JUC集合&JUC辅助类&读写锁
JUC集合
List
CopyOnWriteArrayList
- CopyOnWriteArrayList 写入时复制。cow,是计算机程序设计领域的一种优化策略。
- 多个线程并发调用list时,为解决写入的时候避免覆盖造成数据的问题,
- 写入的时候复制一个数据出来,写入后再插入进去
- 性能 vector(synchronized)<CopyOnWriteArrayList (cow Arrays.copyOf())
我们知道ArrayList和LinkedList实现的List都是非线程安全的,于是就有了Vector,它是基于ArrayList的线程安全集合,但Vector无论是add方法还是get方法都加上了synchronized修饰,当多线程读写List必须排队执行,很显然这样效率比较是低下的。那有没有一种办法让效率提升,让当读List的时候线程是异步的,当写List是同步的呢?答案是CopyOnWriteArrayList,它是读写分离的,好处是提高线程访问效率。
import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; public class CopyOnWriteArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 线程不安全ArrayList => ConcurrentModificationException并发修改异常。 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();*/ //List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<String>()); //List<String> list = new Vector<String>(); List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 5)); System.out.println(list); }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); } } }
CopyOnWriteArrayList底层
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * 将指定元素附加到此列表的末尾。*/ public boolean add(E e) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;//加锁,线程安全 lock.lock(); try { Object[] elements = getArray();//获取当前数据 int len = elements.length;//当前数组长度 Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);//参数1:要复制的数组;参数2:返回新数组的长度 newElements[len] = e;//新数组的最后位置是新插入的值e setArray(newElements);//新数组替换旧数组 return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
Set
CopyOnWriteArraySet
//Set<String> set = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>()); Set<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { set.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 5)); System.out.println(set); }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); }
CopyOnWriteArraySet底层
CopyOnWriteArraySet的实现原理是通过CopyOnWriteArrayList的机制来实现的
class CopyOnWriteArraySet{ private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<E> al; /** * Creates an empty set. */ public CopyOnWriteArraySet() { //内部维护的是一个CopyOnWriteArrayList, //所以CopyOnWriteArraySet的实现原理是通过CopyOnWriteArrayList的机制来实现的; al = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<E>(); } /** * Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. * More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if * the set contains no element {@code e2} such that * <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>. * If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set * unchanged and returns {@code false}. * * @param e element to be added to this set * @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified * element * * 如果指定的元素尚不存在,则将其添加到此集合中。 * 更正式地说,将指定元素 {@code e} 添加到此集合中, * 如果该集合不包含元素 {@code e2} 添加到集合中; * 如果这个集合已经包含该元素,则调用离开集合不变并返回 {@code false}。 */ public boolean add(E e) { return al.addIfAbsent(e); } /** * Appends the element, if not present. * 如果不存在,追加元素。 * @param e element to be added to this list, if absent * @return {@code true} if the element was added */ public boolean addIfAbsent(E e) { Object[] snapshot = getArray(); return indexOf(e, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length) >= 0 ? false : addIfAbsent(e, snapshot); } /** * A version of addIfAbsent using the strong hint that given * recent snapshot does not contain e. */ private boolean addIfAbsent(E e, Object[] snapshot) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { Object[] current = getArray(); int len = current.length; if (snapshot != current) { // Optimize for lost race to another addXXX operation int common = Math.min(snapshot.length, len); for (int i = 0; i < common; i++) if (current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(e, current[i])) return false; if (indexOf(e, current, common, len) >= 0) return false; } Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(current, len + 1); newElements[len] = e;//新数组替换旧数组 setArray(newElements);//设置新数组 return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
扩展HashSet底层:
HashSet底层是是一个map
//PRESENT 固定的常量
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
//map key是无序不重复的。
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
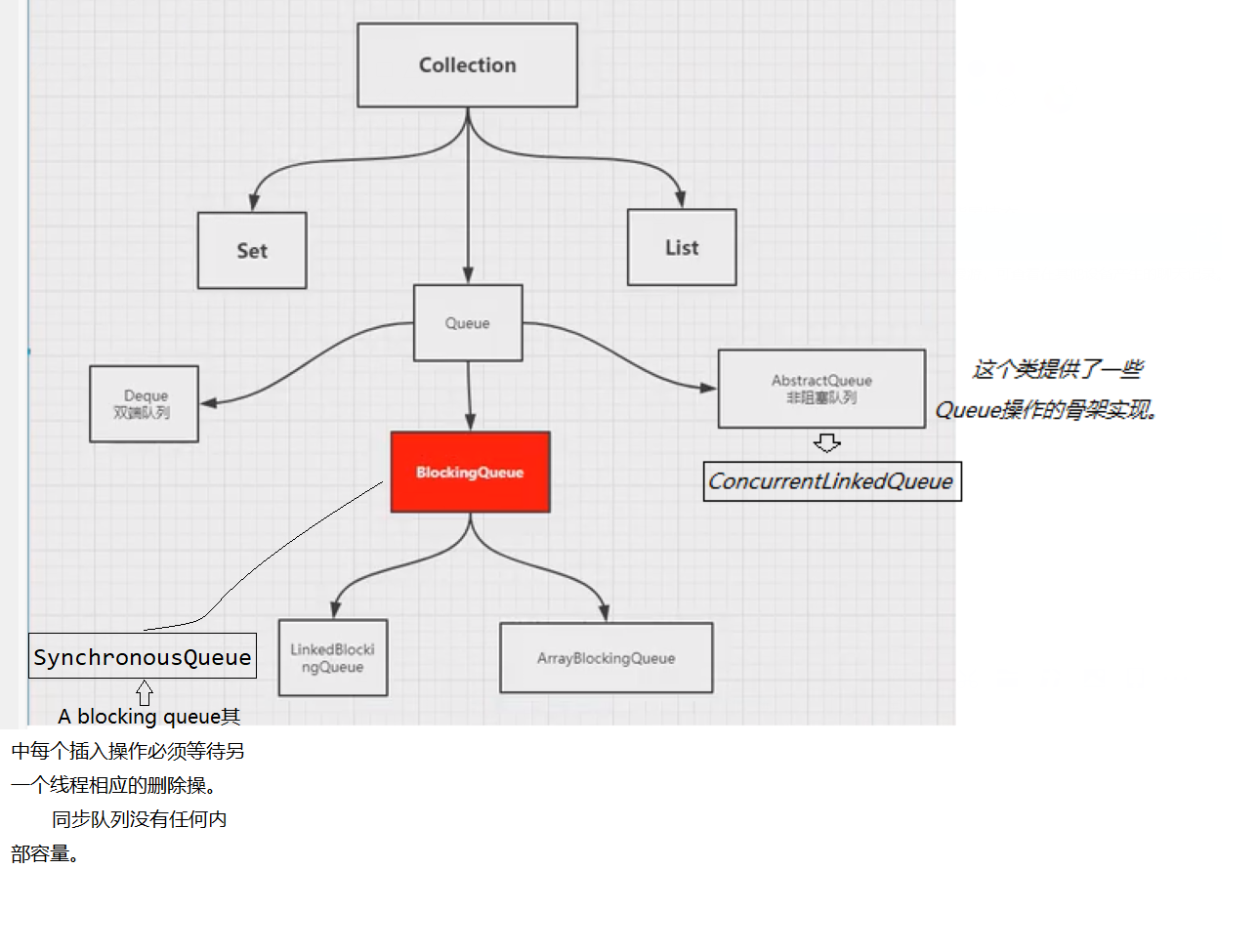
BlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 不抛出异常 | 等待超时 | 阻塞等待 |
| 添加 | add | offer |
blockingQueue.offer(element,2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); |
put |
| 删除 | remove | poll |
blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); |
take |
| 检测队首元素 | element | peek |
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ArrayBlockingQueueTest { static BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); public static void main(String[] args) { // throwsException(); // noThrowsException(); // blockingWait(); waitTimeOut(); } /** * 超时等待 */ private static void waitTimeOut() { try { System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(1) = " + blockingQueue.offer(1)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(2) = " + blockingQueue.offer(2)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(3) = " + blockingQueue.offer(3)); //blockingQueue.offer(4,2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 阻塞等待 */ private static void blockingWait() { try { blockingQueue.put(1); blockingQueue.put(2); blockingQueue.put(3); //blockingQueue.put(4);//一直阻塞,不能blockingQueue.take()。 System.out.println("blockingQueue.take() = " + blockingQueue.take()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.take() = " + blockingQueue.take()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.take() = " + blockingQueue.take()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.take() = " + blockingQueue.take());//一直阻塞。 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 不抛出异常 */ private static void noThrowsException() { System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(1) = " + blockingQueue.offer(1)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(2) = " + blockingQueue.offer(2)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(3) = " + blockingQueue.offer(3)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.offer(4) = " + blockingQueue.offer(4)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("检测队首元素 = " + blockingQueue.peek()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.poll() = " + blockingQueue.poll()); System.out.println("检测队首元素 = " + blockingQueue.peek());//队列为空时,返回null } /** * 抛出异常 */ private static void throwsException() { System.out.println("blockingQueue.add(1) = " + blockingQueue.add(1)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.add(2) = " + blockingQueue.add(2)); System.out.println("blockingQueue.add(3) = " + blockingQueue.add(3)); //blockingQueue.add(4);//java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full System.out.println("blockingQueue.remove() = " + blockingQueue.remove()); System.out.println("检测队首元素 = " + blockingQueue.element()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.remove() = " + blockingQueue.remove()); System.out.println("检测队首元素 = " + blockingQueue.element()); System.out.println("blockingQueue.remove() = " + blockingQueue.remove()); //System.out.println("blockingQueue.remove() = " + blockingQueue.remove());//java.util.NoSuchElementException System.out.println("检测队首元素 = " + blockingQueue.element());//队列为空时,java.util.NoSuchElementException } }
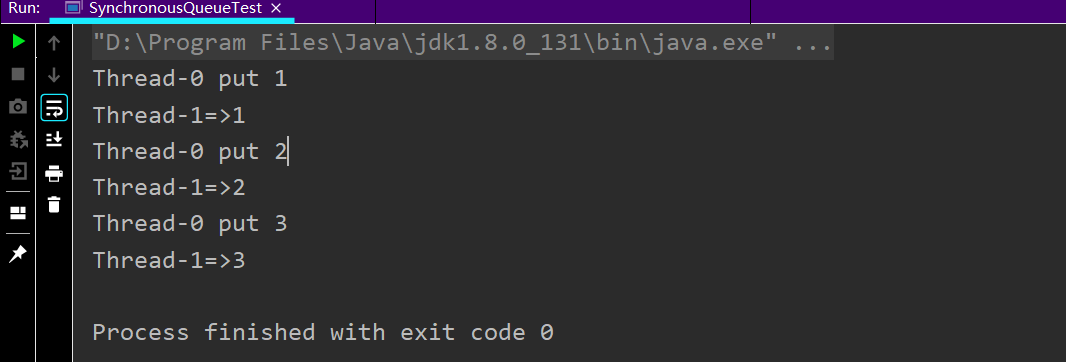
SynchronousQueue
/** * A blocking queue其中每个插入操作必须等待另一个线程相应的删除操。 * 同步队列没有任何内部容量。 */ public class SynchronousQueueTest { public static void main(String[] args) { BlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>(); new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 1"); blockingQueue.put(1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 2"); blockingQueue.put(2); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 3"); blockingQueue.put(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); new Thread(() -> { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + blockingQueue.take()); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + blockingQueue.take()); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + blockingQueue.take()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } }
Map
ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap底层
读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock
读写、写写线程不能共存
写写线程可以共存
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; public class ReentrantReadWriteLockTest { public static void main(String[] args) { useLock(); } public static void useLock() { MyCacheUseLock myCache = new MyCacheUseLock(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { final int temp = i; new Thread(() -> { myCache.read(String.valueOf(temp)); }, String.valueOf("线程") + temp).start(); } for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { final int temp = i; new Thread(() -> { myCache.write(String.valueOf(temp), String.valueOf(temp)); }, String.valueOf("线程") + temp).start(); } } public static void notUseLock() { MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { final int temp = i; new Thread(() -> { myCache.read(String.valueOf(temp)); }, String.valueOf("线程") + temp).start(); } for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { final int temp = i; new Thread(() -> { myCache.write(String.valueOf(temp), String.valueOf(temp)); }, String.valueOf("线程") + temp).start(); } } } /** * 使用读写锁 */ class MyCacheUseLock { private volatile Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); public void read(String key) { Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); try { readLock.lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取" + key); map.get(key); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取完毕" + key); } finally { readLock.unlock(); } } public void write(String key, String value) { Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); try { writeLock.lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入" + key); map.put(key, value); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入完毕" + key); } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } } } /** * 不适用读写锁 */ class MyCache { private volatile Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); public void read(String key) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取" + key); map.get(key); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取完毕" + key); } public void write(String key, String value) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入" + key); map.put(key, value); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入完毕" + key); } }
JUC辅助工具类
CountDownLatch减法计数器
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassRoom room = new ClassRoom();
room.liveSchool();
}
}
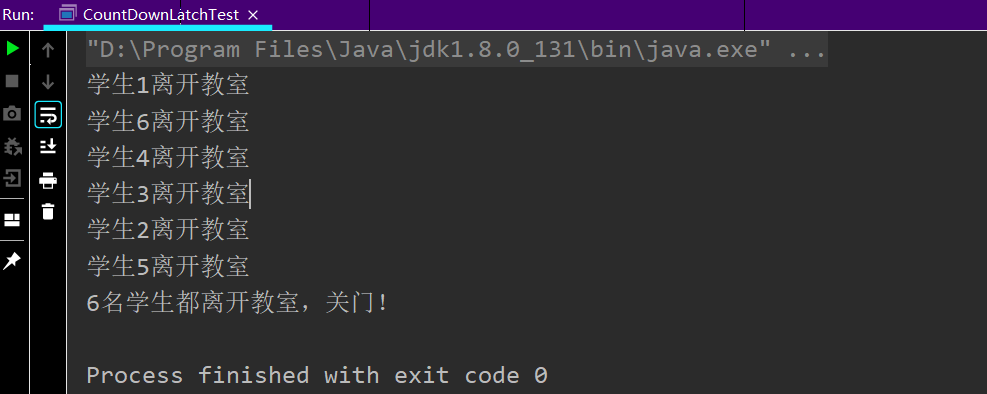
/**
*所有学生都离开教室才能锁门
*/
class ClassRoom{
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);//6个学生都离开教师,才能锁教室门
public void liveSchool(){
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"离开教室");
countDownLatch.countDown();//每次调用计数器都减1
},String.valueOf("学生"+i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();//计数器归0,才能向下执行
System.out.println("6名学生都离开教室,关门!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CyclicBarrier 加法计数器
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
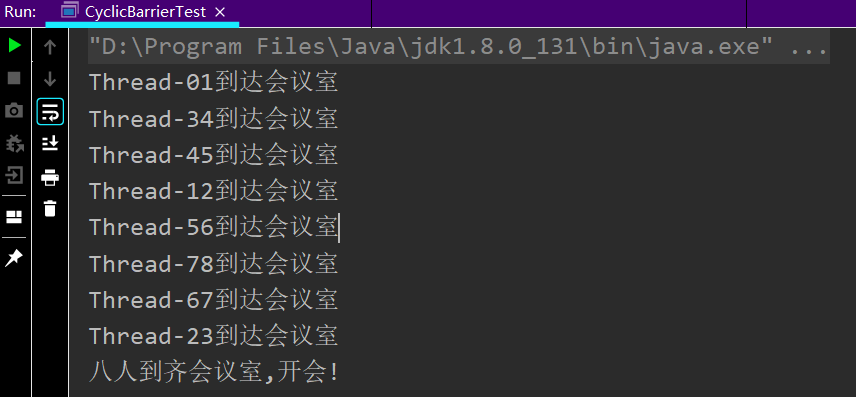
/**
* 八人到齐会议室才能开会
*/
public class CyclicBarrierTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(8,()->{
System.out.println("八人到齐会议室,开会!");
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
final int temp = i;
new Thread(()->{//new Thread()是一个类,要访问其他类的属性,只能是常量
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + temp + "到达会议室");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { }
}).start();
}
}
}
Semaphore
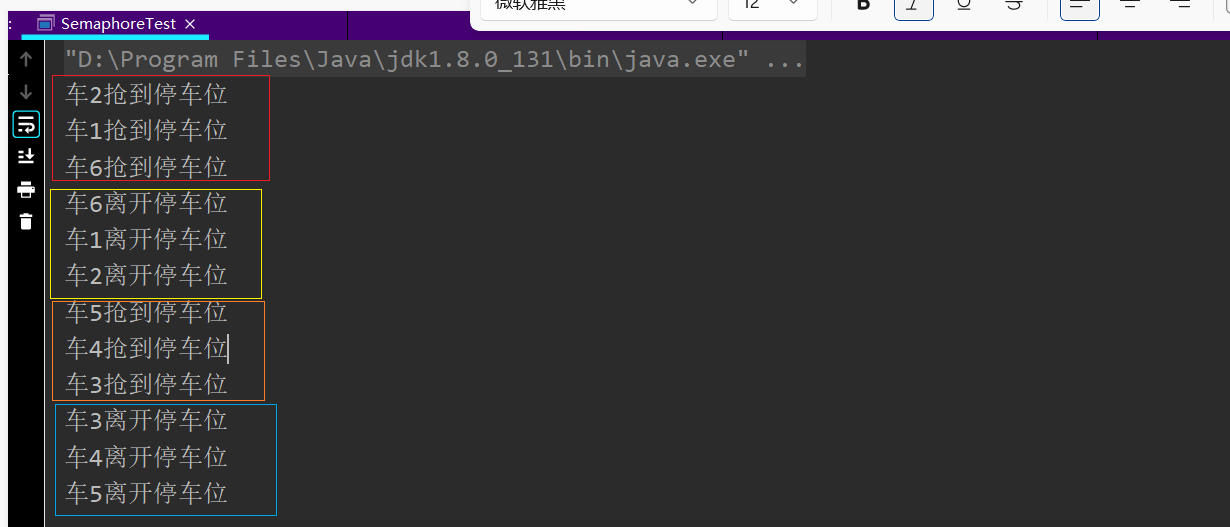
/**
* 限流停车
* 3个停车位,6辆车
*/
public class SemaphoreTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);//3个停车位
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {//六辆车争抢停车位
new Thread(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到停车位");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"离开停车位");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}finally {
semaphore.release();
}
},String.valueOf("车"+i)).start();
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号