day:31 pymysql(1)
一、pymysql下载
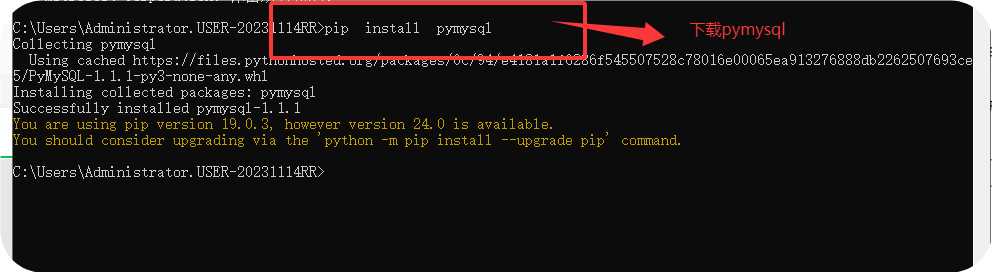
1、dos下安装:
pip3 install pymysql 或pip install pymysql
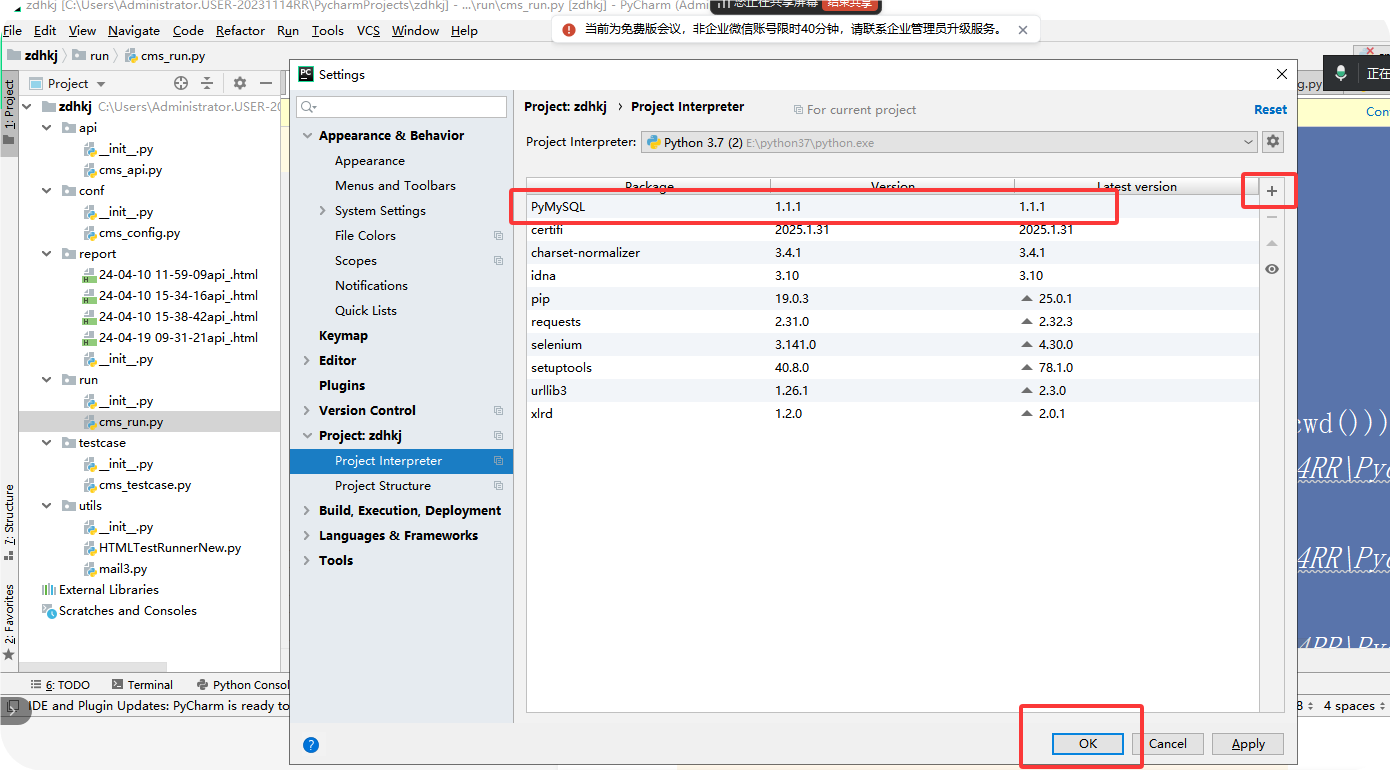
2、在pycharm中下载
二、pymysql连接
(1)数据安装好,能连接

(2)连接数据库
1、连接方式:pymysql.Connection 或者pymysql.connect
2、包含内容
a.host 主机:填写IP地址
b.user 数据库用户名
c.password 或passwd 密码:
d.databases 或db 库名
e.port 端口 :默认3306
f.charset ='utf8' 编码格式
案例:
import pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.19.137",user="root",passwd="123456",
port=3306,database="hh",charset="utf8")
(2)将连接内容设置成一个变量,然后创建一个游标对象
yb=lj.cursor
(3)使用游标对象去执行sql语句
(4)在根据需要显示内容使用 fetchone,fetchall,fetchmany
代码:
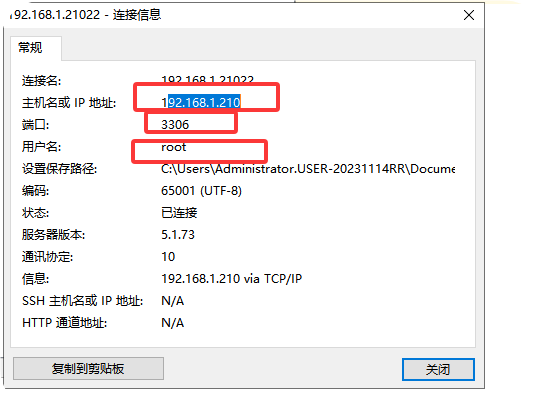
import pymysql #导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect( host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8"
) #pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor() #创建游标对象
sql="select * from student" #sql语句
yb.execute(sql) #执行sql语句
one=yb.fetchone() #查看执行一行数据
print(one)
many=yb.fetchmany(size=3)
print(many)
all=yb.fetchall()
print(all)
三、pymysql操作数据库的增删改查
1.删除数据
代码:
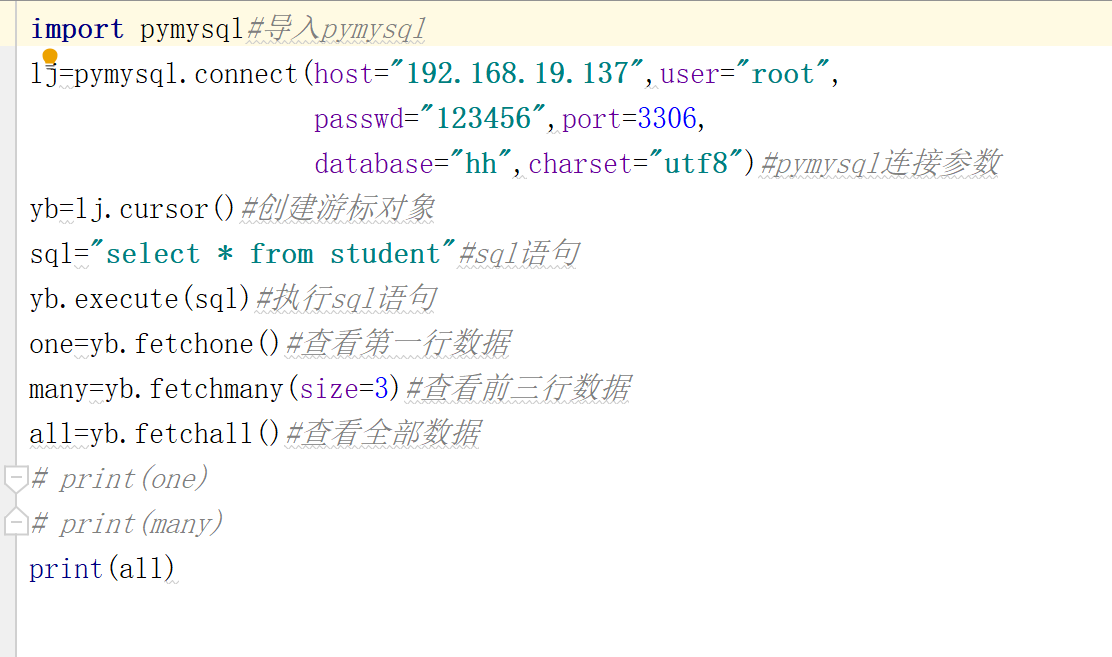
sql="delete from student where id=1"
yb.execute(sql)#执行sql语句
案例:
import pymysql #导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(
host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8"
) #pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor() #创建游标对象
sql="delete from student where id=1 "
yb.execute(sql)
2.插入数据
代码:
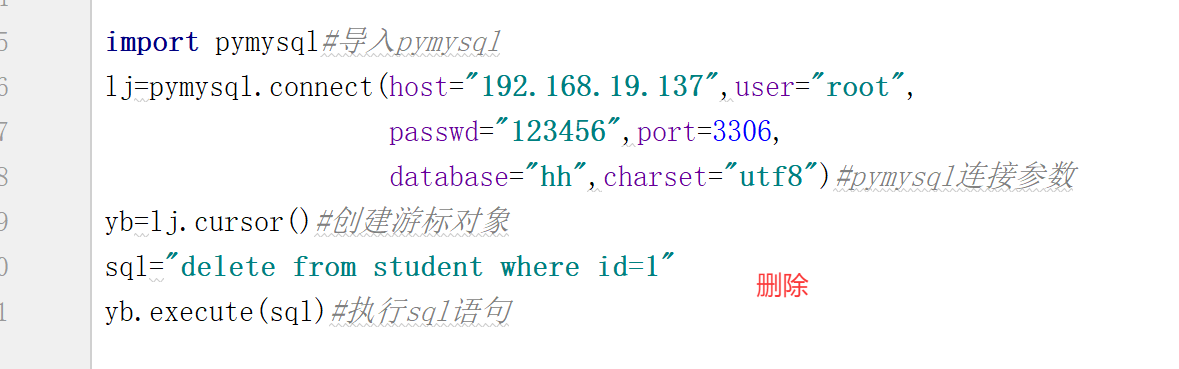
sql="insert into student(id) values(1)"#增加数据
yb.execute(sql)#执行sql语句
案例:
import pymysql #导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(
host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8"
) #pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor() #创建游标对象
插入数据:
sql="INSERT into student(id) VALUES (1)"
yb.execute(sql)
3.修改数据
代码:
sql="UPDATE student set id=30 where id=1;"#更改数据
yb.execute(sql)#运行sql语句
案例1:
import pymysql #导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(
host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8"
) #pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor() #创建游标对象
插入数据:
sql="UPDATE student set id=30 where id=20;"
yb.execute(sql)

案例2:
import pymysql #导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(
host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8"
) #pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor() #创建游标对象
插入数据:
sql="UPDATE student set id=40 where id=30;"
yb.execute(sql)
sql2="select * from student"
yb.execute(sql2)
print(yb.fetchall())

4.查看数据
代码:
one=yb.fetchone()#查看第一行数据
many=yb.fetchmany(size=3)#查看前三行数据
all=yb.fetchall()#查看全部数据
案例:
import pymysql#导入pymysql
lj=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.19.137",user="root",
passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh",charset="utf8")#pymysql连接参数
yb=lj.cursor()#创建游标对象
sql="select * from student"#sql语句
yb.execute(sql)#执行sql语句
one=yb.fetchone()#查看第一行数据
many=yb.fetchmany(size=3)#查看前三行数据
all=yb.fetchall()#查看全部数据
print(one)
print(many)
print(all)

四、数据库封装
import pymysql
class Sjk(object):
def init(self,host,user,passwd,port,database):
self.host=host
self.user=user
self.passwd=passwd
self.port=port
self.database=database
def lj(self):
ljsql= pymysql.connect(
host=self.host,user=self.user,port=self.port,passwd=self.passwd,
database=self.database,charset="utf8"
)
return ljsql
def one(self,sql1):
s=self.lj()
yb=s.cursor()
yb.execute(sql1)
print(yb.fetchone())
def many(self, sql2,x):
s = self.lj()
yb = s.cursor()
yb.execute(sql2)
print(yb.fetchmany(size=x))
def all(self, sql3):
s = self.lj()
yb = s.cursor()
yb.execute(sql3)
# print(yb.fetchall())
sy=yb.fetchall()
for i in sy:
print (i)
if name == 'main':
dx=Sjk(host="192.168.1.210",user="root",passwd="123456",port=3306,
database="hh")
# dx.one("select * from student")
# dx.many("select * from student",3)
dx.all("select * from student")
封装的作用
在测试,你可以通过数据库造数据,删除数据,修改数据,
断言
1.查询后台数据
2.造数据
3.删除数据,让数据不冗余

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号