java线程——详解Callable、Future和FutureTask
回顾:
接上篇博客
java线程——三种创建线程的方式 ,这篇博客主要介绍第三种方式Callable和Future。比较继承Thread类和实现Runnable接口,接口更加灵活,使用更广泛。但这两种方式都没有返回值,要想返回相应的数据,就要使用Callable和Future方式。
基础:
1、Callable
还是从定义开始,Callable接口有返回值,并且可以抛出异常。
- /**(有返回值的任务,可能抛出异常)
- * A task that returns a result and may throw an exception.
- * Implementors define a single method with no arguments called
- * {@code call}.
-
- * @see Executor
- * @since 1.5
- * @author Doug Lea
- * @param <V> the result type of method {@code call}
- */
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Callable<V> {
-
- V call() throws Exception;
- }
2、Future
Future同样也是一个接口,主要方法如下,方法的功能比较容易理解,所以就没有写注释。主要作用:获取任务执行结果,中断任务等。
- package java.util.concurrent;
-
- public interface Future<V> {
-
-
- boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
-
-
- boolean isCancelled();
-
-
- boolean isDone();
-
-
- V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
-
-
- V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
- }
3、FutureTask
- public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
- ......
- }
-
- public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
- ......
- }
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口继承了Runnable和Future。也就是说,它既可以作为Runnable被线程执行,也可以作为Future得到Callable返回值。
使用:
方法一:Callable+Future
- public class CallableAndFuture {
- /**
- * 实现Callable接口
- *
- * @author YANG
- *
- */
- public static class MyCallable implements Callable {
-
- private int flag = 0;
-
- public MyCallable(int flag) {
-
- this.flag = flag;
-
- }
-
- // 重写call方法
- public String call() throws Exception {
- // 情况一:flag=0 返回0
- if (this.flag == 0) {
-
- return "flag = 0";
-
- }
- // 情况二:flag=1 返回looping 陷入死循环
- if (this.flag == 1) {
-
- try {
-
- while (true) {
-
- System.out.println("looping.");
-
- Thread.sleep(2000);
-
- }
- // 情况三:出现异常
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
- System.out.println("Interrupted");
-
- }
-
- return "false";
-
- } else {
-
- throw new Exception("Bad flag value!");
-
- }
-
- }
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- // 定义3个Callable类型的任务,构造方法中制定flag的值
- MyCallable task1 = new MyCallable(0);
-
- MyCallable task2 = new MyCallable(1);
-
- MyCallable task3 = new MyCallable(2);
-
- // 创建一个执行任务的服务
-
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
-
- try {
-
- // 提交并执行任务,任务启动时返回了一个Future对象,
-
- // 如果想得到任务执行的结果或者是异常可对这个Future对象进行操作
-
- Future future1 = null;
-
- future1 = es.submit(task1);
-
- // 获得第一个任务的结果,如果调用get方法,当前线程会等待任务执行完毕后才往下执行
-
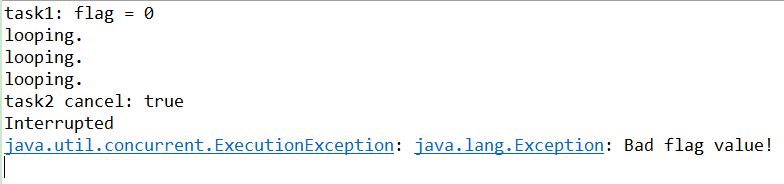
- System.out.println("task1: " + future1.get());
-
- Future future2 = es.submit(task2);
-
- // 等待5秒后,再停止第二个任务。因为第二个任务进行的是无限循环
-
- Thread.sleep(5000);
-
- System.out.println("task2 cancel: " + future2.cancel(true));
-
- // 测试抛出异常
-
- Future future3 = es.submit(task3);
-
- System.out.println("task3: " + future3.get());
-
- } catch (Exception e) {
-
- System.out.println(e.toString());
-
- }
-
- // 停止任务执行服务
-
- es.shutdownNow();
-
- }
- }
方法二:Callable+FutureTask
分析两种方法不同之处就在于Future和FutureTask,其中一个是接口,一个是类。因此,只有main方法调用部分不同,上面的MyCallable类中的内容保持不变。
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- MyCallable task1 = new MyCallable(0);
- FutureTask ft1 = new FutureTask(task1);
- MyCallable task2 = new MyCallable(1);
- FutureTask ft2 = new FutureTask(task2);
- MyCallable task3 = new MyCallable(2);
- FutureTask ft3 = new FutureTask(task3);
-
- try {
- //启动task1
- new Thread(ft1, "子线程").start();
- System.out.println(ft1.get());
-
-
- //等待5秒后,停止task2
- new Thread(ft2, "子线程").start();
- Thread.sleep(5000);
- System.out.println("task2 cancel:" + ft2.cancel(true));
-
- //启动task3
- new Thread(ft3, "子线程").start();
- System.out.println("task3:" + ft3.get());
- } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
-
- System.out.println(e.toString());
- }
-
- }
其执行结果与方法一完全相同,对比这两种方式,第二种比较容易读懂,第一种相对困难些。下篇博客我们介绍Executor、ExecutorService等内容,相信之后理解起来就会很轻松了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号