[LeetCode] #94 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
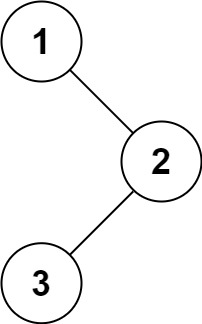
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
二叉树遍历,最经典的方法肯定是递归
递归有三部曲
(1)找整个递归的终止条件:递归应该在什么时候结束? 节点为null
(2)找返回值:应该给上一级返回什么信息?该子树的中序遍历List
(3)本级递归应该做什么:在这一级递归中,应该完成什么任务?该子树List追加左子树List,追加自己的val,追加右子树List
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if (root == null) return res; res.addAll(inorderTraversal(root.left)); res.add(root.val); res.addAll(inorderTraversal(root.right)); return res; } }
递归也可以用迭代的方式实现,两种方式是等价的,区别在于递归的时候隐式地维护了一个栈,而我们在迭代的时候需要显式地将这个栈模拟出来,其他都相同。
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); while (root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) { while (root != null) { stk.push(root); root = root.left; } root = stk.pop(); res.add(root.val); root = root.right; } return res; } }
Morris中序遍历,是另一种遍历二叉树的方法,它能将非递归的中序遍历空间复杂度降为 O(1)。

class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); TreeNode predecessor = null; while (root != null) { if (root.left != null) { // predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止 predecessor = root.left; while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != root) { predecessor = predecessor.right; } // 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树 if (predecessor.right == null) { predecessor.right = root; root = root.left; } // 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接 else { res.add(root.val); predecessor.right = null; root = root.right; } } // 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子 else { res.add(root.val); root = root.right; } } return res; } }
知识点:
java集合类的List.addAll()方法用于将指定collection中的所有元素添加到列表。
总结:
递归也可以用迭代的方式实现


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号