前言
- 可以说,这一阶段才是真正进入了面向对象程序设计的代码设计与编写,在此之前的几次题目集只能算是让我们熟悉从c语言语法到java语法使用的转变,这体现在之前并未要求对类的使用。而这三次题目集,要求使用类并对其内部属性进行封装,
- 第一次题目集的难度较为简单,题目量共5道,那个时候我以为"答题判题程序"只是简单的作为一个题目集的最后一题,编写需要提高难度,完全没注意它其实是"答题判题程序-1"!!!,因为是第一次出现,这题的要求较未简单,所以我也是简单地使用了正则表达式以及类数组。
- 第二次题目集的配置是3道简单题+更为困难的答题判题程序,最后一题在第一次题目集的基础上增加了要求,并且各种信息也是乱序输入的,虽然我因为本次第一题要求使用链表,学习了链表的简单使用方法,但最后一题考虑到稳中求胜,还是使用了自己熟悉的类数组与正则表达式用法,并且在类数组里套数组【苦笑】。
- 第三次题目集2道简单题+答题判题程序,最后一题我愿称之为这三次题目集的KING,这次我使用的是HashMap,这是我之前未使用过的方法,在这次程序编写过程中也是学到了HashMap的get方法、put方法等。这次最后一题难度可以说是直线上升,难度除了有28个测试点之外,还有多种判题信息的输出。有几个测试点不明确错误点,一直不知道怎么修改好。
设计与分析
- 第一次题目集
1. 以下是我此次程序的UML图

2. 以下是我对此次程序设计的类图

3.main函数
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int n = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
test[] t = new test[100];
String[] q = new String[100];
String[] a = new String[100];
String line;
String message = "";
String regex3 = "(?<=#A:).*";
String end = "end";
for(j = 0;j<n;j++)
{
line = in.nextLine();
Pattern pat = Pattern.compile("#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s+#Q:\\s*(.*?)\\s+#A:\\s*(.*)");
Matcher mat = pat.matcher(line);
if(mat.find())
{
i = Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1));
q[i] = new String(mat.group(2));
a[i] = new String(mat.group(3));
}
}
line = in.next();
for(i = 1;i<=n&&!(line.equals(end));i++)
{
Pattern pat3 = Pattern.compile(regex3);
Matcher mat3 = pat3.matcher(line);
if(mat3.find())
{
message = new String(mat3.group());
}
t[i] = new test(q[i],a[i],message);
line = in.next();
}
for(i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
System.out.println(t[i].getQuestion()+"~"+t[i].getMessage());
}
for(i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i == 1)
System.out.printf("%s",t[i].compare());
else
System.out.printf(" %s",t[i].compare());
}
}
}
4. test类设计
class test
{
private String answer;
private String question;
private String message;
public test(){
}
public test(String question,String anwser,String message)
{
this.question = question;
this.answer = anwser;
this.message = message;
}
public String getQuestion()
{
return question;
}
public String getAnswer()
{
return answer;
}
public String getMessage()
{
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message)
{
this.message = message;
}
public boolean compare()
{
boolean ret = (answer.equals(message));
return ret;
}
}
第一次题目集最后一题写得十分简洁,其一是因为题目较为简单(至少不是第三次的难度),其二是因为初步着手写面向对象程序语言,对此类程序的编写规则并不明晰,例如不知道使用类的必要、单一职责原则等。但能够对类内数据进行封装操作。
- 第二次题目集
1. 以下是我此次程序的UML图
2. 以下是我对此次程序设计的类图
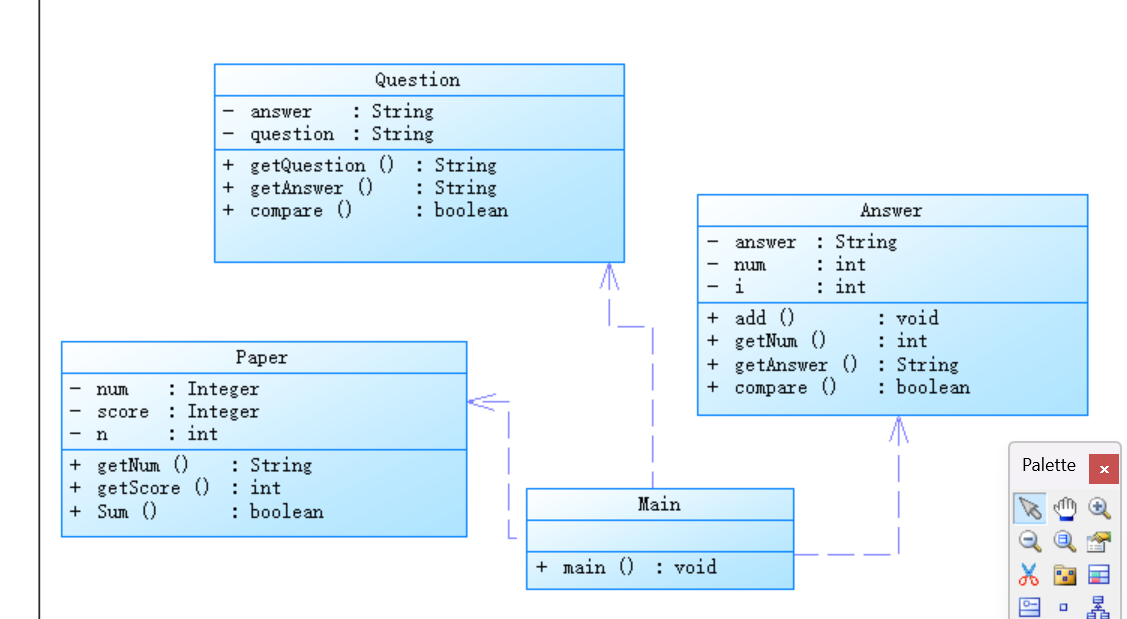
3. 源代码
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;//试卷的编号
int k = 0;//答卷对应的试卷编号
int n = 0;//试卷内题目数量
int m = 0;//答卷的数组编号
int o = 0;
int num = 0;
Question[] q = new Question[1000];
Paper[] p = new Paper[1000];
Answer[] a = new Answer[1000];
String line;
String question;
String answer;
String end = "end";
Pattern pat = Pattern.compile("#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s+#Q:\\s*(.*?)\\s+#A:\\s*(.*)");
Pattern pat1 = Pattern.compile("#T:(\\d+)");
Pattern pat2 = Pattern.compile("#S:(\\d+)");
Pattern pat3 = Pattern.compile("(\\d+)-(\\d+)");
Pattern pat4 = Pattern.compile("#A:(\\S+)");
line = in.nextLine();
while(!line.equals(end))
{
Matcher mat = pat.matcher(line);
Matcher mat1 = pat1.matcher(line);
Matcher mat2 = pat2.matcher(line);
Matcher mat3 = pat3.matcher(line);
Matcher mat4 = pat4.matcher(line);
if(mat.find())
{
i = Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1));
question = new String(mat.group(2));
answer = new String(mat.group(3));
q[i] = new Question(question,answer);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#T:"))
{
if(mat1.find())
j = Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1));
p[j] = new Paper();
// 匹配题目编号和分值
while (mat3.find()) {
p[j].add(mat3.group(1),mat3.group(2),n);
n++;
}
if(p[j].Sum(n))
{
System.out.println("alert: full score of test paper"+j+" is not 100 points");
}
}
else if(line.startsWith("#S:"))
{
if(mat2.find())
k = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(1));
a[m] = new Answer(k);
while (mat4.find()) {
a[m].add(mat4.group(1),o);
o++;
}
m++;
}
line = in.nextLine();
}
for(i = 0;i<m;i++)
{
int[] sum = new int[100];
num = a[i].getNum();//编号
if(p[num]!=null)
{
for(j = 0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i].getAnswer(j)!=null)
{
int r = Integer.parseInt(p[num].getNum(j));
System.out.println(q[r].getQuestion()+"~"+a[i].getAnswer(j)+"~"+a[i].compare(q[r].getAnswer(), j));
if(a[i].compare(q[r].getAnswer(), j))
{
sum[j] = p[num].getScore(j);
}
}
else
{
sum[j] = 0;
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
}
for(k = 0;k<=j;k++)
{
if(k == 0)
{
sum[j] += sum[k];
System.out.printf("%d", sum[k]);
}
else if(k == j)
System.out.printf("~%d\n", sum[k]);
else
{
sum[j] += sum[k];
System.out.printf(" %d", sum[k]);
}
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
}
}
}
}
class Question
{
private String answer;
private String question;
public Question(){
}
public Question(String question,String anwser)
{
this.question = question;
this.answer = anwser;
}
public String getQuestion()
{
return question;
}
public String getAnswer()
{
return answer;
}
public boolean compare(String message)
{
boolean ret = (answer.equals(message));
return ret;
}
}
class Paper
{
private String[] num = new String[1000];//题号
private int[] score = new int[1000];//分值
private int n;
public Paper() {
}
public void add(String num,String score,int i)
{
this.num[i] = num;
int s = Integer.parseInt(score);
this.score[i] = s;
}
public boolean Sum(int n)
{
this.n = n;
int sum = 0;
int j;
boolean ret = true;
for(j = 0;j<n;j++)
{
sum+=score[j];
}
if(sum == 100)
ret = false;
return ret;
}
public String getNum(int j)
{
return num[j];
}
public int getScore(int j)
{
return score[j];
}
}
class Answer
{
private String[] answer = new String[1000];
private int num = 0;
private int i = 0;
public Answer() {
}
public Answer(int num)
{
this.num = num;
}
public void add(String answer,int i)
{
this.answer[i] = answer;
}
public int getNum()
{
return num;
}
public String getAnswer(int i)
{
return answer[i];
}
public boolean compare(String a,int n)
{
return a.equals(answer[n]);
}
}
相比于第一次题目集,我在第二次题目集拆分了多个类,其难点在于乱序输入以及不定数量的字符串;
- 第三次题目集
1. 以下是我此次程序的UML图

2. 以下是我对此次程序设计的类图

3. 以下是我的main函数,可以看出,我对main函数的编写过于冗长,在这一点上没有很好地遵循单一职责原则,我认为这一部分的改进体现在类中方法的增多以及类的增多。例如增加正则表达式类、类中匹配方法等等。
点击查看代码
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean Qisexit,Sisexit,Pisexit;
int Qcount = 0;//题目数量
int Pcount = 0;//试卷数量
int Pnum = 0;//试卷号
int Tcount = 0;//单张试卷中题目数量
int Acount = 0;//答卷数量
int Anum = 0;//答卷号
int Dcount = 0;//单张答卷中答案数量
int Qnum = 0,Snum = 0,Tnum = 0;
int[] score = new int[1000];
int i = 0,j = 0,k = 0,n = 0,num = 0,sum = 0,sid = 0;
HashMap<Integer,Question> q = new HashMap<Integer,Question>();
HashMap<Integer,Answer> a = new HashMap<Integer,Answer>();
HashMap<Integer,Paper> p = new HashMap<Integer,Paper>();
HashMap<Integer,Student> s = new HashMap<Integer,Student>();
String line;
String end = "end";
Pattern pat = Pattern.compile("#N:\\s*(\\d+) +#Q:\\s*(.*?) +#A:\\s*(.*)");
Pattern pat1 = Pattern.compile("#T:(\\d+)");
Pattern pat2 = Pattern.compile("#S:(\\d+) (\\d+)");
Pattern pat3 = Pattern.compile("(\\d+)-(\\d+)");
Pattern pat4 = Pattern.compile("(\\d+) (\\S[A-Za-z]+)");
Pattern pat5 = Pattern.compile("#D:N-(\\d+)");
Pattern pat6 = Pattern.compile("#A:(\\d+)-");
line = in.nextLine();
while(!line.equals(end))
{
Matcher mat = pat.matcher(line);
Matcher mat1 = pat1.matcher(line);
Matcher mat2 = pat2.matcher(line);
Matcher mat3 = pat3.matcher(line);
Matcher mat4 = pat4.matcher(line);
Matcher mat5 = pat5.matcher(line);
Matcher mat6 = pat6.matcher(line);
if(mat.find())//题目信息
{
Qcount = Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1));
Question Qclass = new Question(mat.group(2),mat.group(3));
q.put(Qcount, Qclass);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#T:"))//试卷信息
{
Pcount++;
if(mat1.find())
Pnum = Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1));
Paper Pclass = new Paper(Pnum);
// 匹配题目编号和分值
while (mat3.find()) {
Qisexit = true;
Tcount++;
Tnum = Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(1));
if(q.get(Tnum)==null)
Qisexit = false;
Pclass.add(Tnum,Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(2)),Qisexit,Tcount);
}
p.put(Pcount, Pclass);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#S:"))//答卷信息
{
Sisexit = true;
Pisexit = true;
Acount++;
if(mat2.find())
{
Anum = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(1));
sid = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(2));
}
if(p.get(Anum)==null)
Pisexit = false;
if(s.get(sid)==null)
{
Sisexit = false;
}
Answer Aclass = new Answer(Anum,mat2.group(2),Pisexit,Sisexit);
while(mat6.find())
{
Dcount++;
Aclass.add(Integer.parseInt(mat6.group(1)),"");
}
while (mat3.find())
{
Dcount++;
Aclass.add(Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(1)),mat3.group(2));
}
a.put(Acount, Aclass);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#X:"))//学生信息
{
while(mat4.find())
{
Snum = Integer.parseInt(mat4.group(1));
Student Sclass = new Student(mat4.group(2));
s.put(Snum, Sclass);
}
}
else if(mat5.find())
{
q.get(2).Delete();
}
else
System.out.println("wrong format:"+line);
line = in.nextLine();
}
for(i = 1;i<=Pcount;i++)//试卷满分相关信息的输出
{
if(p.get(i).Sum())
System.out.println("alert: full score of test paper"+i+" is not 100 points");
}
for(i = 1;i<=Acount;i++)//答题信息输出
{
Answer an = a.get(i);
num = an.getAnum();
if(!an.getPisexit())
System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
else
{
Paper pa = p.get(num);
for(j = 1,n = -1;j<=pa.getTcount();j++)
{
n++;
if(!an.getScanf(j))
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
else
{
Qnum = pa.getNum(j);
if(!pa.getExit(j))
{
System.out.println("non-existent question~0");
}
else
{
if(q.get(Qnum).getIsdelete())
{
System.out.println("the question "+Qnum+" invalid~0");
}
else
{
System.out.println(q.get(Qnum).getQuestion()+"~"+an.getAnswer(j)+"~"+an.compare(q.get(Qnum).getAnswer(), j));
if(an.compare(q.get(Qnum).getAnswer(), j))
{
score[n] = pa.getScore(Qnum);
sum += score[n];
}
}
}
}
}
sid = Integer.parseInt(an.getSid());
if(!an.getSisexit())
System.out.println(sid+" not found");
else
{
System.out.printf(sid+" "+s.get(sid).getName()+":");
for(k = 0;k<=n;k++)
{
System.out.printf(" %d",score[k]);
}
System.out.println("~"+sum);
}
}
}
}
}
4. 以下是我四个类的编写
各种类内的编写,方法各职责单一
题目类
class Question//题目信息类
{
private String answer;
private String question;
private boolean isdelete;
public Question(){
}
public Question(String question,String anwser)
{
this.question = question;
this.answer = anwser;
isdelete = false;
}
public String getQuestion()
{
return question;
}
public String getAnswer()
{
return answer;
}
public boolean getIsdelete()
{
return isdelete;
}
public boolean compare(String message)
{
boolean ret = (answer.equals(message));
return ret;
}
public void Delete()
{
isdelete = true;
}
}
试卷类
class Paper//试卷信息类
{
private HashMap<Integer,Integer> num = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();//题号
private HashMap<Integer,Integer> score = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();//分值
private HashMap<Integer,Boolean> exit = new HashMap<Integer,Boolean>();//题号存在
private int Pnum;
private int Tcount = 0;
public Paper(int Pnum) {
this.Pnum = Pnum;
}
public void add(int num,int score,Boolean isexit,int i)
{
this.num.put(i, num);
this.score.put(i, score);
this.exit.put(i, isexit);
Tcount ++;
}
public boolean Sum()
{
int sum = 0;
int j;
boolean ret = true;
for(j = 1;j<=Tcount;j++)
{
sum+=score.get(j);
}
if(sum == 100)
ret = false;
return ret;
}
public int getPnum() {
return Pnum;
}
public int getTcount() {
return Tcount;
}
public int getNum(int j)
{
return num.get(j);
}
public int getScore(int j){
return score.get(j);
}
public boolean getExit(int j) {
return exit.get(j);
}
}
答卷类
class Answer//答卷信息类
{
private HashMap<Integer,Boolean> scanf = new HashMap<Integer,Boolean>();//题号顺序
private HashMap<Integer,String> answer = new HashMap<Integer,String>();//答案
private boolean Pisexit;
private boolean Sisexit;
private String sid;
private int Anum;
private int Dcount = 0;
public Answer(int Asum,String sid,boolean Pisexit,boolean Sisexit)
{
this.Anum = Asum;
this.sid = sid;
this.Pisexit = Pisexit;
this.Sisexit = Sisexit;
}
public void add(int num,String answer)
{
this.scanf.put(num, true);
this.answer.put(num, answer);
Dcount++;
}
public int getDcount() {
return Dcount;
}
public int getAnum() {
return Anum;
}
public boolean getPisexit() {
return Pisexit;
}
public boolean getSisexit() {
return Sisexit;
}
public boolean getScanf(int i)
{
boolean ret = true;
if(scanf.get(i)==null)
ret = false;
return ret;
}
public String getAnswer(int i)
{
return answer.get(i);
}
public String getSid()
{
return sid;
}
public boolean compare(String a,int n)
{
return a.equals(answer.get(n));
}
}
学生类
class Student
{
private String name;
public Student(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
踩坑心得
- 第三次题目集
1. 在增加下图第十个测试样例后,我也相应改进了我的代码。
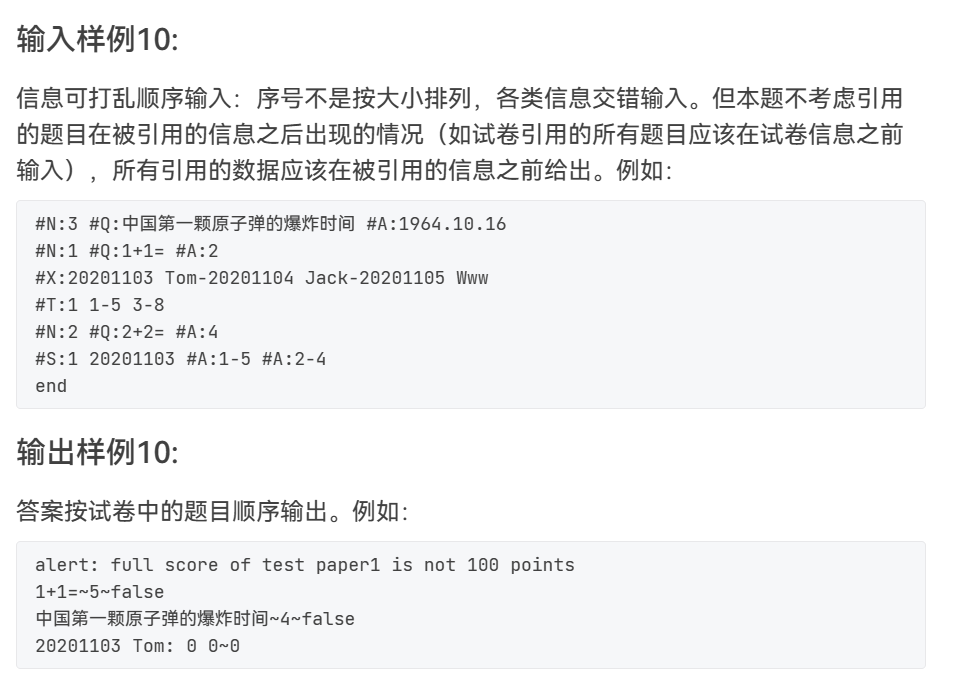
在此之前
我的存储代码是这样的
else if(line.startsWith("#T:"))//试卷信息{
Pcount++;
if(mat1.find())
Pnum = Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1));
Paper Pclass = new Paper(Pnum);
// 匹配题目编号和分值
while (mat3.find()) {
Tcount++;
Pclass.add(Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(1)),Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(2)),Tcount);
}
p.put(Pcount, Pclass);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#S:"))//答卷信息
{
Acount++;
if(mat2.find())
Asum = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(1));
Answer Aclass = new Answer(Asum,mat2.group(2));
while (mat3.find())
{
Dcount++;
Aclass.add(mat3.group(1),mat3.group(2),Dcount);
}
a.put(Acount, Aclass);
}
根据其中的
但本题不考虑引用的题目在被引用的信息之后出现的情况
这句话
我增加了输入答卷信息是题目是否存在的判断以及答卷输入时学生是否已存在
else if(line.startsWith("#T:"))//属于试卷信息{
Pcount++;
if(mat1.find())
Pnum = Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1));
Paper Pclass = new Paper(Pnum);
// 匹配题目编号和分值
while (mat3.find()) {
Qisexit = true;
Tcount++;
Tnum = Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(1));
if(q.get(Tnum)==null)//查找题目是否在此条信息输入时存在
Qisexit = false;
Pclass.add(Tnum,Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(2)),Qisexit,Tcount);
}
p.put(Pcount, Pclass);
}
else if(line.startsWith("#S:"))//答卷信息{
Sisexit = true;
Pisexit = true;
Acount++;
if(mat2.find()){
Anum = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(1));
sid = Integer.parseInt(mat2.group(2));
}
if(p.get(Anum)==null)//查找题目是否在此条信息输入时存在
Pisexit = false;
if(s.get(sid)==null)//查找学生是否在此条信息输入时存在
Sisexit = false;
Answer Aclass = new Answer(Anum,mat2.group(2),Pisexit,Sisexit);
while(mat6.find()){
Dcount++;
Aclass.add(Integer.parseInt(mat6.group(1)),"");
}
while (mat3.find()){
Dcount++;
Aclass.add(Integer.parseInt(mat3.group(1)),mat3.group(2));
}
a.put(Acount, Aclass);
}
改进建议
测试点的说明可以尽量详细些,有个别测试点不明白为什么错,所以修改时卡了很久。
总结
1. 收获
在编写这几次代码的过程中,我有以下收获
- 链表的简单使用
- HashMap的使用
- HashMap的内部存储空间表示
- 正则表达式的写法。
- 类的封装
- 类与类间的使用
2. 发现
java作为面向对象程序,需要考虑到类的分工使用,以及单一职责原则,因此代码量也大大提升,但代码具有了良好的低耦合度,在修改时也非常便利。
3. 改进
我的main函数总是过于冗长,这是下次题目集需要改进的一点,将部分可以增加进类的方法不在main函数内实现,实现低耦合度这一特点,否则,太多操作堆积在main函数内,不仅使代码的可阅读性降低,还会导致后期修改时十分繁琐。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号