关于SpringBoot全解
1、SpringBoot入门程序
所需依赖:
<!-- 父级依赖 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!-- 使用SpringMV和Spring的jar包 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- 使用jdk1.80 --> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
程序代码:
package com.qianfeng.controller; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @EnableAutoConfiguration //开启自动配置 @Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/") @ResponseBody public String first(){ return "hello world!"; } //入口 public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(IndexController.class, args); } }
2.SpringBoot启动自动配置注解:
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启用自动配置,该注解会使用SpringBoot根据项目依赖的jar包自动配置项目的配置项。例如:我们添加了spring-boot-starter-web的依赖,
项目中也就会引入SpringMVC的依赖,SpringBoot就会自动配置Tomcat和SpringMVC。
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={RedisAutoConfiguration.class}):关闭自动配置
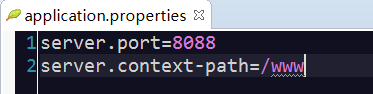
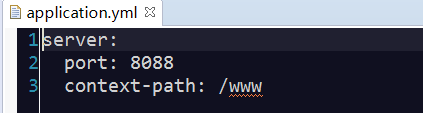
3.SpringBoot全局配置文件:
SpringBoot项目使用一个全局的配置文件application.properties或者是application.yml,在resources目录下或者类路径下的/config下,一般我们放到resources下。
区别:主要是书写格式不同;.yml格式不支持@PropertySource注解导入配置
4.SpringBootstarter pom:
SpringBoot为我们提供了
企业级开发绝大多数场景的starter pom,只要使用了应用场景所需的starter pom,相关技术配置将会相除,就可以得到SpringBoot为我们提供的自动配置的been。
5.SpringBoot获取自定义配置的值:
全局配置:

程序代码:
package com.qianfeng.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @EnableAutoConfiguration @Controller public class BookController { @Value("${book.author}") private String author; @Value("${book.name}") private String name; @RequestMapping("/book") @ResponseBody public String showInfo(){ return author+":"+name; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(BookController.class, args); } }
6.SpringBoot获取自定义配置的值(类型安全的配置):
使用@Value注入每个自定义配置在项目中闲的很麻烦,当自定义属性很多时需要注入很多次
SpringBoot还提供了基于类型安全的配置方式,通过 @ConfigurationProperties 将properties 中的属性和一个Bean的属性关联,从而实现类型安全的配置。
package com.qianfeng.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @EnableAutoConfiguration @Controller @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="book")//取properties文件中book开头的属性值 public class BookController { //@Value("${book.author}") private String author; //@Value("${book.name}") private String name; @RequestMapping("/book") @ResponseBody public String showInfo(){ return author+":"+name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(BookController.class, args); } }
7.SpringBootProfile配置:
Profile 是针对不同的环境对不同的配置提供支持的,全局Profile配置使用application-*.properties(application-prod.properties, application-sit.properties, applicaiton-dev.properties)
通过在appliation.properties 中设置spring.profiles.active=prod 来指定活动的Profile。
spring.profiles.active=dev
8.SpringBoot整合测试:
所需依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
被测试类程序代码:
package com.qianfeng.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SpringController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String yes(){
return "hello";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringController.class, args);
}
}
测试类程序代码:
package com.qianfeng.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration; import com.qianfeng.controller.SpringController; import junit.framework.TestCase; @SpringBootTest(classes=SpringController.class) //测试哪个类 测试谁? @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //实现测试的类 谁来测试? @WebAppConfiguration public class TestSpringController { @Autowired private SpringController springController; @Test public void test1(){ TestCase.assertEquals(this.springController.yes(), "hello"); } }
9.SpringBootApplication 注解 和 RestController注解:
@SpringBootApplication:包含了@ComponentScan @Configuration @EnableAutoConfiguration注解
@ComponentScan:让spring Boot扫描到Configuration类并把它加入到程序上下文。
@Configuration :等同于spring的XML配置文件;使用Java代码可以检查类型安全。
@EnableAutoConfiguration :自动配置。
@ComponentScan :组件扫描,注解在类上,扫描标注了@Controller等注解的类,注册为bean 。@ComponentScan 为 @Configuration注解的类配置组件扫描指令。@ComponentScan 注解会自动扫描指定包下
的全部标有 @Component注解的类,并注册成bean,当然包括 @Component下的子注解@Service、@Repository、@Controller。
@Component可配合CommandLineRunner使用,在程序启动后执行一些基础任务。
@RestController:注解是@Controller和@ResponseBody的合集,表示这是个控制器bean,并且是将函数的返回值直 接填入HTTP响应体中,是REST风格的控制器。
10.SpringBoot 的日志管理:
Spring Boot 支持 Java Util Logging, Log4j2, Lockback 作为日志框架,如果你使用 Starters 启动器,Spring Boot 将使用 Logback 作为默认日志框架,Spring Boot支持Java Util Logging,Log4j2,Lockback作为日志框架,如果你使用starters启动器,Spring Boot将使用Logback作为默认日志框架。无论使用哪种日志框架,Spring Boot都支持配置将日志输出到控制台或者文件中。
spring-boot-starter启动器包含spring-boot-starter-logging启动器并集成了slf4j日志抽象及Logback日志框架。
SpringBoot的日志级别有7个从低到高:
TRACE<DEBUG<INFO<WARN<ERROR<FATAL<OFF
SpringBoot 中默认配置 ERROR、WARN和 INFO级别的日志输出到控制台。
11.配置工程为开发模式:
<!-- 配置工厂为开发模式:加入以下依赖,代码做了修改,不用重新运行 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>springloaded</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
12.SpringBoot的Web开发:
SpringBoot 提供了spring-boot-starter-web 为Web开发予以支持,spring-boot-starter-web提供了嵌入的Tomcat以及SpringMVC的依赖,Web相关的自动配置存储在spring-boot-sutoconfigure.jar的org.srpingframework.boot.autoconfigure.web下。
13.访问静态资源:
在SpringBoot 中加载静态资源和普通的web应用中不太一样。默认情况下,SpringBoot从classPath的 /static,/public 或 /META-INF/resources 文件夹或从ServletContext 跟目录供静态资源。
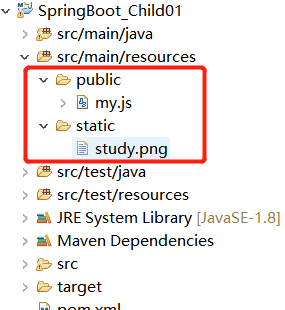
设定静态文件路径,js,css,image等
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/static/
14.自定义消息转换器:
只需要在类中添加消息转换器的@Bean,就会被SpringBoot自动加入到容器中。
//消息转换器 解决乱码问题。 //SpringBoot默认配置了消息转换器 @Bean public StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConvert(){ StringHttpMessageConverter convert=new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); return convert; }
15.使用FastJson解析Json数据:
所需依赖:
<!--FastJson依赖--!>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
第一种方式(启动类继承并重写方法):
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.qianfeng.controller"})//组合注解 public class SpringApplications extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{ @Override public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { //创建FastJson的消息转换器 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter convert=new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); //配置FastJson的配置对象 FastJsonConfig config=new FastJsonConfig(); //对Json数据进行格式化 config.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat); convert.setFastJsonConfig(config); converters.add(convert); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); } }
实体类:
package com.qianfeng.pojo; import java.util.Date; import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField; public class Person { private int id; private String name; @JSONField(format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")//验证使用的是FastJson解析 private Date date;
public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Date getDate() { return date; } public void setDate(Date date) { this.date = date; } }
package com.qianfeng.controller; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import com.qianfeng.pojo.Person; @Controller public class PersonController { @RequestMapping("/person") @ResponseBody public Object show(){ Person ren=new Person(); ren.setId(66); ren.setName("赵四"); ren.setDate(new Date()); return ren; } }
乱码解决:把SpringBoot的response 编码设置为utf-8这个功能开启就好:
spring.http.encoding.force=true
第二种方式:
@Bean public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonMessageConvert(){ //创建FastJson的消息转换器 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter convert=new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); //配置FastJson的配置对象 FastJsonConfig config=new FastJsonConfig(); //对Json数据进行格式化 config.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat); convert.setFastJsonConfig(config); HttpMessageConverter<T> con=(HttpMessageConverter<T>) convert; return new HttpMessageConverters(con); }
16.自定义拦截器:
有些时候我们需要自己配置SpringMVC而不是采用默认,比如说增加一个拦截器,这个时候就得通过继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 然后重写父类中的方法进行扩展。
package com.qianfeng.interceptor; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; /* * 注解在类上,表示这是一个IOC容器,相当于spring的配置文件,java配置的方式。 IOC容器的配置类一般与 @Bean 注解配合使用,用 @Configuration * 注解类等价与 XML 中配置 beans,用@Bean 注解方法等价于 XML 中配置 bean。 */ @Configuration public class MyInterceptor extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {HandlerInterceptor inter=new HandlerInterceptor(){ @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, Exception arg3) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, ModelAndView arg3) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2) throws Exception { System.out.println("自定义拦截器....."); return true; } }; //拦截路径 registry.addInterceptor(inter).addPathPatterns("/**"); } }
17.定义全局异常处理器(AOP思想):
package com.qianfeng.controller; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; //全局异常处理器 @ControllerAdvice public class GlobalExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseBody public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception exception){ Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();//封装异常信息 map.put("errorCode",500); map.put("erroMsg", exception.toString()); return map; } }
18.异步调用:
在项目中,当访问其他接口较慢或者做耗时任务时,不想程序一直卡在耗时任务上,想程序能够并发执行,我们可以使用多线程来并行的处理任务,SpringBoot提供了异步处理方式 @Async
package com.qianfeng.service; import java.util.concurrent.Future; public interface AsyncService { Future<String> doTask1() throws Exception; Future<String> doTask2() throws Exception; Future<String> doTask3() throws Exception; }
package com.qianfeng.service; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService { private static Random random=new Random(); @Async @Override public Future<String> doTask1() throws Exception { System.out.println("任务一开始执行"); long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务一结束:"+(end-start)+"ms"); return new AsyncResult<>("任务一结束"); } @Async @Override public Future<String> doTask2() throws Exception { System.out.println("任务二开始执行"); long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务二结束:"+(end-start)+"ms"); return new AsyncResult<>("任务二结束"); } @Async @Override public Future<String> doTask3() throws Exception { System.out.println("任务三开始执行"); long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000)); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务三结束:"+(end-start)+"ms"); return new AsyncResult<>("任务三结束"); } }
package com.qianfeng.controller; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import com.qianfeng.service.AsyncService; @Controller public class SpringController { @Autowired private AsyncService asyncService; @RequestMapping("/async") @ResponseBody public String asyncTest() throws Exception{ long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); Future<String> task1=asyncService.doTask1(); Future<String> task2=asyncService.doTask2(); Future<String> task3=asyncService.doTask3(); while(true){ if(task1.isDone()&&task2.isDone()&&task3.isDone()){ break; } Thread.sleep(1000); } long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); return "全部执行完成,总耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms"; } }
package com.qianfeng.app; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; //@EnableAutoConfiguration /* * 注解在类上,扫描标注了@Controller等注解的类,注册为bean 。@ComponentScan 为 @Configuration注解的类配置组件 * 扫描指令。@ComponentScan 注解会自动扫描指定包下的全部标有 @Component注解的类,并注册成bean,当然包括 @Component * 下的子注解@Service、@Repository、@Controller。 */ //@ComponentScan("com.qianfeng.controller") @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.qianfeng.controller","com.qianfeng.service"})//默认情况下扫描的是对当前包及其包的子包 @EnableAsync //开启异步调用 public class SpringApplications { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); } }
控制台输出: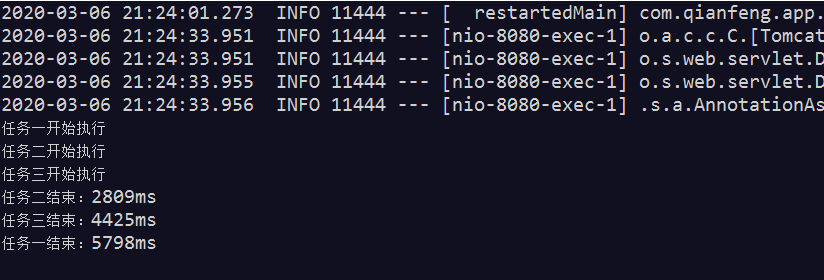
19.SpringBoot整合JSP:
SpringBoot 官方不推荐使用jsp ,因为jsp相对于一些模板引擎,性能都比较低,官方推荐使用 thymeleaf。
所需依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 整合jsp需要的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- maven项目packaging为war类型时,必须要加这个插件 -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
全局配置:
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/jsp/ spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
20.SpringBoot 整合Freemarker
SpringBoot不建议使用JSP,使用模板引擎,比如:themleaf,velocity,freemarker。
所需依赖:
<!-- 整合freemarker需要的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
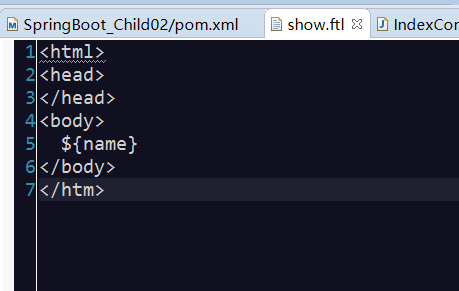
21.SpringBoot 整合Thymeleaf:
所需依赖:
<!-- 整合Thymeleaf -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId>
<artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId>
<version>1.9.22</version>
</dependency>
全局配置:
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
22.SpringBoot 整合QuartZ:
package com.qianfeng.job; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyJob { /* * 用来开启定时任务 :每隔1秒输出 */ @Scheduled(fixedRate=1000) public void run(){ System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").format(new Date())); } }
package com.qianfeng.app; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.qianfeng.service","com.qianfeng.controller","com.qianfeng.dao","com.qianfeng.email"}) @EnableScheduling //任务调度 public class SpringApp { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringApp.class, args); } }
23.SpringBoot 整合jdbcTemplate:
所需依赖:
<!-- 整合jdbcTemplate依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 对mysql依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
全局配置:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo
程序代码:
package com.qianfeng.dao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.qianfeng.pojo.Users; @Repository public class UserDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void addUser(Users user){ jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user(uid,uname,usex) values(?,?,?)", new Object[]{user.getUid(),user.getUname(),user.getUsex()}); } }
24.SpringBoot整合Mybatis(xml方式):
所需依赖:
<!-- 对mysql依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springBoot 整合mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- alibaba的druid数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.11</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 分页插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
25.SpringBoot区分多数据源分析:
在项目中我们通常会进行数据库拆分或是引入其他数据库,从而我们需要配置多个数据源:
如何区分多个数据源:
1.通过包来区分;
2.使用注解来区分;
26.区分多数据源实现:
27.SpringBoot的事务管理:
在SpringBoot中推荐使用@Transactional 注解来声明事务
当我们使用 spring-boot-starter-jdbc 或 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa依赖的时候,SpringBoot 会自动默认分别注入 DataSourceTransactionManager或 JpaTransactionManager。
package com.qianfeng.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.qianfeng.dao.UserDao; import com.qianfeng.pojo.Users; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Transactional public void saveUser(Users user){ userDao.addUser(user); int i=6/0; } }
28.打包发布到独立的tomcat:
1:需要打包成war包
2.所需依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
3.启动类继承SpringBootServletInitializer,重写configure方法
package com.qianfeng.app; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.qianfeng.service","com.qianfeng.controller","com.qianfeng.dao","com.qianfeng.email"}) //@EnableScheduling //任务调度 public class SpringApp extends SpringBootServletInitializer{ @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return builder.sources(SpringApp.class); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringApp.class, args); } }
29.MongoDB:
MongoDB 是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库。旨在为WEB应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。MongoDB是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品。是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。它支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似json的bson格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。Mongo最大的特点是它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,而且支持对数据建立索引。
所需依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId> </dependency>
配置.yml:
spring:
data:
mongodb:
host:
port:27017
databases:mydb
30.SpringBoot整合 ActiveMQ:
所需依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemg</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置:
spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://192.168.25.129:61616 spring.activemq.in-memory=true spring.activemq.user=admin spring.activemq.password=admin #如果此处设置为true,需要加如下面的依赖包,否则会自动配置失败,JmsMessagingTemplate spring.activemq.pool.enabled=false




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号