Spring:(二)DI依赖注入方式
DI 依赖注入
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入,说简单一点就将类里面的属性在创建类的过程中给属性赋值,即将对象依赖属性(简单值,集合,对象)通过配置设值给该对象。
属性注入的方式
- 构造方法的方式
- set方法的方式
- 工厂方法注入
主要学习前两种方式
构造方法的方式
当是构造方法时注入Bean的属性值(简单值,集合,对象)
利用<constructor-arg>标签进行属性的注入
name:被设置属性的名
value:被设置属性的值
编写用构造方法的pojo
1 package spring_test1.pojo; 2 3 public class UserConstructor { 4 private String name; 5 private int id; 6 7 public UserConstructor(String name, int id) { 8 super(); 9 this.name = name; 10 this.id = id; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public String toString() { 15 return "User_constructor [name=" + name + ", id=" + id + "]"; 16 } 17 }
XML配置编写
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- Spring构造方法注入 --> <bean name="user_cons" class="spring_test1.pojo.UserConstructor"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="Roy"/> <constructor-arg name="id" value="1001"/> </bean> </beans>
编写测试类
1 package spring_test1.test; 2 3 import static org.junit.Assert.*; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 7 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 8 9 import spring_test1.pojo.UserConstructor; 10 11 public class UserConstructorTest { 12 13 @Test 14 public void test() { 15 //创建Spring的工厂 16 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 17 //得到User对象 18 UserConstructor userConstructor = (UserConstructor) applicationContext.getBean("user_cons"); 19 System.out.println(userConstructor); 20 } 21 }
运行结果

set方法的方式
我在Spring:(一)那一篇中的第一个Spring程序便是set方法时的属性注入方式
利用<property>标签
name:被设置属性的名
value:被设置属性的值
标准XML格式
编写pojo
1 package spring_test1.pojo; 2 3 /** 4 * @author jyroy 5 * 6 */ 7 public class User { 8 private String name; 9 private int id; 10 11 public String getName() { 12 return name; 13 } 14 public void setName(String name) { 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 public int getId() { 18 return id; 19 } 20 public void setId(int id) { 21 this.id = id; 22 } 23 @Override 24 public String toString() { 25 return "User [name=" + name + ", id=" + id + "]"; 26 } 27 }
编写XML配置文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xsi:schemaLocation=" 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 8 9 <!--Spring的set方法的属性注入--> 10 <bean name="user" class="spring_test1.pojo.User"> 11 <property name="name" value="李东"/> 12 <property name="id" value="1007" /> 13 </bean> 14 15 16 </beans>
编写测试类
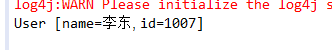
1 package spring_test1.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 import spring_test1.pojo.User; 8 9 public class UserTest { 10 11 @Test 12 public void demo1() { 13 //创建Spring的工厂 14 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 15 //得到User对象 16 User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user"); 17 System.out.println(user); 18 } 19 }
运行结果
p命名空间的方式
看上面的XML配置,似乎用<property/>标签还是比较臃肿。
于是从2.0开始,Spring支持使用名称空间的可扩展配置格式。这些名称空间都是基于一种XML Schema定义。p命名空间就可以用bean 元素的属性代替<property/>元素。
还需要在使用p命名空间时先声明使用对应的命名空间,即在bean元素上添加 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
1 <!-- p命名空间的方式 --> 2 <bean id="user" class="spring_test1.pojo.User" p:name="Roy" p:id="1004"></bean>
c命名空间的方式
C命名空间与p命名空间类似,但是使用c命名空间可以用内联的构造参数代替嵌套的constructor-arg元素
同样先声明使用对应的命名空间,即在bean元素上添加 xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 标准XML格式 --> <bean id="foo" class="x.y.Foo"> <constructor-arg name="bar" ref="bar"/> <constructor-arg name="baz" ref="baz"/> <constructor-arg name="email" value="foo@bar.com"/> </bean> <!-- c命名空间格式 --> <bean id="foo" class="x.y.Foo" c:bar-ref="bar" c:baz-ref="baz" c:email="foo@bar.com"/> <!-- 还可以使用c命名空间的参数索引格式 --> <bean id="foo" class="x.y.Foo" c:_0-ref="bar" c:_1-ref="baz" c:_2="foo@bar.com"/> </beans>
SpEL表达式方式
Spring 表达式语言 (Spring Expression Language),打算整理完整的一篇
集合类型属性注入
1 <bean id="collectionBean" class="com.roy.spring.demo5.CollectionBean"> 2 <!-- 数组类型 --> 3 <property name="arrs"> 4 <list> 5 <value>数组一</value> 6 <value>数组二</value> 7 </list> 8 </property> 9 <!-- 注入list集合类型 --> 10 <property name="list"> 11 <list> 12 <value>list一</value> 13 <value>list二</value> 14 </list> 15 </property> 16 17 <!-- 注入set集合类型--> 18 <property name="set"> 19 <set> 20 <value>set一</value> 21 <value>set二</value> 22 </set> 23 </property> 24 25 <!-- 注入Map集合 --> 26 <property name="map"> 27 <map> 28 <entry key="aaa" value="111"></entry> 29 <entry key="bbb" value="222"></entry> 30 <entry key="ccc" value="333"></entry> 31 </map> 32 </property> 33 34 <!-- 注入property集合 --> 35 <property name="properties"> 36 <props> 37 <prop key="key1">value1</prop> 38 <prop key="key2">value2</prop> 39 <prop key="key3">value3</prop> 40 </props> 41 </property> 42 </bean>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号