IO流
File类
• 文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式。一个File对象可以代表一个文件或目录
• 可以实现获取文件和目录属性等功能
• 可以实现对文件和目录的创建、删除等功能
• File不能访问文件内容
路径可以是绝对路径和相对路径,分隔符采用\\或者/
1. File file = new File("d:\\test\\java.txt");
2. File file = new File("d:/test/java.txt");
3. File file = new File("java.txt");
• 通过File对象可以访问文件的属性。
public String getName() public String getPath()
public boolean isFile() public boolean isDirectory()
public boolean canRead() public boolean canWrite()
public boolean exists() public long length()
public boolean isHidden() public long lastModified()
public File [] listFiles();
• 通过File对象创建空文件或目录(在该对象所指的文件或目录不存在的情况下)。
public boolean createNewFile()throws IOException
public boolean delete()
public boolean mkdir(), mkdirs() 注意两个的区别!

1 public class TestFile { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 File f = new File("d:/src3/TestObject.java"); 4 File f2 = new File("d:/src3"); 5 File f3 = new File(f2,"TestThis.java"); 6 File f4 = new File(f2,"TestFile666.java"); 7 try { 8 f4.createNewFile(); 9 } catch (IOException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 f4.delete(); 13 File f5 = new File("d:/src3/aa/bb/cc/ee/ddd"); 14 f5.mkdirs(); 15 if(f.isFile()){ 16 System.out.println("是一个文件"); 17 } 18 if(f2.isDirectory()){ 19 System.out.println("是一个目录"); 20 } 21 22 } 23 }
打印目录树状结构_递归算法:

1 public class FileTree { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 File f = new File("d:/aaa"); 4 printFile(f, 0); 5 } 6 7 static void printFile(File file,int level){ 8 for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) { 9 System.out.print("-"); 10 } 11 System.out.println(file.getName()); 12 13 if(file.isDirectory()){ 14 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 15 for (File temp : files) { 16 printFile(temp, level+1); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 }
流的原理
• 在Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流” (stream) 方式进行;
• J2SDK提供了各种各样的“流”类,用以获取不同种类的数据;程序中通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
• Java的流类型一般位于java.io包中
流的概念
• 数据源
• data source. 提供原始数据的原始媒介。常见的:数据库、文件、其他程序、内存、网络连接、IO设备。
• 数据源就像水箱,流就像水管中流着的水流,程序就是我们最终的用户。 流是一个抽象、动态的概念,是一连串连续动态的数据集合。
流的分类
• 流的方向:
• 输入流:数据源到程序(InputStream、Reader读进来)
• 输出流:程序到目的地(OutPutStream、Writer写出去)
• 处理数据单元:
• 字节流:按照字节读取数据(InputStream、OutputStream),可以处理所有文件
• 字符流:按照字符读取数据(Reader、Writer),只能处理纯文本
• 功能不同:
• 节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据。
• 处理流(包装流):不直接连接到数据源或目的地,是其他流进行封装。目的主要是简化操作和提高性能.
• 节点流和处理流的关系:
• 节点流处于io操作的第一线,所有操作必须通过他们进行;
• 处理流可以对其他流进行处理(提高效率或操作灵活性).
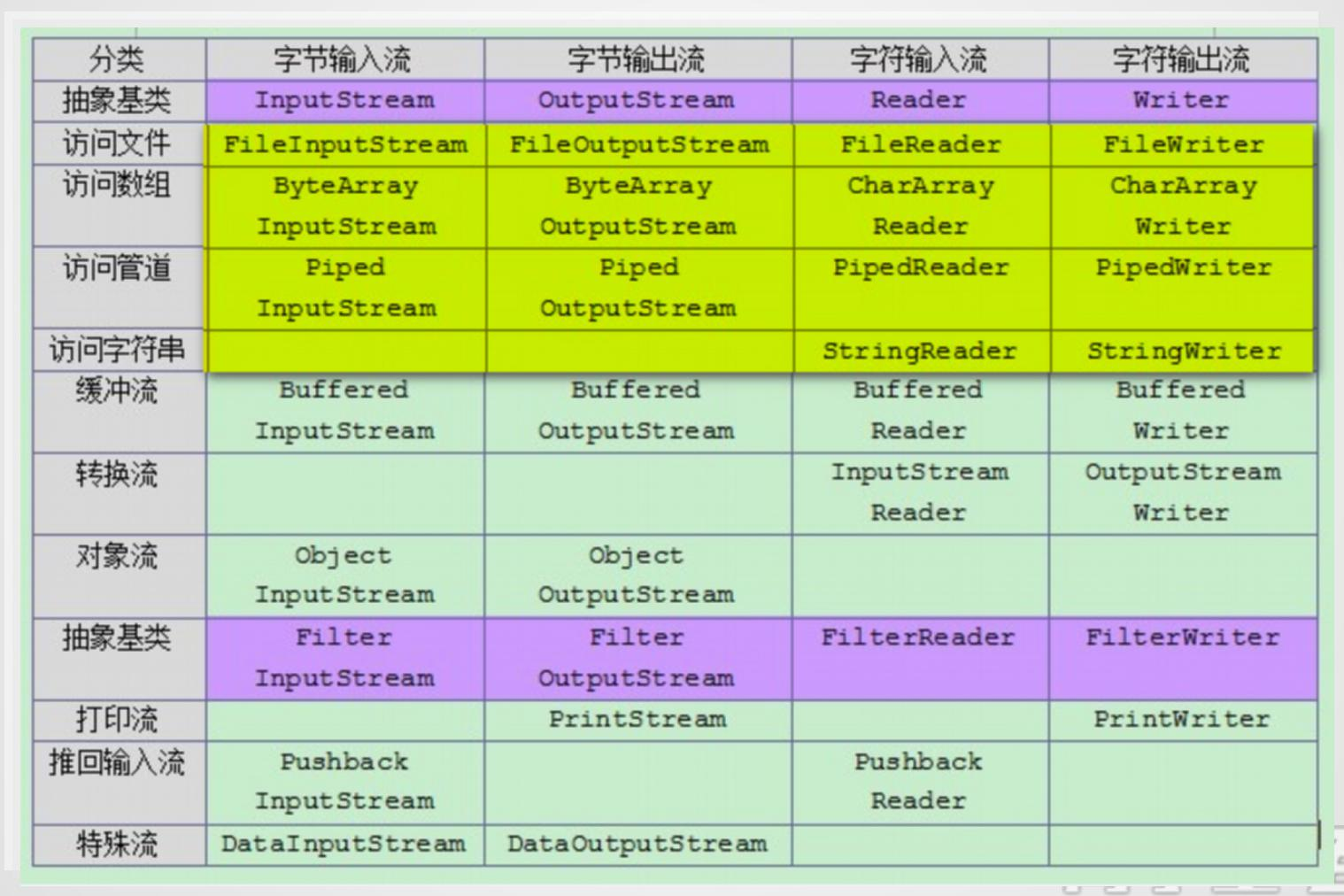
IO流类的体系
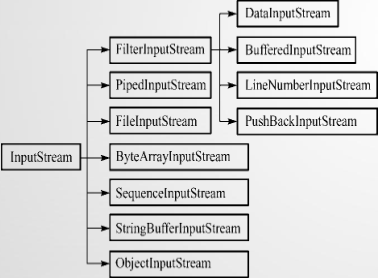
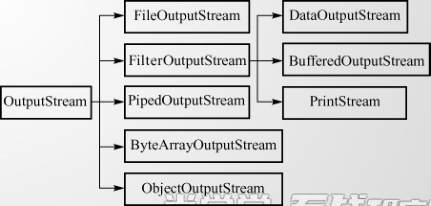
• InputStream和OutputStream
• Java语言中最基本的两个字节输入输出类。
• 其他所有字节输入输出流类都继承自这两个基类。
• 这两个类都是抽象类,不能创建它们的实例,只能使用它们的子类.
• Reader和Writer
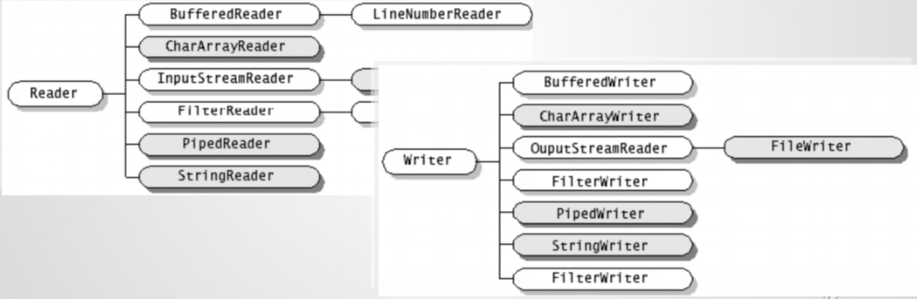
• Java语言中最基本的两个字符输入输出类。
• 其他所有字符输入输出流类都继承自这两个基类。
• 这两个类都是抽象类,不能创建它们的实例,只能使用它们的子类.
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
• 使用FileInputStream读取文件内容
• abstract int read( );
• int read( byte b[ ] );
• int read( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
• int available( );
• close( );
• 使用FileOutputStream写内容到文件
• abstract void write( int b );
• void write( byte b[ ] );
• void write( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
• void flush( );
• void close( );
• 使用FileInputStream/FileOutputStream复制文件

1 /** 2 * 文件操作 3 * 1、文件拷贝 4 * 2、文件夹拷贝 拒绝自己拷贝给自己 5 * @author Administrator 6 * 7 */ 8 public class FileUtil { 9 /** 10 * 拷贝文件夹 11 * @param src 源路径 12 * @param dest 目标路径 13 * @throws IOException 14 * @throws FileNotFoundException 15 */ 16 public static void copyDir(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{ 17 //拒绝自己拷贝给自己 18 if(srcPath.equals(destPath)){ 19 return ; 20 } 21 File src=new File(srcPath); 22 File dest =new File(destPath); 23 copyDir(src,dest); 24 } 25 26 27 28 /** 29 * 拷贝文件夹 30 * @param src 源File对象 31 * @param dest 目标File对象 32 * @throws IOException 33 * @throws FileNotFoundException 34 */ 35 public static void copyDir(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{ 36 if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 37 dest =new File(dest,src.getName()); 38 if(dest.getAbsolutePath().contains(src.getAbsolutePath())){ 39 System.out.println("父目录不能拷贝到子目录中"); 40 return; 41 } 42 } 43 copyDirDetail(src,dest); 44 } 45 46 /** 47 * 拷贝文件夹细节 48 * @param src 49 * @param dest 50 */ 51 public static void copyDirDetail(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{ 52 if(src.isFile()){ //文件 53 try { 54 FileUtil.copyFile(src, dest); 55 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 56 //e.printStackTrace(); 57 throw e; 58 } catch (IOException e) { 59 //e.printStackTrace(); 60 throw e; 61 } 62 }else if(src.isDirectory()){ //文件夹 63 //确保目标文件夹存在 64 dest.mkdirs(); 65 //获取下一级目录|文件 66 for(File sub:src.listFiles()){ 67 copyDirDetail(sub,new File(dest,sub.getName())); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 72 73 /** 74 * 文件的拷贝 75 * @param 源文件路径 76 * @param 目录文件路径 77 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException 78 * @return 79 */ 80 public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { 81 //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) 82 copyFile(new File(srcPath),new File(destPath)); 83 } 84 /** 85 * 文件的拷贝 86 * @param 源文件File对象 87 * @param 目录文件File对象 88 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException 89 * @return 90 */ 91 public static void copyFile(File src,File dest) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { 92 if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null 93 System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); 94 throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); 95 } 96 //dest为已经存在的文件夹,不能建立于文件夹同名的文件 97 if(dest.isDirectory()){ 98 System.out.println(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立于文件夹同名的文件"); 99 throw new IOException(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立于文件夹同名的文件"); 100 } 101 102 103 //2、选择流 104 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 105 OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); 106 //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 107 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; 108 int len =0; 109 //读取 110 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ 111 //写出 112 os.write(flush, 0, len); 113 } 114 os.flush(); //强制刷出 115 116 //关闭流 117 os.close(); 118 is.close(); 119 } 120 }
FileReader和FileWriter
• 使用FileReader读取文件内容
• read()
• read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
• close()
• 使用FileWriter写内容到文件
• write(int c)
• write(String str, int off, int len)
• close()
• 使用FileReader和FileWriter完成文件复制

1 /** 2 * 纯文本拷贝 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class CopyFile { 7 8 /** 9 * @param args 10 */ 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 //创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本 13 File src =new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"); 14 File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/char.txt"); 15 //选择流 16 Reader reader =null; 17 Writer wr =null; 18 try { 19 reader =new FileReader(src); 20 wr =new FileWriter(dest); 21 //读取操作 22 char[] flush =new char[1024]; 23 int len =0; 24 while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ 25 wr.write(flush, 0, len); 26 } 27 wr.flush();//强制刷出 28 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 System.out.println("源文件不存在"); 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 System.out.println("文件读取失败"); 34 }finally{ 35 try { 36 if (null != wr) { 37 wr.close(); 38 } 39 } catch (Exception e2) { 40 } 41 try { 42 if (null != reader) { 43 reader.close(); 44 } 45 } catch (Exception e2) { 46 } 47 } 48 49 } 50 51 }
缓冲字节流(处理流)
• BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
• FileInputStream和FileOutputStream是节点流
• BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream是处理流(包装流)
• 读文件和写文件都使用了缓冲区,减少了读写次数,从而提高了效率
• 当创建这两个缓冲流的对象时时,会创建了内部缓冲数组,缺省使用32字节大小的缓冲区.
• 当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区
• 当写入数据时,首先写入缓冲区,当缓冲区满时,其中的数据写入所连接的输出流。使用方法flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流
• 关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反.只要关闭高层流即可,关闭高层流其实关闭的底层节点流
• Flush的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件

1 /** 2 * 字节流文件拷贝+缓冲流 ,提高性能 3 * 缓冲流(节点流) 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class BufferedByteDemo { 8 9 /** 10 * @param args 11 */ 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 14 } 15 /** 16 * 文件的拷贝 17 * @param 源文件路径 18 * @param 目录文件路径 19 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException 20 * @return 21 */ 22 public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { 23 //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) 24 File src =new File(srcPath); 25 File dest =new File(destPath); 26 if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null 27 System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); 28 throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); 29 } 30 //2、选择流 31 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 32 OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(dest)); 33 //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 34 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; 35 int len =0; 36 //读取 37 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ 38 //写出 39 os.write(flush, 0, len); 40 } 41 os.flush(); //强制刷出 42 43 //关闭流 44 os.close(); 45 is.close(); 46 } 47 48 }
缓冲字符流(处理流)
• BufferedReader
• readLine() 读取一个文本行的数据
• BufferedWriter
• newLine(); 写入一个行分隔符。

1 /** 2 * 字符缓冲流 +新增方法(不能发生多态) 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class BufferedCharDemo { 7 8 /** 9 * @param args 10 */ 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 //创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本 13 File src =new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"); 14 File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/char.txt"); 15 //选择流 16 BufferedReader reader =null; 17 BufferedWriter wr =null; 18 try { 19 reader =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); 20 wr =new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); 21 //读取操作 22 /* 23 char[] flush =new char[1024]; 24 int len =0; 25 while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ 26 wr.write(flush, 0, len); 27 }*/ 28 //新增方法的操作 29 String line =null; 30 while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){ 31 wr.write(line); 32 //wr.append("\r\n"); 33 wr.newLine(); //换行符号 34 } 35 wr.flush();//强制刷出 36 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 System.out.println("源文件不存在"); 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 System.out.println("文件读取失败"); 42 }finally{ 43 try { 44 if (null != wr) { 45 wr.close(); 46 } 47 } catch (Exception e2) { 48 } 49 try { 50 if (null != reader) { 51 reader.close(); 52 } 53 } catch (Exception e2) { 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 }
转换流(处理流)
• InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
• 为处理流
• 用于将字节流转化成字符流,字符流与字节流之间的桥梁,处理乱码编码集、解码集(乱码出现的原因:1.编码解码不统一;2.字节丢失)
• InputStreamReader的作用是把InputStream转换成Reader
• OutputStreamWriter的作用是把OutputStream转换成Writer
• 存在将字节流转换成字符流的转换流,因为字符流操作文本更简单
• 不存在把字符流转换成字节流的转换流,因为没有必要
• System.in代表标准输入,即键盘输入,是InputStream的实例

1 /** 2 * 转换流: 字节转为字符 3 * 1、输出流 OutputStreamWriter 编码 4 * 2、输入流 InputStreamReader 解码 5 * 6 * 确保源不能为乱码 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9 */ 10 public class ConverDemo02 { 11 12 /** 13 * @param args 14 * @throws IOException 15 */ 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 17 //指定解码字符集 18 BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader( 19 new InputStreamReader( 20 new BufferedInputStream( 21 new FileInputStream( 22 new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java"))),"UTF-8") 23 ); 24 //写出文件 编码 25 BufferedWriter bw =new BufferedWriter( 26 new OutputStreamWriter( 27 new BufferedOutputStream( 28 new FileOutputStream(new File("E:/xp/test/encode.java"))))); 29 30 String info =null; 31 while(null!=(info=br.readLine())){ 32 //System.out.println(info); 33 bw.write(info); 34 bw.newLine(); 35 } 36 bw.flush(); 37 bw.close(); 38 br.close(); 39 } 40 41 }
其它流
1. 字节/字符数组/字符串流(节点流)
• ByteArrayInutStream和ByteArrayOutputStream(可以不关流,这个流就是在内存中,内存不用了会自动释放,关不关都可以)
• 数据源或目的地为:字节数组
• 只有字节流,没有字符流
• 节点流

1 /** 2 * 字节数组 节点流 3 * 数组的长度有限 ,数据量不会很大 4 * 5 * 文件内容不用太大 6 * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 7 * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 8 * 9 * 10 * 11 * @author Administrator 12 * 13 */ 14 public class ByteArrayDemo01 { 15 16 /** 17 * @param args 18 * @throws IOException 19 */ 20 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 21 read(write()); 22 } 23 /** 24 * 输出流 操作与文件输出流 有些不同, 有新增方法,不能使用多态 25 * @throws IOException 26 */ 27 public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ 28 //目的地 29 byte[] dest; 30 //选择流 不同点 31 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 32 //操作 写出 33 String msg ="操作与 文件输入流操作一致"; 34 byte[] info =msg.getBytes(); 35 bos.write(info, 0, info.length); 36 //获取数据 37 dest =bos.toByteArray(); 38 //释放资源 39 bos.close(); 40 return dest; 41 42 43 } 44 45 46 47 /** 48 * 输入流 操作与 文件输入流操作一致 49 * 读取字节数组 50 * @throws IOException 51 */ 52 public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ 53 //数据源传入 54 55 //选择流 56 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream( 57 new ByteArrayInputStream( 58 src 59 ) 60 ); 61 //操作 62 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; 63 int len =0; 64 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ 65 System.out.println(new String(flush,0,len)); 66 } 67 //释放资源 68 is.close(); 69 70 71 72 } 73 74 } 75 76 /** 77 *1、文件 --程序->字节数组 78 *1)、文件输入流 79 * 字节数组输出流 80 * 81 * 82 * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 83 * 1)、字节数组输入流 84 * 文件输出流 85 * @author Administrator 86 * 87 */ 88 public class ByteArrayDemo02 { 89 90 /** 91 * @param args 92 * @throws IOException 93 */ 94 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 95 byte[] data =getBytesFromFile("e:/xp/test/1.jpg"); 96 toFileFromByteArray(data,"e:/xp/test/arr.jpg"); 97 } 98 /** 99 * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 100 */ 101 public static void toFileFromByteArray(byte[] src,String destPath) throws IOException{ 102 //创建源 103 //目的地 104 File dest=new File(destPath); 105 106 //选择流 107 //字节数组输入流 108 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(src)); 109 //文件输出流 110 OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); 111 112 //操作 不断读取字节数组 113 byte[] flush =new byte[1]; 114 int len =0; 115 while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ 116 //写出到文件中 117 os.write(flush, 0, len); 118 } 119 os.flush(); 120 121 //释放资源 122 os.close(); 123 is.close(); 124 125 126 } 127 128 129 130 /** 131 * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 132 * @return 133 * @throws IOException 134 */ 135 public static byte[] getBytesFromFile(String srcPath) throws IOException{ 136 //创建文件源 137 File src =new File(srcPath); 138 //创建字节数组目的地 139 byte[] dest =null; 140 141 //选择流 142 //文件输入流 143 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); 144 //字节数组输出流 不能使用多态 145 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 146 147 148 //操作 不断读取文件 写出到字节数组流中 149 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; 150 int len =0; 151 while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ 152 //写出到字节数组流中 153 bos.write(flush, 0, len); 154 } 155 bos.flush(); 156 157 //获取数据 158 dest =bos.toByteArray(); 159 160 bos.close(); 161 is.close(); 162 return dest; 163 } 164 165 }
• CharArrayReader和CharArrayWriter
• 数据源或目的地为:字符数组
• 只有字符流,没有字节流
• 节点流
• StringReader和StringWriter
• 数据源或目的地为:字符串
• 只有字符流,没有字节流
• 节点流
2. 基本类型+String(处理流) 作用:保留数据+类型
• 输入流:DataInputStream
• 输出流:DataOutputStream

1 /** 2 * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 3 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() 4 * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() 5 * 新增方法不能使用多态 6 * 7 * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 8 * @author Administrator 9 * 10 */ 11 public class DataDemo01 { 12 13 /** 14 * @param args 15 */ 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 try { 18 //write("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); 19 //read("e:/xp/test/arr.txt"); //非法内容 20 read("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 26 27 28 } 29 /** 30 * 从文件读取数据+类型 31 * @throws IOException 32 */ 33 public static void read(String destPath) throws IOException{ 34 //创建源 35 File src =new File(destPath); 36 //选择流 37 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( 38 new BufferedInputStream( 39 new FileInputStream(src) 40 ) 41 ); 42 43 //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致(不一致,数据存在问题) 必须存在才能读取 44 double num1 =dis.readDouble(); 45 long num2 =dis.readLong(); 46 47 String str =dis.readUTF(); 48 49 dis.close(); 50 System.out.println(num2+"-->"+str); 51 52 } 53 /** 54 * 数据+类型输出到文件 55 * @throws IOException 56 */ 57 public static void write(String destPath) throws IOException{ 58 double point =2.5; 59 long num=100L; 60 String str ="数据类型"; 61 62 //创建源 63 File dest =new File(destPath); 64 //选择流 DataOutputStream 65 DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( 66 new BufferedOutputStream( 67 new FileOutputStream(dest) 68 ) 69 ); 70 //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 71 dos.writeDouble(point); 72 dos.writeLong(num); 73 dos.writeUTF(str); 74 dos.flush(); 75 76 //释放资源 77 dos.close(); 78 79 } 80 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 85 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() 86 * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() 87 * 新增方法不能使用多态 88 * 89 * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 90 * @author Administrator 91 * 92 */ 93 public class DataDemo02 { 94 95 /** 96 * @param args 97 */ 98 public static void main(String[] args) { 99 try { 100 byte[] data=write(); 101 read(data); 102 System.out.println(data.length); 103 } catch (IOException e) { 104 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 105 e.printStackTrace(); 106 } 107 108 109 110 } 111 /** 112 * 从字节数组读取数据+类型 113 * @throws IOException 114 */ 115 public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ 116 //选择流 117 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( 118 new BufferedInputStream( 119 new ByteArrayInputStream(src) 120 ) 121 ); 122 123 //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 124 double num1 =dis.readDouble(); 125 long num2 =dis.readLong(); 126 String str =dis.readUTF(); 127 128 dis.close(); 129 130 System.out.println(num1+"-->"+num2+"-->"+str); 131 132 } 133 /** 134 * 数据+类型输出到字节数组中 135 * @throws IOException 136 */ 137 public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ 138 //目标数组 139 byte[] dest =null; 140 double point =2.5; 141 long num=100L; 142 String str ="数据类型"; 143 144 145 //选择流 ByteArrayOutputStream DataOutputStream 146 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 147 DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( 148 new BufferedOutputStream( 149 bos 150 ) 151 ); 152 //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 153 dos.writeDouble(point); 154 dos.writeLong(num); 155 dos.writeUTF(str); 156 dos.flush(); 157 158 dest =bos.toByteArray(); 159 160 //释放资源 161 dos.close(); 162 163 return dest; 164 165 } 166 167 }
3. 引用类型(处理流) 作用:保留数据+类型
• 反序列化:输入流ObjectInputStream readObject()
• 序列化:输出流ObjectOutputStream writeObject()
注意:1)先序列化后反序列化,反序列化顺序必须与序列化顺序一致;2)不是所有的对象都可以序列化,不是所有的属性都需要序列化(不需要序列化使用transient)
对象序列化
• 对象序列化 (Serialization)
• 将Java对象转换成字节序列(IO字节流)
• 对象反序列化 (DeSerialization)
• 从字节序列中恢复Java对象
• 为什么序列化
• 序列化以后的对象可以保存到磁盘上,也可以在网络上传输,使得不同的计算机可以共享对象.(序列化的字节序列是平台无关的)
• 对象序列化的条件
• 只有实现了Serializable接口的类的对象才可以被序列化。Serializable接口中没有任何的方法,实现该接口的类不需要实现额外的方法。
• 如果对象的属性是对象,属性对应类也必须实现Serializable接口
• 如何实现序列化
• 创建ObjectOutputStream对象
• 调用writeObject()输出对象
• 如何实现反序列化
• 创建ObjectInputStream对象
• 调用readObject()读取对象

1 /** 2 * 空接口只是标识 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable { 7 //不需要序列化 8 private transient String name; 9 private double salary; 10 public Employee() { 11 } 12 public Employee(String name, double salary) { 13 super(); 14 this.name = name; 15 this.salary = salary; 16 } 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 public double getSalary() { 24 return salary; 25 } 26 public void setSalary(double salary) { 27 this.salary = salary; 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 不是所有的对象都可以序列化 java.io.NotSerializableException 34 * 不是所有的属性都需要序列化 transient 35 * @author Administrator 36 * 37 */ 38 public class ObjectDemo01 { 39 40 /** 41 * @param args 42 * @throws ClassNotFoundException 43 */ 44 public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { 45 try { 46 seri("e:/xp/test/ser.txt"); 47 read("e:/xp/test/ser.txt"); 48 } catch (IOException e) { 49 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 //反序列化 54 public static void read(String destPath) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ 55 //创建源 56 File src =new File(destPath); 57 //选择流 58 ObjectInputStream dis =new ObjectInputStream( 59 new BufferedInputStream( 60 new FileInputStream(src) 61 ) 62 ); 63 64 //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 65 //不一致,数据存在问题 66 Object obj =dis.readObject(); 67 if(obj instanceof Employee){ 68 Employee emp=(Employee)obj; 69 System.out.println(emp.getName()); 70 System.out.println(emp.getSalary()); 71 } 72 73 obj =dis.readObject(); 74 int[] arr=(int[])obj; 75 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 76 dis.close(); 77 } 78 79 //序列化 80 public static void seri(String destPath) throws IOException{ 81 Employee emp =new Employee("bjsxt",1000000); 82 int[] arr ={1,2,3,45}; 83 //创建源 84 File dest =new File(destPath); 85 //选择流 ObjectOutputStream 86 ObjectOutputStream dos =new ObjectOutputStream( 87 new BufferedOutputStream( 88 new FileOutputStream(dest) 89 ) 90 ); 91 //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 92 dos.writeObject(emp); 93 dos.writeObject(arr); 94 //释放资源 95 dos.close(); 96 } 97 }
• 序列化能保存的元素
• 只能保存对象的非静态成员变量
• 不能保存任何成员方法和静态的成员变量
• 不保存transient成员变量
• 如果一个对象的成员变量是一个对象,这个对象的成员变量也会保存
• 串行化保存的只是变量的值,对于变量的任何修饰符,都不能保存
• 使用对象流把一个对象写到文件时不仅保证该对象是序列化的,而且该对象的成员对象也必须是可序列化的。
• 如果一个可序列化的对象包含对某个不可序列化的对象的引用,那么整个序列化操作将会失败,并且会抛出一个NotSerializableException。我们可以将这个引用标记为transient,那么对象仍然可以序列化。
• 同一个对象多次序列化的处理
• 所有保存到磁盘中的对象都有一个序列化编号
• 序列化一个对象中,首先检查该对象是否已经序列化过
• 如果没有,进行序列化
• 如果已经序列化,将不再重新序列化,而是输出编号即可
• 如果不希望某些属性(敏感)序列化,或不希望出现递归序列
• 为属性添加transient关键字(完成排除在序列化之外)
• 自定义序列化(不仅可以决定哪些属性不参与序列化,还可以定义属性具体如何序列化)
• 序列化版本不兼容
• 修改了实例属性后,会影响版本号,从而导致反序列化不成功
• 解决方案:为Java对象指定序列化版本号serialVersionUID
打印流
• PrintStream
• PrintStream提供了一系列的print()和println(),可以实现将基本数据类型格式化成字符串输出。对象类型将先调用toString(),然后输出该方法返回的字符串
• System.out就是PrintStream的一个实例,代表显示器
• System.err 也是PrintStream的一个实例,代表显示器
• PrintStream的输出功能非常强大,通常需要输出文本内容,都可以将输出流包装成PrintStream后进行输出
• PrintStream的方法都不抛出IOException
• PrintWriter
• PrintStream的对应字符流,功能相同,方法对应。
• PrintWriter的方法也不抛出IOException
• 复制文件时可以使用PrintWriter代替BufferedWriter完成,更简单

1 /** 2 * PrintStream 打印流 -->处理流 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class PrintStreamDemo01 { 7 8 /** 9 * @param args 10 * @throws FileNotFoundException 11 */ 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 13 System.out.println("test"); 14 PrintStream ps =System.out; 15 ps.println(false); 16 17 18 //输出到文件 19 File src = new File("e:/xp/test/print.txt"); 20 ps = new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(src))); 21 ps.println("io is so easy...."); 22 23 ps.close(); 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * 三个常量 30 * 1、System.in 输入流 键盘输入 31 * 2、System.out 输出流 控制台输出 32 * System.err 33 * 34 * ==>重定向 35 * setIn() 36 * setOut() 37 * setErr() 38 * FileDescriptor.in 39 * FileDescriptor.out 40 * @author Administrator 41 * 42 */ 43 public class SystemDemo01 { 44 45 /** 46 * @param args 47 * @throws FileNotFoundException 48 */ 49 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 50 //test1(); 51 //test2(); 52 //重定向 53 System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e:/xp/test/print.txt")),true)); 54 System.out.println("a"); //控制台 -->文件 55 System.out.println("test"); 56 //回控制台 57 System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)),true)); 58 System.out.println("back...."); 59 } 60 public static void test2() throws FileNotFoundException{ 61 InputStream is =System.in; //键盘输入 62 is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:/xp/test/print.txt")); 63 Scanner sc = new Scanner(is); 64 //System.out.println("请输入:"); 65 System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); 66 } 67 68 public static void test1(){ 69 System.out.println("test"); 70 System.err.println("err"); 71 } 72 73 } 74 75 /** 76 * 封装输入 77 * @author Administrator 78 * 79 */ 80 public class BuffereIn { 81 82 /** 83 * @param args 84 * @throws IOException 85 */ 86 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 87 InputStream is =System.in; 88 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); 89 System.out.println("请输入。。。。"); 90 String msg =br.readLine(); 91 System.out.println(msg); 92 } 93 94 }
文件的分割与合并

1 public class SplitFile { 2 //文件的路径 3 private String filePath; 4 //文件名 5 private String fileName; 6 //文件大小 7 private long length; 8 //块数 9 private int size; 10 //每块的大小 11 private long blockSize; 12 //分割后的存放目录 13 private String destBlockPath; 14 //每块的名称 15 private List<String> blockPath; 16 17 public SplitFile(){ 18 blockPath = new ArrayList<String>(); 19 } 20 public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath){ 21 this(filePath,destBlockPath,1024); 22 } 23 public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath,long blockSize){ 24 this(); 25 this.filePath= filePath; 26 this.destBlockPath =destBlockPath; 27 this.blockSize=blockSize; 28 init(); 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 初始化操作 计算 块数、确定文件名 33 */ 34 public void init(){ 35 File src =null; 36 //健壮性 37 if(null==filePath ||!(((src=new File(filePath)).exists()))){ 38 return; 39 } 40 if(src.isDirectory()){ 41 return ; 42 } 43 //文件名 44 this.fileName =src.getName(); 45 46 //计算块数 实际大小 与每块大小 47 this.length = src.length(); 48 //修正 每块大小 49 if(this.blockSize>length){ 50 this.blockSize =length; 51 } 52 //确定块数 53 size= (int)(Math.ceil(length*1.0/this.blockSize)); 54 //确定文件的路径 55 initPathName(); 56 } 57 58 private void initPathName(){ 59 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 60 this.blockPath.add(destBlockPath+"/"+this.fileName+".part"+i); 61 } 62 } 63 64 /** 65 * 文件的分割 66 * 0)、第几块 67 * 1、起始位置 68 * 2、实际大小 69 * @param destPath 分割文件存放目录 70 */ 71 public void split(){ 72 long beginPos =0; //起始点 73 long actualBlockSize =blockSize; //实际大小 74 //计算所有块的大小、位置、索引 75 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 76 if(i==size-1){ //最后一块 77 actualBlockSize =this.length-beginPos; 78 } 79 spiltDetail(i,beginPos,actualBlockSize); 80 beginPos+=actualBlockSize; //本次的终点,下一次的起点 81 } 82 83 } 84 /** 85 * 文件的分割 输入 输出 86 * 文件拷贝 87 * @param idx 第几块 88 * @param beginPos 起始点 89 * @param actualBlockSize 实际大小 90 */ 91 private void spiltDetail(int idx,long beginPos,long actualBlockSize){ 92 //1、创建源 93 File src = new File(this.filePath); //源文件 94 File dest = new File(this.blockPath.get(idx)); //目标文件 95 //2、选择流 96 RandomAccessFile raf = null; //输入流 97 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 98 try { 99 raf=new RandomAccessFile(src,"r"); 100 bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); 101 102 //读取文件 103 raf.seek(beginPos); 104 //缓冲区 105 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; 106 //接收长度 107 int len =0; 108 while(-1!=(len=raf.read(flush))){ 109 if(actualBlockSize-len>=0){ //查看是否足够 110 //写出 111 bos.write(flush, 0, len); 112 actualBlockSize-=len; //剩余量 113 }else{ //写出最后一次的剩余量 114 bos.write(flush, 0, (int)actualBlockSize); 115 break; 116 } 117 } 118 119 120 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 121 e.printStackTrace(); 122 } catch (IOException e) { 123 e.printStackTrace(); 124 }finally{ 125 FileUtil.close(bos,raf); 126 } 127 128 } 129 /** 130 * 文件的合并 131 */ 132 public void merge(String destPath){ 133 //创建源 134 File dest =new File(destPath); 135 //选择流 136 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 137 SequenceInputStream sis =null ;//输入流 138 //创建一个容器 139 Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<InputStream>(); 140 try { 141 for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) { 142 vi.add(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i))))); 143 } 144 bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加 145 sis=new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements()); 146 147 //缓冲区 148 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; 149 //接收长度 150 int len =0; 151 while(-1!=(len=sis.read(flush))){ 152 bos.write(flush, 0, len); 153 } 154 bos.flush(); 155 FileUtil.close(sis); 156 } catch (Exception e) { 157 }finally{ 158 FileUtil.close(bos); 159 } 160 161 } 162 /** 163 * 文件的合并 164 */ 165 public void merge1(String destPath){ 166 //创建源 167 File dest =new File(destPath); 168 //选择流 169 BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流 170 try { 171 bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加 172 BufferedInputStream bis = null; 173 for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) { 174 bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i)))); 175 176 //缓冲区 177 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; 178 //接收长度 179 int len =0; 180 while(-1!=(len=bis.read(flush))){ 181 bos.write(flush, 0, len); 182 } 183 bos.flush(); 184 FileUtil.close(bis); 185 } 186 } catch (Exception e) { 187 }finally{ 188 FileUtil.close(bos); 189 } 190 191 } 192 193 /** 194 * @param args 195 */ 196 public static void main(String[] args) { 197 SplitFile split = new SplitFile("E:/xp/20130502/test/学员设置(20130502).xls","E:/xp/20130502",51); 198 199 //System.out.println(split.size); 200 201 //split.split(); 202 203 split.merge("E:/xp/20130502/test1.xls"); 204 } 205 206 }
SequenceInputStream
把多个流合并起来
总结
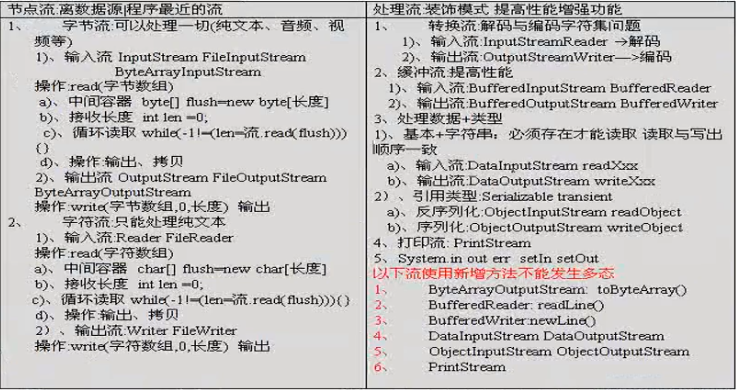
• IO基础
• 流的原理
• 对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流” (stream) 方式进行
• 数据源就像水箱,流就像水管中流着的水流,程序就是我们最终的用户
• 流的分类
• 输入流和输出流
• 字节流和字符流
• 节点流和处理流(包装流 装饰流)
• 流的体系
• InputStream 字节输入流和OutputStream 字节输出流
• Reader 字符输入流和Writer 字符输出流
• 具体IO介绍
• 文件流:节点流
• FileInputStream和FileOutputStream FileReader和FileWriter
• 缓冲流:包装流
• BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
• 转换流:包装流 字节流转换成字符流 System.in
• InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
• 打印流:包装流 只有输出流 System.out
• PrintStream和PrintWriter
• 数据流:包装流 只有字节流 基本类型和String
• DataInputStream和DataOutputStream
• 对象流:包装流 只有字节流 序列化 对象
• ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream
• 字节数组流:节点流 字节流
• ByteArrayInutStream和ByteArrayOutputStream



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号