> limit(n: %d)
""", bucket, deviceId, limit);
return executeQueryForSensorData(flux);
}
// 查询指定时间范围的传感器数据
public List<SensorData> getSensorDataByTimeRange(String deviceId, String sensorType,
Instant start, Instant end) {
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: %s, stop: %s)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "sensor_data")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["device_id"] == "%s")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["sensor_type"] == "%s")
|> sort(columns: ["_time"])
""", bucket, start, end, deviceId, sensorType);
return executeQueryForSensorData(flux);
}
// 获取聚合数据(按时间窗口)
public List<Map<String, Object>> getAggregatedData(String deviceId, String sensorType,
String timeWindow, int hours) {
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -%dh)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "sensor_data")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["device_id"] == "%s")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["sensor_type"] == "%s")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "value")
|> aggregateWindow(every: %s, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)
|> yield(name: "mean")
""", bucket, hours, deviceId, sensorType, timeWindow);
return executeQueryForAggregatedData(flux);
}
// 获取设备状态统计
public Map<String, Object> getDeviceStatusStats() {
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -5m)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "device_status")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "online")
|> group(columns: ["device_id"])
|> last()
|> group()
|> sum(column: "_value")
""", bucket);
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(flux, org);
Map<String, Object> stats = new HashMap<>();
int onlineCount = 0;
int totalCount = 0;
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
if (record.getValue() != null) {
onlineCount = ((Number) record.getValue()).intValue();
}
}
}
// 获取总设备数
String totalFlux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "device_status")
|> group(columns: ["device_id"])
|> last()
|> group()
|> count()
""", bucket);
List<FluxTable> totalTables = queryApi.query(totalFlux, org);
for (FluxTable table : totalTables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
if (record.getValue() != null) {
totalCount = ((Number) record.getValue()).intValue();
}
}
}
stats.put("onlineCount", onlineCount);
stats.put("totalCount", totalCount);
stats.put("offlineCount", totalCount - onlineCount);
stats.put("onlineRate", totalCount > 0 ? (double) onlineCount / totalCount : 0.0);
return stats;
}
private List<SensorData> executeQueryForSensorData(String flux) {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(flux, org);
List<SensorData> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
SensorData data = new SensorData();
data.setTimestamp(record.getTime());
data.setDeviceId((String) record.getValueByKey("device_id"));
data.setSensorType((String) record.getValueByKey("sensor_type"));
data.setLocation((String) record.getValueByKey("location"));
data.setWorkshop((String) record.getValueByKey("workshop"));
if ("value".equals(record.getField())) {
data.setValue((Double) record.getValue());
} else if ("status".equals(record.getField())) {
data.setStatus(((Number) record.getValue()).intValue());
} else if ("battery".equals(record.getField())) {
data.setBattery((Double) record.getValue());
}
result.add(data);
}
}
return result;
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> executeQueryForAggregatedData(String flux) {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(flux, org);
List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
Map<String, Object> dataPoint = new HashMap<>();
dataPoint.put("timestamp", record.getTime());
dataPoint.put("value", record.getValue());
result.add(dataPoint);
}
}
return result;
}
}4 实时数据采集服务
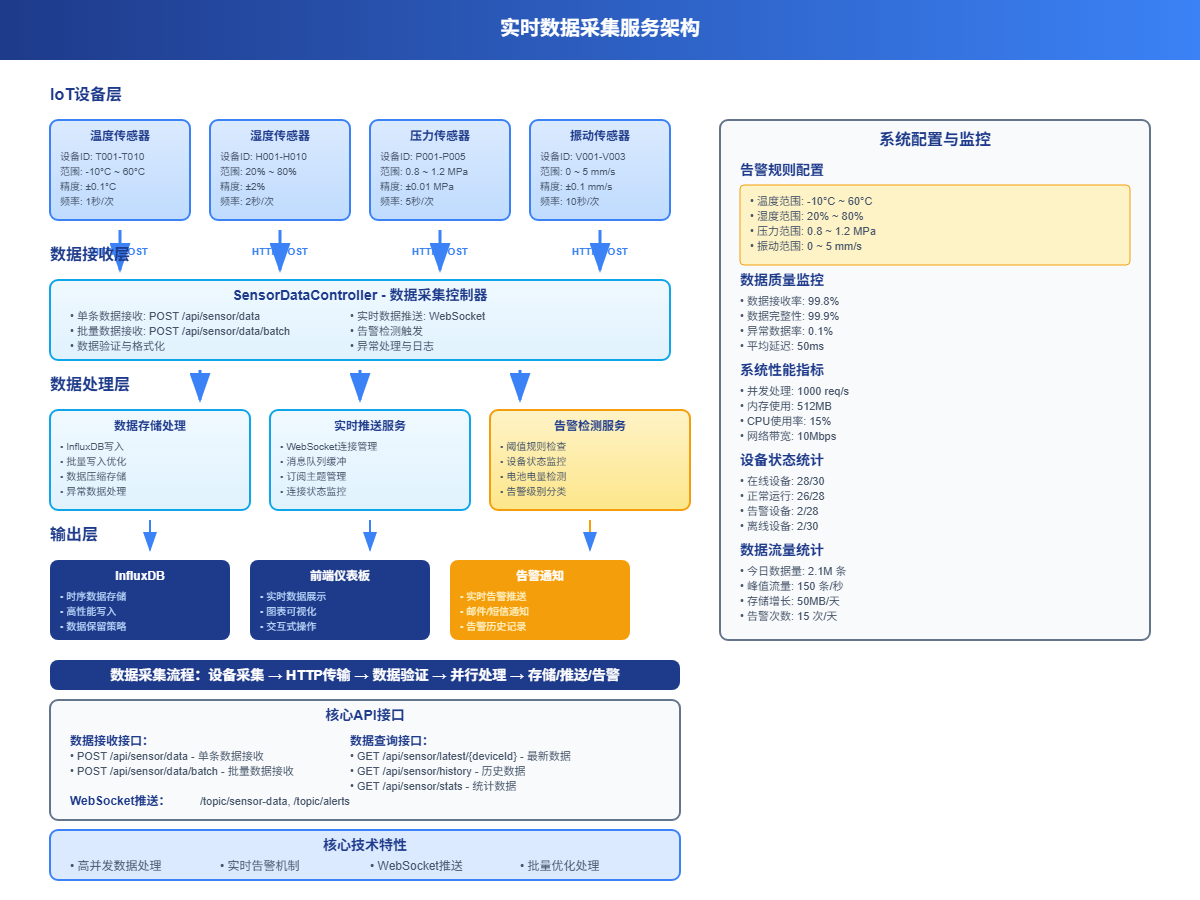
图4-1:实时数据采集服务架构与处理流程
4.1 数据接收控制器
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.messaging.simp.SimpMessagingTemplate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/sensor")
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
public class SensorDataController {
@Autowired
private SensorDataRepository sensorDataRepository;
@Autowired
private SimpMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate;
@Autowired
private AlertService alertService;
// 接收传感器数据
@PostMapping("/data")
public ResponseResult receiveSensorData(@RequestBody SensorDataRequest request) {
try {
// 数据验证
if (request.getDeviceId() == null || request.getValue() == null) {
return ResponseResult.error("设备ID和数值不能为空");
}
// 创建传感器数据对象
SensorData sensorData = new SensorData(
request.getDeviceId(),
request.getSensorType(),
request.getLocation(),
request.getWorkshop(),
request.getValue(),
request.getStatus()
);
if (request.getBattery() != null) {
sensorData.setBattery(request.getBattery());
}
// 写入数据库
sensorDataRepository.writeSensorData(sensorData);
// 实时推送到前端
messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/sensor-data", sensorData);
// 检查告警条件
alertService.checkAlerts(sensorData);
return ResponseResult.success("数据接收成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("数据处理失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 批量接收传感器数据
@PostMapping("/data/batch")
public ResponseResult receiveBatchSensorData(@RequestBody List<SensorDataRequest> requests) {
try {
List<SensorData> sensorDataList = requests.stream()
.map(request -> new SensorData(
request.getDeviceId(),
request.getSensorType(),
request.getLocation(),
request.getWorkshop(),
request.getValue(),
request.getStatus()
))
.toList();
// 批量写入
sensorDataRepository.writeSensorDataBatch(sensorDataList);
// 批量推送
messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/sensor-data-batch", sensorDataList);
return ResponseResult.success("批量数据接收成功,共处理 " + requests.size() + " 条数据");
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("批量数据处理失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 获取最新传感器数据
@GetMapping("/latest/{deviceId}")
public ResponseResult getLatestData(@PathVariable String deviceId,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") int limit) {
try {
List<SensorData> data = sensorDataRepository.getLatestSensorData(deviceId, limit);
return ResponseResult.success(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("查询失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 获取历史数据
@GetMapping("/history")
public ResponseResult getHistoryData(@RequestParam String deviceId,
@RequestParam String sensorType,
@RequestParam String startTime,
@RequestParam String endTime) {
try {
Instant start = Instant.parse(startTime);
Instant end = Instant.parse(endTime);
List<SensorData> data = sensorDataRepository.getSensorDataByTimeRange(
deviceId, sensorType, start, end);
return ResponseResult.success(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("查询历史数据失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 获取聚合统计数据
@GetMapping("/stats")
public ResponseResult getAggregatedStats(@RequestParam String deviceId,
@RequestParam String sensorType,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "5m") String timeWindow,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "24") int hours) {
try {
List<Map<String, Object>> data = sensorDataRepository.getAggregatedData(
deviceId, sensorType, timeWindow, hours);
return ResponseResult.success(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("查询统计数据失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// 请求数据模型
class SensorDataRequest {
private String deviceId;
private String sensorType;
private String location;
private String workshop;
private Double value;
private Integer status;
private Double battery;
// getters and setters...
}
// 响应结果模型
class ResponseResult {
private boolean success;
private String message;
private Object data;
public static ResponseResult success(Object data) {
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult();
result.success = true;
result.data = data;
return result;
}
public static ResponseResult error(String message) {
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult();
result.success = false;
result.message = message;
return result;
}
// getters and setters...
}4.2 告警服务实现
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.messaging.simp.SimpMessagingTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class AlertService {
@Autowired
private SimpMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate;
// 告警规则配置
private final Map<String, AlertRule> alertRules = new HashMap<>();
public AlertService() {
// 初始化告警规则
alertRules.put("temperature", new AlertRule("温度", -10.0, 60.0));
alertRules.put("humidity", new AlertRule("湿度", 20.0, 80.0));
alertRules.put("pressure", new AlertRule("压力", 0.8, 1.2));
alertRules.put("vibration", new AlertRule("振动", 0.0, 5.0));
}
public void checkAlerts(SensorData sensorData) {
AlertRule rule = alertRules.get(sensorData.getSensorType());
if (rule == null) return;
Double value = sensorData.getValue();
if (value == null) return;
// 检查是否超出正常范围
if (value < rule.getMinValue() || value > rule.getMaxValue()) {
Alert alert = new Alert(
sensorData.getDeviceId(),
sensorData.getSensorType(),
rule.getName(),
value,
rule.getMinValue(),
rule.getMaxValue(),
"数值超出正常范围",
Instant.now()
);
// 发送告警
sendAlert(alert);
}
// 检查设备状态
if (sensorData.getStatus() != null && sensorData.getStatus() != 0) {
Alert alert = new Alert(
sensorData.getDeviceId(),
sensorData.getSensorType(),
rule.getName(),
value,
null,
null,
"设备状态异常",
Instant.now()
);
sendAlert(alert);
}
// 检查电池电量
if (sensorData.getBattery() != null && sensorData.getBattery() < 20.0) {
Alert alert = new Alert(
sensorData.getDeviceId(),
"battery",
"电池电量",
sensorData.getBattery(),
20.0,
100.0,
"电池电量过低",
Instant.now()
);
sendAlert(alert);
}
}
private void sendAlert(Alert alert) {
// 推送到前端
messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/alerts", alert);
// 这里可以添加其他告警方式,如邮件、短信等
System.out.println("告警: " + alert.getMessage() +
" - 设备: " + alert.getDeviceId() +
" - 当前值: " + alert.getCurrentValue());
}
}
// 告警规则类
class AlertRule {
private String name;
private Double minValue;
private Double maxValue;
public AlertRule(String name, Double minValue, Double maxValue) {
this.name = name;
this.minValue = minValue;
this.maxValue = maxValue;
}
// getters and setters...
}
// 告警信息类
class Alert {
private String deviceId;
private String sensorType;
private String sensorName;
private Double currentValue;
private Double minValue;
private Double maxValue;
private String message;
private Instant timestamp;
public Alert(String deviceId, String sensorType, String sensorName,
Double currentValue, Double minValue, Double maxValue,
String message, Instant timestamp) {
this.deviceId = deviceId;
this.sensorType = sensorType;
this.sensorName = sensorName;
this.currentValue = currentValue;
this.minValue = minValue;
this.maxValue = maxValue;
this.message = message;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
// getters and setters...
}5 监控仪表板实现
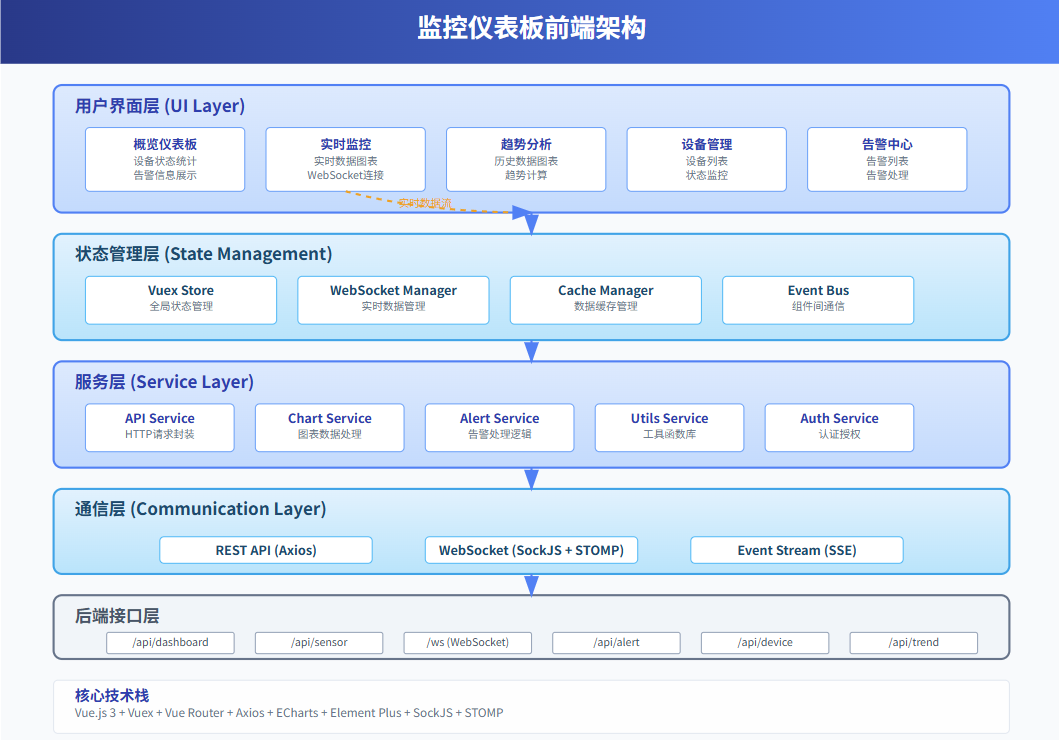
图5-1:监控仪表板前端架构与组件设计
5.1 设备监控控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/dashboard")
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
public class DashboardController {
@Autowired
private SensorDataRepository sensorDataRepository;
// 获取仪表板概览数据
@GetMapping("/overview")
public ResponseResult getDashboardOverview() {
try {
Map<String, Object> overview = new HashMap<>();
// 设备状态统计
Map<String, Object> deviceStats = sensorDataRepository.getDeviceStatusStats();
overview.put("deviceStats", deviceStats);
// 最新数据统计
overview.put("latestDataCount", getLatestDataCount());
// 告警统计
overview.put("alertStats", getAlertStats());
return ResponseResult.success(overview);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("获取概览数据失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 获取实时数据流
@GetMapping("/realtime/{deviceId}")
public ResponseResult getRealtimeData(@PathVariable String deviceId) {
try {
List<SensorData> data = sensorDataRepository.getLatestSensorData(deviceId, 50);
return ResponseResult.success(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("获取实时数据失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// 获取趋势分析数据
@GetMapping("/trend")
public ResponseResult getTrendData(@RequestParam String deviceId,
@RequestParam String sensorType,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1h") String timeWindow,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "24") int hours) {
try {
List<Map<String, Object>> trendData = sensorDataRepository.getAggregatedData(
deviceId, sensorType, timeWindow, hours);
// 计算趋势指标
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("data", trendData);
result.put("trend", calculateTrend(trendData));
return ResponseResult.success(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseResult.error("获取趋势数据失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private int getLatestDataCount() {
// 这里可以实现获取最近5分钟的数据量统计
return 1250; // 示例数据
}
private Map<String, Object> getAlertStats() {
Map<String, Object> alertStats = new HashMap<>();
alertStats.put("totalAlerts", 15);
alertStats.put("criticalAlerts", 3);
alertStats.put("warningAlerts", 12);
return alertStats;
}
private Map<String, Object> calculateTrend(List<Map<String, Object>> data) {
if (data.size() < 2) {
return Map.of("direction", "stable", "change", 0.0);
}
Double firstValue = (Double) data.get(0).get("value");
Double lastValue = (Double) data.get(data.size() - 1).get("value");
if (firstValue == null || lastValue == null) {
return Map.of("direction", "stable", "change", 0.0);
}
double change = ((lastValue - firstValue) / firstValue) * 100;
String direction = change > 5 ? "up" : change < -5 ? "down" : "stable";
return Map.of("direction", direction, "change", Math.round(change * 100.0) / 100.0);
}
}5.2 WebSocket配置
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.messaging.simp.config.MessageBrokerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocketMessageBroker;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.StompEndpointRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry config) {
// 启用简单消息代理
config.enableSimpleBroker("/topic");
// 设置应用程序目标前缀
config.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app");
}
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
// 注册STOMP端点
registry.addEndpoint("/ws")
.setAllowedOriginPatterns("*")
.withSockJS();
}
}6 数据模拟器

图6-1:数据模拟器生成流程与策略设计
为了测试系统,我们创建一个数据模拟器来生成传感器数据:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
@Component
public class SensorDataSimulator {
@Autowired
private SensorDataRepository sensorDataRepository;
private final Random random = new Random();
private final String[] deviceIds = {"TEMP_001", "TEMP_002", "HUM_001", "HUM_002", "PRESS_001"};
private final String[] locations = {"车间A", "车间B", "车间C", "仓库", "办公区"};
private final String[] workshops = {"WS001", "WS002", "WS003", "WS004", "WS005"};
// 每30秒生成一批模拟数据
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000)
public void generateSimulatedData() {
List<SensorData> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String deviceId : deviceIds) {
String sensorType = getSensorType(deviceId);
SensorData data = new SensorData(
deviceId,
sensorType,
locations[random.nextInt(locations.length)],
workshops[random.nextInt(workshops.length)],
generateSensorValue(sensorType),
random.nextInt(100) < 95 ? 0 : 1 // 95%概率正常状态
);
// 随机设置电池电量
if (random.nextBoolean()) {
data.setBattery(80.0 + random.nextDouble() * 20.0);
}
dataList.add(data);
}
// 批量写入
sensorDataRepository.writeSensorDataBatch(dataList);
System.out.println("生成了 " + dataList.size() + " 条模拟传感器数据");
}
private String getSensorType(String deviceId) {
if (deviceId.startsWith("TEMP")) return "temperature";
if (deviceId.startsWith("HUM")) return "humidity";
if (deviceId.startsWith("PRESS")) return "pressure";
return "unknown";
}
private Double generateSensorValue(String sensorType) {
switch (sensorType) {
case "temperature":
return 20.0 + random.nextGaussian() * 5.0; // 平均20度,标准差5度
case "humidity":
return 50.0 + random.nextGaussian() * 10.0; // 平均50%,标准差10%
case "pressure":
return 1.0 + random.nextGaussian() * 0.1; // 平均1.0,标准差0.1
default:
return random.nextDouble() * 100;
}
}
}7 性能优化与最佳实践

图7-1:性能优化策略对比分析与效果评估
7.1 批量写入优化
@Service
public class OptimizedDataService {
@Autowired
private InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
@Value("${influxdb.bucket}")
private String bucket;
@Value("${influxdb.org}")
private String org;
// 使用异步写入API提高性能
public void writeDataAsync(List<SensorData> dataList) {
WriteApi writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApi(
WriteOptions.builder()
.batchSize(1000)
.flushInterval(5000)
.bufferLimit(10000)
.build()
);
writeApi.writeMeasurements(WritePrecision.NS, dataList);
writeApi.close(); // 确保数据被刷新
}
// 数据压缩和预处理
public List<SensorData> preprocessData(List<SensorData> rawData) {
return rawData.stream()
.filter(data -> data.getValue() != null) // 过滤空值
.filter(data -> isValidRange(data)) // 过滤异常值
.map(this::normalizeData) // 数据标准化
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private boolean isValidRange(SensorData data) {
Double value = data.getValue();
String type = data.getSensorType();
switch (type) {
case "temperature":
return value >= -50 && value <= 100;
case "humidity":
return value >= 0 && value <= 100;
case "pressure":
return value >= 0 && value <= 10;
default:
return true;
}
}
private SensorData normalizeData(SensorData data) {
// 数据精度控制
if (data.getValue() != null) {
data.setValue(Math.round(data.getValue() * 100.0) / 100.0);
}
return data;
}
}7.2 查询性能优化
@Service
public class OptimizedQueryService {
@Autowired
private InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
@Value("${influxdb.bucket}")
private String bucket;
@Value("${influxdb.org}")
private String org;
// 使用连接池和缓存优化查询
@Cacheable(value = "sensorData", key = "#deviceId + '_' + #hours")
public List<Map<String, Object>> getCachedAggregatedData(String deviceId, int hours) {
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -%dh)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "sensor_data")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["device_id"] == "%s")
|> aggregateWindow(every: 5m, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)
""", bucket, hours, deviceId);
return executeOptimizedQuery(flux);
}
// 分页查询大数据集
public List<SensorData> getPagedSensorData(String deviceId, int page, int size) {
int offset = page * size;
String flux = String.format("""
from(bucket: "%s")
|> range(start: -24h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "sensor_data")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["device_id"] == "%s")
|> sort(columns: ["_time"], desc: true)
|> limit(n: %d, offset: %d)
""", bucket, deviceId, size, offset);
return executeQueryForSensorData(flux);
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> executeOptimizedQuery(String flux) {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
// 使用流式查询减少内存占用
List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>();
queryApi.query(flux, org, (cancellable, record) -> {
Map<String, Object> dataPoint = new HashMap<>();
dataPoint.put("timestamp", record.getTime());
dataPoint.put("value", record.getValue());
result.add(dataPoint);
});
return result;
}
}这个物联网监控系统展示了InfluxDB在实际项目中的应用。通过合理的数据模型设计、高效的批量写入、实时数据推送和智能告警机制,我们构建了一个完整的时序数据处理平台。
系统的核心优势包括:高并发数据写入能力、灵活的查询和聚合功能、实时监控和告警、可扩展的架构设计。这些特性让它能够很好地适应各种物联网和监控场景的需求。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号