Mybatis学习03--动态SQL
动态SQL
动态SQL就是根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL语句,在JDBC中,通常需要使用条件判断并拼接SQL字符串,而拼接SQL字符串的工作非常繁琐,使用Mybatis的动态SQL,可以避免这样的工作。
动态SQL由以下元素实现:
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
下面来看几个例子:
if
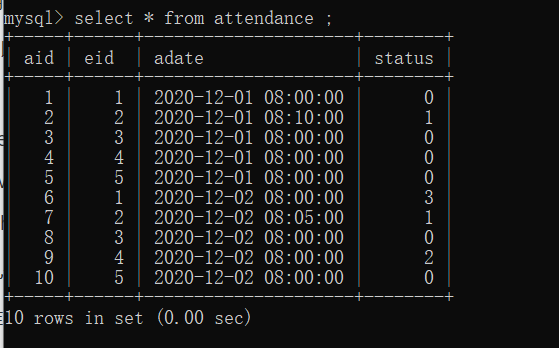
先在数据库中建表
Java实体类
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Attendance {
int id;
Employee employee;
Date adate;
int status;
public String toString(){
return "Attendance:"+id+" Employee:"+employee+
" Time:"+adate.toString()+" Status:"+
utils.status[this.status];
}
}
实现根据考勤id,员工id,打卡时间的多条件组合查询:
public interface AttendanceMapper {
public List<Attendance> selectByMutiColumn(@Param("eid") Integer eid, @Param("adate") Date adate, @Param("status") Integer status);
}
@Test
public void selectByMutiColumn() throws ParseException {
logger.info("info:");
Date date=new Date();
SqlSession session=MybatisUtil.getSession();
AttendanceMapper mapper=session.getMapper(AttendanceMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectByMutiColumn(1,date,0));
System.out.println(mapper.selectByMutiColumn(1,date,null));
}
映射器AttendanceMapper.xml:
<select id="selectByMutiColumn" resultMap="AttendMap">
select * from attendance
where eid=#{eid}
<!-- test中adate是数据库列名 -->
<if test="adate!=null">
and adate < #{adate}
</if>
<if test="status!=null">
and status=#{status}
</if>
</select>
<select id="selectEmployee" resultMap="EmployeeMap">
select * from employee
where id=#{eid}
</select>
<resultMap id="AttendMap" type="Attendance">
<id column="aid" property="id"/>
<result column="adate" property="adate"/>
<result column="status" property="status"/>
<association property="employee" column="eid"
javaType="Employee" select="selectEmployee"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="EmployeeMap" type="Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="ename" property="name"/>
</resultMap>
运行结果
choose (when, otherwise)
有时,我们只想在多个条件中选择一项使用,类似与switch语句的逻辑:按照顺序执行第一个满足条件的case子句,后面的即使满足条件也不执行,在动态SQL中可以用choose实现。
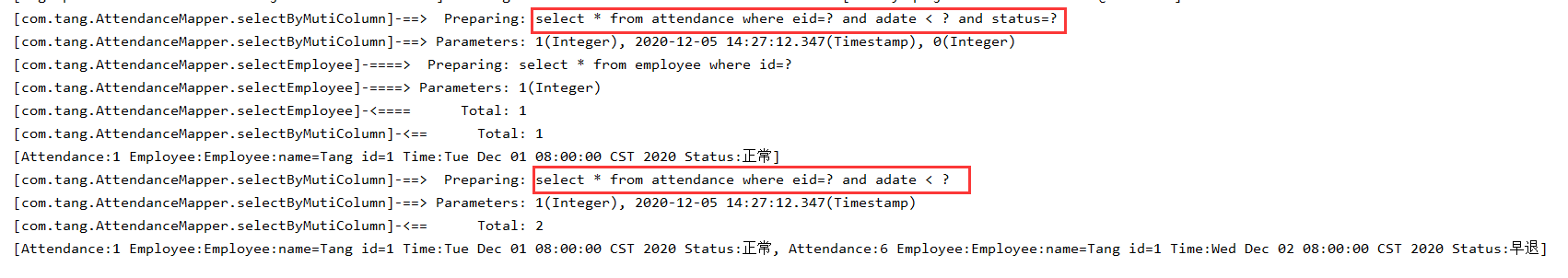
将刚才的例子if改成choose:
<choose>
<when test="adate!=null">
and adate < #{adate}
</when>
<when test="status!=null">
and status=#{status}
</when>
</choose>
运行结果可以看到,一旦满足条件adate!=null,之后的status子句就不会再判断和执行,两个查询生成的SQL语句相同,在数据库中只执行了一次,第二次直接使用了缓存。

trim (where, set)
在前面的例子中存在一个问题:如果第一个参数eid也使用if元素,会怎么样呢?
select * from attendance
where
<if test="eid!=null">
eid=#{eid}
</if>
<if test="adate!=null">
and adate < #{adate}
</if>
<if test="status!=null">
and status=#{status}
</if>
如果eid传入了null,那么SQL语句会被拼接成这样:
select * from attendance
where and adate=? and status=?
显然不正确,所以引入where元素,改写上面的SQL:
select * from attendance
<where>
<if test="eid!=null">
eid=#{eid}
</if>
<!-- < 表示 < -->
<if test="adate!=null">
and adate < #{adate}
</if>
<if test="status!=null">
and status=#{status}
</if>
</where>
还可以使用trim元素来定制SQL语句
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>
update功能的动态SQL语句可以用set完成
update attendance
<set>
<if test="aid!=null">
eid=#{eid},
</if>
...
<if test="status!=null">
status=#{status}
</if>
where aid=#{aid}
</set>
foreach
foreach用于对集合进行遍历
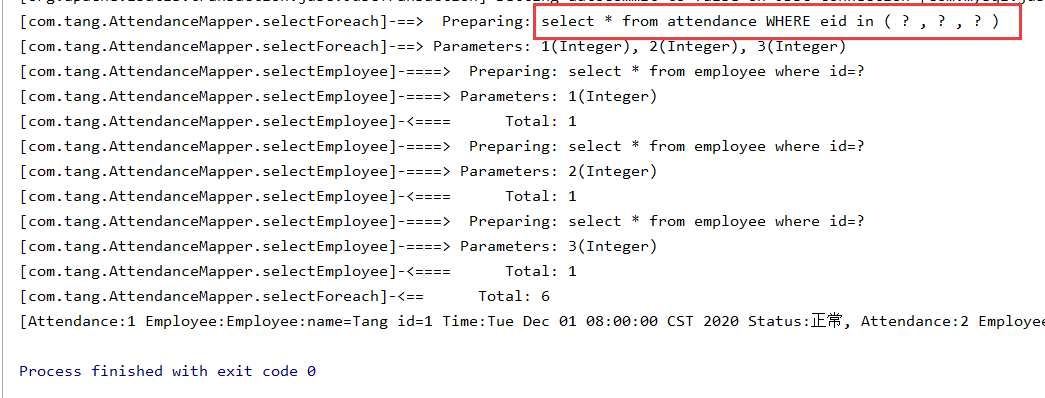
例如:查询员工(1,2,3)的考勤
<select id="selectForeach" resultMap="AttendMap">
select * from attendance
<!-- collection:传入Java接口方法的集合名称 item:集合元素名字,与传入#{}的参数对应
open:SQL语句开始的符号 separator:分割符 close:结束符
下面的foreach等价于:(item,item,...) -->
<where>
eid in
<foreach collection="eids" item="item"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
测试类:
@Test
public void selectForeach(){
logger.info("info:");
SqlSession session=MybatisUtil.getSession();
AttendanceMapper mapper=session.getMapper(AttendanceMapper.class);
Map<String,List<Integer>> map=new HashMap<>();
List<Integer> eidlist=new ArrayList<>();
eidlist.add(1);eidlist.add(2);eidlist.add(3);
map.put("eids",eidlist);
System.out.println(mapper.selectForeach(map));
}
运行结果


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号