Linux 多线程编程
@
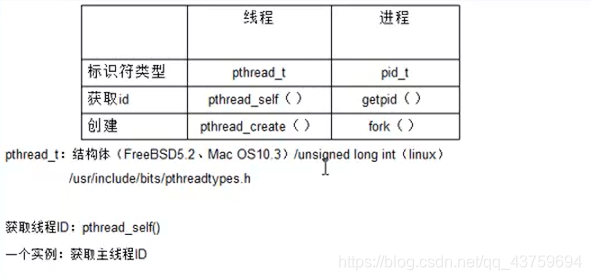
线程ID
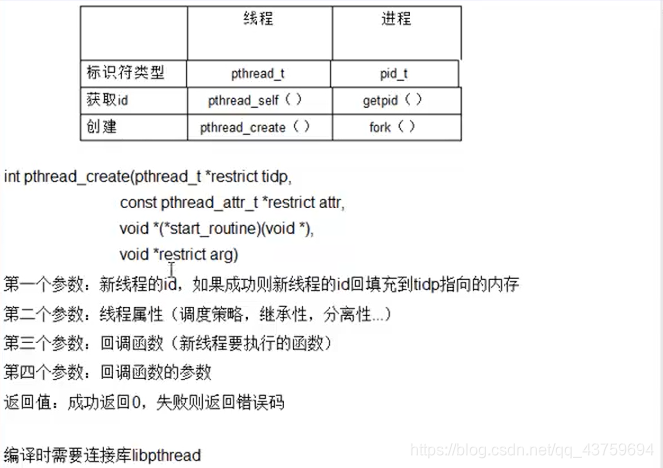
创建一个新的线程:
创建新线程:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
struct message{
int i;
char j[20];
};
void *thread_func(void *s){
printf("i = %d h = %s \n",((struct message *)s)->i,((struct message *)s)->j);
return(void *)0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
pthread_t newtid;
int err;
struct message msg;
msg.i=10;
memcpy(msg.j,"aaaa",20);
err = pthread_create(&newtid,NULL,thread_func,(void *)(&msg));
if(err!=0){
printf("创建新线程失败 \n");
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<argc;i++ ){
printf("main thread agrs is %s \n",argv[i]);
}
sleep(2);
return 0;
}
}
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
void print_id(char *s){
pid_t pid;
pthread_t tid;
pid = getpid();
tid = pthread_self();
printf("%s pid is %u, tid is 0x%x",s,pid,tid);
}
void *thread_fun(void *arg){
print_id(arg);
return(void *)0;
}
int main(){
pthread_t newtid;
int err;
err = pthread_create(&newtid,NULL,thread_fun,"new thread")
if(err!=0){
printf("创建新线程失败");
return 0;
}
print_id("main thread:");
sleep(2);
return 0;
}
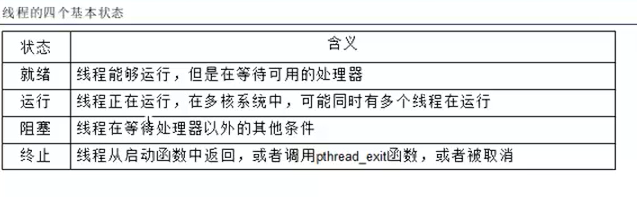
线程的四个状态
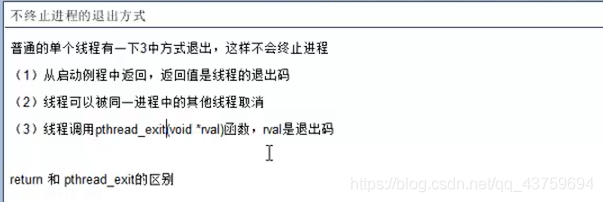
线程的退出
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
//////////三种退出方式
void *thread_fun(void *arg){
if(strcmp("1",(char*)arg)==0){
printf("new thread trurn !\n");
return (void *)1; //不会退出进程
}
if(strcmp("2",(char*)arg)==0){
printf("new thread prhread_exit !\n"); //不会退出进程
pthread_exit((void*)2);
}
if(strcmp("3",(char*)arg)==0){ //会导致进程推出,主线程关闭
printf("new thread exit !\n");
exit(3);
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int err;
pthread_t tid;
err = pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_fun,(void *)argv[1]);
if (err!=0){
printf("create failed \n");
return 0;
}
sleep(1);
printf("main thread exit \n");
return 0;
}
连接线程
函数pthread_join用来等待一个线程的结束,线程间同步的操作。
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **value_ptr);
thread:等待退出线程的线程号。
value_ptr:退出线程的返回值。

#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
void *thread_fun1(void *arg){
printf("I am the first thread \n");
return(void *)1;
}
void *thread_fun2(void *arg){
printf("I am the first thread \n");
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); //分离
pthread_exit((void *)2); /////已经分离无法连接
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int err1;
int err2;
pthread_t tid1;
pthread_t tid2;
void *rval1, *rval2;
err1 = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
err2 = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if (err1 || err2){
printf("create failed \n");
return 0;
}
printf("this is main thread\n");
printf("join 1 raval:%d\n",pthread_join(tid1,&rval1));
printf("join 2 raval:%d\n",pthread_join(tid2,&rval2)); //连接错误
/////////////返回函数保存在raval中
printf("thread 1 exit code is:%d\n",(int *)rval1);
printf("thread 2 exit code is:%d\n",(int *)rval2);
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
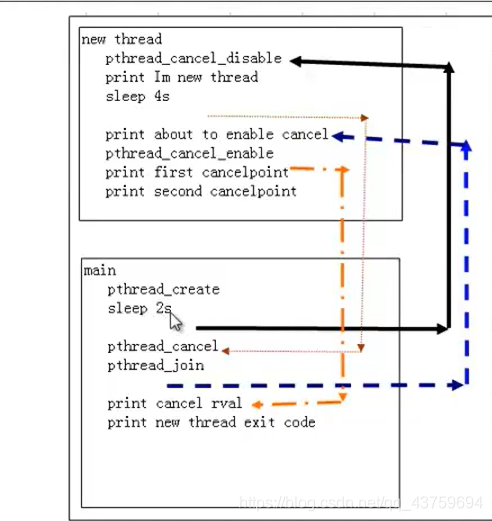
线程的取消
在这里插入图片描述




取消操作
信号默认处理


#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
void *thread_fun(void *arg){
sleep(1);
printf("this is new thread \n");
return (void *)0;
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid;
int err;
int s;
void *rval;
err = pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_fun,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("erro! \n");
trturn;
}
// sleep(1);
s = pthread_kill(tid,SIGQUIT); //终止线进程的运行信号
if(s == ESRCH){ //如果线程已经退出 返回为ESRCH
printf("thread tid is nor found \n");
}
pthread_join(tid,&rval);
return 0;
}

#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
void sig_hander1(int arg){
printf("Thread 1 get signal \n");
return;
}
void sig_hander2(int arg){
printf("Thread 2 get signal \n");
return;
}
void *thread_fun1(void * arg){
printf(" new thread 1 \n");
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act,0,sizeof(act));
act.sa_handler = sig_hander1;
sigaddset(&act.sa_mask,SIGQUIT);
sigaction(SIGQUIT,&act,NULL);
pthread_sigmask(SIG_BLOCK,&act.sa_mask,NULL);
sleep(2);
}
void *thread_fun2(void * arg){
printf(" new thread 2 \n");
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act,0,sizeof(act));
sigaddset(&act.sa_mask,SIGQUIT);
act.sa_handler = sig_hander2;
sigaction(SIGQUIT,&act,NULL);
// pthread_sigmask(SIG_BLOCK,&act.sa_mask,NULL);
sleep(2);
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err,s;
void *rval1,*rval2;
err = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("erro! \n");
}
err = pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("erro! \n");
}
sleep(1);
s = pthread_kill(tid1,SIGQUIT);
if(s!=0){
printf("send signal erro \n");
}
s = pthread_kill(tid2,SIGQUIT);
if(s!=0){
printf("send signal erro \n");
}
pthread_join(tid1,&rval1);
pthread_join(tid2,&rval2);
return 0;
}
线程清理程序

#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <signal.h>
void *first_clean(void *arg){
printf(" first clean \n");
return (void *)0;
}
void *second_clean(void *arg){
printf(" secend clean \n");
return (void *)0;
}
void *thread_fun1(void * arg){
printf("new thread 1 \n");
pthread_cleanup_push(first_clean,"thread1");
pthread_cleanup_push(second_clean,"thread1");
pthread_cleanup_pop(1); //先注册后执行
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
return (void *)1;
}
void *thread_fun2(void * arg){
printf("new thread 2 \n");
pthread_cleanup_push(first_clean,"thread12");
pthread_cleanup_push(second_clean,"thread2");
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_exit((void *)2);
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err;
err = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf(" create erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf(" create erro \n");
return;
}
sleep(2);
return 0;
}
互斥操作的必要性
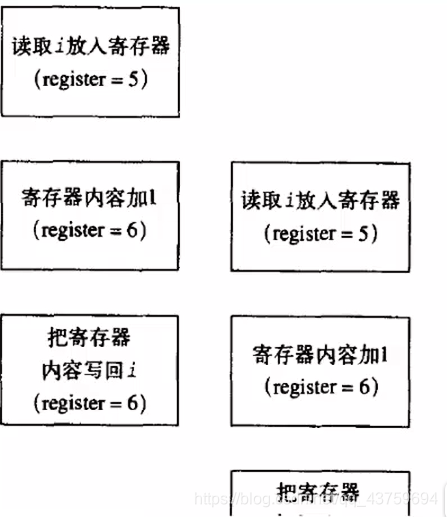
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <signal.h>
struct student{
int age;
int id;
}stu;
int i;
void *thread_fun1(void *arg){
while(1){
stu.age = i;
stu.id = i;
i++;
if(stu.age!=stu.id){
printf("%d %d\n",stu.age,stu.id);
break;
}
}
return (void *)1;
}
void *thread_fun2(void *arg){
while(1){
stu.age = i;
stu.id = i;
i++;
if(stu.age!=stu.id){
printf("%d %d\n",stu.age,stu.id);
break;
}
}
return(void*)1;
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err;
err = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("erro \n");
return;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
互斥量
其本身为一个锁

加锁解锁

///////将会一直运行下去
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <signal.h>
struct student{
int age;
int id;
}stu;
int i;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *thread_fun1(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
stu.age = i;
stu.id = i;
i++;
if(stu.age!=stu.id){
printf("%d %d",stu.age,stu.id);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return (void *)1;
}
void *thread_fun2(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
stu.age = i;
stu.id = i;
i++;
if(stu.age!=stu.id){
printf("%d %d",stu.age,stu.id);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return(void*)1;
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("init mutex erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("1 erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf("2 erro \n");
return;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
读写锁




读写锁是用来解决读者写者问题的,读操作可以共享,写操作是排他的,读可以有多个在读,写只有唯一个在写,同时写的时候不允许读。
互斥锁与读写锁的区别:
当访问临界区资源时(访问的含义包括所有的操作:读和写),需要上互斥锁;
当对数据(互斥锁中的临界区资源)进行读取时,需要上读取锁,当对数据进行写入时,需要上写入锁。
读写锁的优点:
对于读数据比修改数据频繁的应用,用读写锁代替互斥锁可以提高效率。因为使用互斥锁时,即使是读出数据(相当于操作临界区资源)都要上互斥锁,而采用读写锁,则可以在任一时刻允许多个读出者存在,提高了更高的并发度,同时在某个写入者修改数据期间保护该数据,以免任何其它读出者或写入者的干扰。
读写锁描述:
获取一个读写锁用于读称为共享锁,获取一个读写锁用于写称为独占锁,因此这种对于某个给定资源的共享访问也称为共享-独占上锁。
有关这种类型问题(多个读出者和一个写入者)的其它说法有读出者与写入者问题以及多读出者-单写入者锁。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <signal.h>
int num = 0;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
void *thread_fun1(void *arg){
int err;
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); //读加锁
printf("thread 1 print num:%d\n",num);
sleep(3);
printf("Thread 1 over \n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); //读解锁
return(void *)1;
}
void *thread_fun2(void *arg){
int err;
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
printf("thread 2 print num:%d\n",num);
sleep(3);
printf("Thread 2 over \n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
return(void *)1;
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err;
err = pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf(" create lock erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread_fun1,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf(" create thread 1 erro \n");
return;
}
err = pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread_fun2,NULL);
if(err!=0){
printf(" create thread 2 erro \n");
return;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
return 0;
}
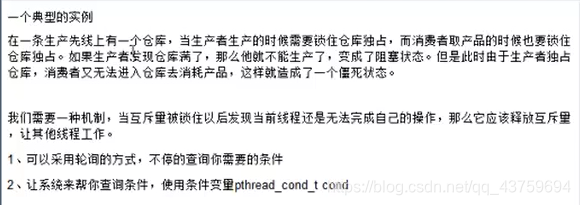
条件变量
///////////////////////////////
//这个老师的存取算法存在 bug,待改
//////////////////////////////
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 4
#define PRODUC_CNT 20
struct product_cons{
int buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; //仓库大小
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁
int writePoi,readPoi; //读写位置
pthread_cond_t noEmpty; //条件变量,非空&非满
pthread_cond_t noFull;
}buffer;
////////////////////初始化
void init(struct product_cons *p){
pthread_mutex_init(&p->mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&p->noEmpty,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&p->noFull,NULL);
p->readPoi=0;
p->writePoi=0;
}
/////////////////结束
void finish(struct product_cons *p){
pthread_mutex_destroy(&p->mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&p->noEmpty);
pthread_cond_destroy(&p->noFull);
p->readPoi=0;
p->writePoi=0;
}
////////////////存储数据到buffer
void put(struct product_cons *p,int data){
pthread_mutex_lock(&p->mutex);
if((p->readPoi+1)%BUFFER_SIZE==p->readPoi){
printf("producer wait for coustorm...\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&p->noFull,&p->mutex);
}
p->buffer[p->writePoi] = data;
p->writePoi++;
if(p->writePoi>=BUFFER_SIZE){
p->writePoi = 0;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&p->noEmpty);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&p->mutex);
}
///////////////移除数据从buffer
int get(struct product_cons *p){
int data;
pthread_mutex_lock(&p->mutex);
if(p->readPoi==p->writePoi){
printf("customer wait product... \n");
pthread_cond_wait(&p->noEmpty,&p->mutex);
}
data = p->buffer[p->readPoi];
p->readPoi++;
if(p->readPoi==BUFFER_SIZE){
p->readPoi=0;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&p->noFull);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&p->mutex);
return data;
}
///////////////子线程 生产产品
void *product(void *data){
int n;
for(n=1;n<=PRODUC_CNT;n++){
sleep(1);
printf("product the %d \n",n);
put(&buffer,n);
printf("put the %d produce into buffer \n",n);
}
printf("the product thread success \n");
return NULL;
}
//////////////子线程 消费产品
void *customer(void *data){
static int cnt = 0; //子程序中的静态变量当离开子程序时仍存在,因此当再次进入时可以直接使用原来的值
int num;
while(1){
sleep(2);
printf("get the produce ...\n");
num = get(&buffer);
printf("get the product %d success\n",num);
printf("################test#####%d\n",cnt);
if(++cnt==PRODUC_CNT){
break;
}
}
printf("custorm stopped \n");
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pthread_t tidp,tidc;
void *rval;
init(&buffer);
pthread_create(&tidp,NULL,product,NULL);
pthread_create(&tidc,NULL,customer,NULL);
pthread_join(tidp,&rval);
pthread_join(tidc,&rval);
finish(&buffer);
return 0;
}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号