[数据结构/Java/ListUtils] 深入解读:List(有序列表)
0 序:研究背景
- 2025-07,在某项目中,遭遇了对海量(百万级 / 千万级)有序列表数据的转换处理。
结合此项目的诉求,经过实际验证,ArrayList 比 LinkedList 的性能高出了 20%+ 的读取性能。
1 概述:List(有序列表)
- 在 Java 中,
List是一个接口(java.util.List),属于 Java 集合框架(Collection Framework)的一部分。
主要用于存储有序、可重复的元素集合。
它是Collection接口的子接口,相比Set(无序、不可重复),List更强调元素的【顺序】和【可访问性】。
源码: java.util.List
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package java.util;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
/**
* An ordered collection (also known as a <i>sequence</i>). The user of this
* interface has precise control over where in the list each element is
* inserted. The user can access elements by their integer index (position in
* the list), and search for elements in the list.<p>
*
* Unlike sets, lists typically allow duplicate elements. More formally,
* lists typically allow pairs of elements {@code e1} and {@code e2}
* such that {@code e1.equals(e2)}, and they typically allow multiple
* null elements if they allow null elements at all. It is not inconceivable
* that someone might wish to implement a list that prohibits duplicates, by
* throwing runtime exceptions when the user attempts to insert them, but we
* expect this usage to be rare.<p>
*
* The {@code List} interface places additional stipulations, beyond those
* specified in the {@code Collection} interface, on the contracts of the
* {@code iterator}, {@code add}, {@code remove}, {@code equals}, and
* {@code hashCode} methods. Declarations for other inherited methods are
* also included here for convenience.<p>
*
* The {@code List} interface provides four methods for positional (indexed)
* access to list elements. Lists (like Java arrays) are zero based. Note
* that these operations may execute in time proportional to the index value
* for some implementations (the {@code LinkedList} class, for
* example). Thus, iterating over the elements in a list is typically
* preferable to indexing through it if the caller does not know the
* implementation.<p>
*
* The {@code List} interface provides a special iterator, called a
* {@code ListIterator}, that allows element insertion and replacement, and
* bidirectional access in addition to the normal operations that the
* {@code Iterator} interface provides. A method is provided to obtain a
* list iterator that starts at a specified position in the list.<p>
*
* The {@code List} interface provides two methods to search for a specified
* object. From a performance standpoint, these methods should be used with
* caution. In many implementations they will perform costly linear
* searches.<p>
*
* The {@code List} interface provides two methods to efficiently insert and
* remove multiple elements at an arbitrary point in the list.<p>
*
* Note: While it is permissible for lists to contain themselves as elements,
* extreme caution is advised: the {@code equals} and {@code hashCode}
* methods are no longer well defined on such a list.
*
* <p>Some list implementations have restrictions on the elements that
* they may contain. For example, some implementations prohibit null elements,
* and some have restrictions on the types of their elements. Attempting to
* add an ineligible element throws an unchecked exception, typically
* {@code NullPointerException} or {@code ClassCastException}. Attempting
* to query the presence of an ineligible element may throw an exception,
* or it may simply return false; some implementations will exhibit the former
* behavior and some will exhibit the latter. More generally, attempting an
* operation on an ineligible element whose completion would not result in
* the insertion of an ineligible element into the list may throw an
* exception or it may succeed, at the option of the implementation.
* Such exceptions are marked as "optional" in the specification for this
* interface.
*
* <h2><a id="unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a></h2>
* <p>The {@link List#of(Object...) List.of} and
* {@link List#copyOf List.copyOf} static factory methods
* provide a convenient way to create unmodifiable lists. The {@code List}
* instances created by these methods have the following characteristics:
*
* <ul>
* <li>They are <a href="Collection.html#unmodifiable"><i>unmodifiable</i></a>. Elements cannot
* be added, removed, or replaced. Calling any mutator method on the List
* will always cause {@code UnsupportedOperationException} to be thrown.
* However, if the contained elements are themselves mutable,
* this may cause the List's contents to appear to change.
* <li>They disallow {@code null} elements. Attempts to create them with
* {@code null} elements result in {@code NullPointerException}.
* <li>They are serializable if all elements are serializable.
* <li>The order of elements in the list is the same as the order of the
* provided arguments, or of the elements in the provided array.
* <li>The lists and their {@link #subList(int, int) subList} views implement the
* {@link RandomAccess} interface.
* <li>They are <a href="../lang/doc-files/ValueBased.html">value-based</a>.
* Programmers should treat instances that are {@linkplain #equals(Object) equal}
* as interchangeable and should not use them for synchronization, or
* unpredictable behavior may occur. For example, in a future release,
* synchronization may fail. Callers should make no assumptions about the
* identity of the returned instances. Factories are free to
* create new instances or reuse existing ones.
* <li>They are serialized as specified on the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/serialized-form.html#java.util.CollSer">Serialized Form</a>
* page.
* </ul>
*
* <p>This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements in this list
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see Set
* @see ArrayList
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @see Arrays#asList(Object[])
* @see Collections#nCopies(int, Object)
* @see Collections#EMPTY_LIST
* @see AbstractList
* @see AbstractSequentialList
* @since 1.2
*/
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
Query Operations
int size()boolean isEmpty()boolean contains(Object o)Iterator<E> iterator()Object[] toArray()<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
// Query Operations
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list. If this list contains
* more than {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE} elements, returns
* {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE}.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
int size();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return {@code true} if this list contains no elements
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
boolean contains(Object o);
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
Iterator<E> iterator();
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must
* allocate a new array even if this list is backed by an array).
* The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence
* @see Arrays#asList(Object[])
*/
Object[] toArray();
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of
* the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits
* in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new
* array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and
* the size of this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e.,
* the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array
* immediately following the end of the list is set to {@code null}.
* (This is useful in determining the length of the list <i>only</i> if
* the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.)
*
* <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* <p>Suppose {@code x} is a list known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
* <pre>{@code
* String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);
* }</pre>
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of this list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of this list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
Modification Operations
boolean add(E e)boolean remove(Object o)boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator)default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c)void clear()
// Modification Operations
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list (optional
* operation).
*
* <p>Lists that support this operation may place limitations on what
* elements may be added to this list. In particular, some
* lists will refuse to add null elements, and others will impose
* restrictions on the type of elements that may be added. List
* classes should clearly specify in their documentation any restrictions
* on what elements may be added.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code add} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this list
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present (optional operation). If this list does not contain
* the element, it is unchanged. More formally, removes the element with
* the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list changed
* as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove} operation
* is not supported by this list
*/
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Modification Operations
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection to be checked for containment in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection
* @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements
* in the specified collection are incompatible with this
* list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator (optional operation). The behavior of this
* operation is undefined if the specified collection is modified while
* the operation is in progress. (Note that this will occur if the
* specified collection is this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code addAll} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the specified
* collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements, or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @see #add(Object)
*/
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list at the specified position (optional operation). Shifts the
* element currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent
* elements to the right (increases their indices). The new elements
* will appear in this list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the
* operation is in progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified
* collection is this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code addAll} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the specified
* collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements, or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
/**
* Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation).
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code removeAll} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
/**
* Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation). In other words, removes
* from this list all of its elements that are not contained in the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code retainAll} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
/**
* Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the
* operator to that element. Errors or runtime exceptions thrown by
* the operator are relayed to the caller.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code list}:
* <pre>{@code
* final ListIterator<E> li = list.listIterator();
* while (li.hasNext()) {
* li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
* }
* }</pre>
*
* If the list's list-iterator does not support the {@code set} operation
* then an {@code UnsupportedOperationException} will be thrown when
* replacing the first element.
*
* @param operator the operator to apply to each element
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this list is unmodifiable.
* Implementations may throw this exception if an element
* cannot be replaced or if, in general, modification is not
* supported
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified operator is null or
* if the operator result is a null value and this list does
* not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();
while (li.hasNext()) {
li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
}
}
/**
* Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified
* {@link Comparator}. The sort is <i>stable</i>: this method must not
* reorder equal elements.
*
* <p>All elements in this list must be <i>mutually comparable</i> using the
* specified comparator (that is, {@code c.compare(e1, e2)} must not throw
* a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and {@code e2}
* in the list).
*
* <p>If the specified comparator is {@code null} then all elements in this
* list must implement the {@link Comparable} interface and the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used.
*
* <p>This list must be modifiable, but need not be resizable.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation obtains an array containing all elements in
* this list, sorts the array, and iterates over this list resetting each
* element from the corresponding position in the array. (This avoids the
* n<sup>2</sup> log(n) performance that would result from attempting
* to sort a linked list in place.)
*
* @implNote
* This implementation is a stable, adaptive, iterative mergesort that
* requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons when the input array is
* partially sorted, while offering the performance of a traditional
* mergesort when the input array is randomly ordered. If the input array
* is nearly sorted, the implementation requires approximately n
* comparisons. Temporary storage requirements vary from a small constant
* for nearly sorted input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly
* ordered input arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param c the {@code Comparator} used to compare list elements.
* A {@code null} value indicates that the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used
* @throws ClassCastException if the list contains elements that are not
* <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the list's list-iterator does
* not support the {@code set} operation
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* if the comparator is found to violate the {@link Comparator}
* contract
* @since 1.8
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Object[] a = this.toArray();
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();
for (Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list (optional operation).
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code clear} operation
* is not supported by this list
*/
void clear();
Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o)int hashCode()E get(int index)E set(int index, E element)void add(int index, E element)E remove(int index)
// Comparison and hashing
/**
* Compares the specified object with this list for equality. Returns
* {@code true} if and only if the specified object is also a list, both
* lists have the same size, and all corresponding pairs of elements in
* the two lists are <i>equal</i>. (Two elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} are <i>equal</i> if {@code Objects.equals(e1, e2)}.)
* In other words, two lists are defined to be
* equal if they contain the same elements in the same order. This
* definition ensures that the equals method works properly across
* different implementations of the {@code List} interface.
*
* @param o the object to be compared for equality with this list
* @return {@code true} if the specified object is equal to this list
*/
boolean equals(Object o);
/**
* Returns the hash code value for this list. The hash code of a list
* is defined to be the result of the following calculation:
* <pre>{@code
* int hashCode = 1;
* for (E e : list)
* hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
* }</pre>
* This ensures that {@code list1.equals(list2)} implies that
* {@code list1.hashCode()==list2.hashCode()} for any two lists,
* {@code list1} and {@code list2}, as required by the general
* contract of {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this list
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #equals(Object)
*/
int hashCode();
// Positional Access Operations
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
E get(int index);
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element (optional operation).
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code set} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
E set(int index, E element);
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list
* (optional operation). Shifts the element currently at that position
* (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their
* indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code add} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
void add(int index, E element);
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list (optional
* operation). Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one
* from their indices). Returns the element that was removed from the
* list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
E remove(int index);
Search Operations
int indexOf(Object o)int lastIndexOf(Object o)
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
int indexOf(Object o);
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
List Iterators
ListIterator<E> listIterator()ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
// List Iterators
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence).
*
* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence)
*/
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* The specified index indicates the first element that would be
* returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}.
* An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would
* return the element with the specified index minus one.
*
* @param index index of the first element to be returned from the
* list iterator (by a call to {@link ListIterator#next next})
* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
View
- 方法列表
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
default Spliterator<E> spliterator()
static <E> List<E> of()
static <E> List<E> of(E e1)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8, E e9)
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8, E e9, E e10)
static <E> List<E> of(E... elements)
static <E> List<E> copyOf(Collection<? extends E> coll)
- 源码
// View
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations supported
* by this list.<p>
*
* This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>{@code
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* }</pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@code indexOf} and
* {@code lastIndexOf}, and all of the algorithms in the
* {@code Collections} class can be applied to a subList.<p>
*
* The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @param fromIndex low endpoint (inclusive) of the subList
* @param toIndex high endpoint (exclusive) of the subList
* @return a view of the specified range within this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException for an illegal endpoint index value
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size ||
* fromIndex > toIndex})
*/
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
/**
* Creates a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Implementations should document the
* reporting of additional characteristic values.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation creates a
* <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* spliterator as follows:
* <ul>
* <li>If the list is an instance of {@link RandomAccess} then the default
* implementation creates a spliterator that traverses elements by
* invoking the method {@link List#get}. If such invocation results or
* would result in an {@code IndexOutOfBoundsException} then the
* spliterator will <em>fail-fast</em> and throw a
* {@code ConcurrentModificationException}.
* If the list is also an instance of {@link AbstractList} then the
* spliterator will use the list's {@link AbstractList#modCount modCount}
* field to provide additional <em>fail-fast</em> behavior.
* <li>Otherwise, the default implementation creates a spliterator from the
* list's {@code Iterator}. The spliterator inherits the
* <em>fail-fast</em> of the list's iterator.
* </ul>
*
* @implNote
* The created {@code Spliterator} additionally reports
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
if (this instanceof RandomAccess) {
return new AbstractList.RandomAccessSpliterator<>(this);
} else {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing zero elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @return an empty {@code List}
*
* @since 9
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <E> List<E> of() {
return (List<E>) ImmutableCollections.EMPTY_LIST;
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing one element.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the single element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified element
* @throws NullPointerException if the element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1) {
return new ImmutableCollections.List12<>(e1);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing two elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2) {
return new ImmutableCollections.List12<>(e1, e2);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing three elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing four elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing five elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing six elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @param e6 the sixth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5,
e6);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing seven elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @param e6 the sixth element
* @param e7 the seventh element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5,
e6, e7);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing eight elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @param e6 the sixth element
* @param e7 the seventh element
* @param e8 the eighth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5,
e6, e7, e8);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing nine elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @param e6 the sixth element
* @param e7 the seventh element
* @param e8 the eighth element
* @param e9 the ninth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8, E e9) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5,
e6, e7, e8, e9);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing ten elements.
*
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param e1 the first element
* @param e2 the second element
* @param e3 the third element
* @param e4 the fourth element
* @param e5 the fifth element
* @param e6 the sixth element
* @param e7 the seventh element
* @param e8 the eighth element
* @param e9 the ninth element
* @param e10 the tenth element
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
static <E> List<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5, E e6, E e7, E e8, E e9, E e10) {
return ImmutableCollections.listFromTrustedArray(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5,
e6, e7, e8, e9, e10);
}
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable list containing an arbitrary number of elements.
* See <a href="#unmodifiable">Unmodifiable Lists</a> for details.
*
* @apiNote
* This method also accepts a single array as an argument. The element type of
* the resulting list will be the component type of the array, and the size of
* the list will be equal to the length of the array. To create a list with
* a single element that is an array, do the following:
*
* <pre>{@code
* String[] array = ... ;
* List<String[]> list = List.<String[]>of(array);
* }</pre>
*
* This will cause the {@link List#of(Object) List.of(E)} method
* to be invoked instead.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param elements the elements to be contained in the list
* @return a {@code List} containing the specified elements
* @throws NullPointerException if an element is {@code null} or if the array is {@code null}
*
* @since 9
*/
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
static <E> List<E> of(E... elements) {
switch (elements.length) { // implicit null check of elements
case 0:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
var list = (List<E>) ImmutableCollections.EMPTY_LIST;
return list;
case 1:
return new ImmutableCollections.List12<>(elements[0]);
case 2:
return new ImmutableCollections.List12<>(elements[0], elements[1]);
default:
return ImmutableCollections.listFromArray(elements);
}
}
/**
* Returns an <a href="#unmodifiable">unmodifiable List</a> containing the elements of
* the given Collection, in its iteration order. The given Collection must not be null,
* and it must not contain any null elements. If the given Collection is subsequently
* modified, the returned List will not reflect such modifications.
*
* @implNote
* If the given Collection is an <a href="#unmodifiable">unmodifiable List</a>,
* calling copyOf will generally not create a copy.
*
* @param <E> the {@code List}'s element type
* @param coll a {@code Collection} from which elements are drawn, must be non-null
* @return a {@code List} containing the elements of the given {@code Collection}
* @throws NullPointerException if coll is null, or if it contains any nulls
* @since 10
*/
static <E> List<E> copyOf(Collection<? extends E> coll) {
return ImmutableCollections.listCopy(coll);
}
}
核心特点
- 有序性:元素按插入顺序保存,每个元素都有对应的索引(从 0 开始),可通过索引访问元素。
- 可重复性:允许存储重复元素(即
equals()方法返回true的元素)。 - 动态大小:与数组不同,
List的大小可以动态调整,无需预先指定容量。
常用实现类
List 是接口,无法直接实例化,需使用其实现类,常见的有:
ArrayList:基于动态数组实现,查询效率高(通过索引直接访问),增删元素(尤其是中间位置)效率较低,线程不安全。LinkedList:基于双向链表实现,增删元素(尤其是首尾位置)效率高,查询效率较低(需遍历链表),线程不安全,还实现了Queue接口,可作为队列使用。Vector:古老的动态数组实现,线程安全(方法加了synchronized),但效率较低,现已很少使用。Stack:继承自Vector,模拟栈结构(后进先出),但推荐使用Deque接口的实现类(如ArrayDeque)替代。
- 小结
List适合需要按顺序存储、频繁访问元素(如通过索引)或允许重复元素的场景,根据操作需求选择ArrayList(查询多)或LinkedList(增删多)作为实现类。
常用方法
List 继承了 Collection 的方法,并新增了基于索引的操作:
-
添加元素:
add(E e):在末尾添加元素。add(int index, E e):在指定索引插入元素。addAll(Collection<? extends E> c):添加另一个集合的所有元素。
-
获取元素:
get(int index):返回指定索引的元素。
-
修改元素:
set(int index, E e):替换指定索引的元素,返回被替换的旧元素。
-
删除元素:
remove(int index):删除指定索引的元素,返回被删除的元素。remove(Object o):删除第一个匹配的元素(基于equals())。
-
查询索引:
indexOf(Object o):返回元素首次出现的索引,不存在则返回-1。lastIndexOf(Object o):返回元素最后出现的索引。
-
子列表:
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex(包含)到toIndex(不包含)的子列表(视图,修改会影响原列表)。
-
其他:
size():返回元素数量。isEmpty():判断是否为空。contains(Object o):判断是否包含指定元素。clear():清空所有元素。
示例代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Java");
list.add("Python");
list.add("Java"); // 允许重复
System.out.println(list.get(0)); // 输出:Java
System.out.println(list.indexOf("Java")); // 输出:0
list.set(1, "C++"); // 替换索引1的元素
list.remove(2); // 删除索引2的元素
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s); // 输出:Java、C++
}
}
}
M FAQ for List(有序列表)
Q:说说你自己对 ArrayList 的理解?
很多面试官喜欢这样子开头,考察面试同学对 ArrayList 有没有总结经验,介于 ArrayList 内容很多,建议先回答总体架构,再从某个细节出发作为突破口,比如这样:
ArrayList 底层数据结构是个数组,其 API 都做了一层对数组底层访问的封装,比如说 add 方法的过程是……(这里可以引用我们在 ArrayList 源码解析中 add 的过程)。
一般面试官看你回答得井井有条,并且没啥漏洞的话,基本就不会深究了,这样面试的主动权就掌握在自己手里面了,如果你回答得支支吾吾,那么面试官可能就会开启自己面试的套路了。
Q:说说你自己对 LinkedList 的理解也是同样套路。
Q: 扩容类问题
Q:ArrayList 无参数构造器构造,现在 add 一个值进去,此时数组的大小是多少,下一次扩容前最大可用大小是多少?
答:此处数组的大小是 1,下一次扩容前最大可用大小是 10,因为 ArrayList 第一次扩容时,是有默认值的,默认值是 10,在第一次 add 一个值进去时,数组的可用大小被扩容到 10 了。
Q:如果我连续往 list 里面新增值,增加到第 11 个的时候,数组的大小是多少?
答:这里的考查点就是扩容的公式,当增加到 11 的时候,此时我们希望数组的大小为 11,但实际上数组的最大容量只有 10,不够了就需要扩容,扩容的公式是:oldCapacity + (oldCapacity>> 1),oldCapacity 表示数组现有大小,目前场景计算公式是:10 + 10 /2 = 15,然后我们发现 15 已经够用了,所以数组的大小会被扩容到 15。
Q:数组初始化,被加入一个值后,如果我使用 addAll 方法,一下子加入 15 个值,那么最终数组的大小是多少?
答:第一题中我们已经计算出来数组在加入一个值后,实际大小是 1,最大可用大小是 10 ,现在需要一下子加入 15 个值,那我们期望数组的大小值就是 16,此时数组最大可用大小只有 10,明显不够,需要扩容,扩容后的大小是:10 + 10 /2 = 15,这时候发现扩容后的大小仍然不到我们期望的值 16,这时候源码中有一种策略如下:
// newCapacity 本次扩容的大小,minCapacity 我们期望的数组最小大小
// 如果扩容后的值 < 我们的期望值,我们的期望值就等于本次扩容的大小
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
所以最终数组扩容后的大小为 16。
Q:现在我有一个很大的数组需要拷贝,原数组大小是 5k,请问如何快速拷贝?
答:因为原数组比较大,如果新建新数组的时候,不指定数组大小的话,就会频繁扩容,频繁扩容就会有大量拷贝的工作,造成拷贝的性能低下,所以回答说新建数组时,指定新数组的大小为 5k 即可。
Q:为什么说扩容会消耗性能?
答:扩容底层使用的是 System.arraycopy 方法,会把原数组的数据全部拷贝到新数组上,所以性能消耗比较严重。
Q:源码扩容过程有什么值得借鉴的地方?
答:有两点:
是扩容的思想值得学习,通过自动扩容的方式,让使用者不用关心底层数据结构的变化,封装得很好,1.5 倍的扩容速度,可以让扩容速度在前期缓慢上升,在后期增速较快,大部分工作中要求数组的值并不是很大,所以前期增长缓慢有利于节省资源,在后期增速较快时,也可快速扩容。
扩容过程中,有数组大小溢出的意识,比如要求扩容后的数组大小,不能小于 0,不能大于 Integer 的最大值。
这两点在我们平时设计和写代码时都可以借鉴。
Q:删除类问题
Q:有一个 ArrayList,数据是 2、3、3、3、4,中间有三个 3,现在我通过 for (int i=0;i<list.size ();i++) 的方式,想把值是 3 的元素删除,请问可以删除干净么?最终删除的结果是什么,为什么?删除代码如下:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>() {{
add("2");
add("3");
add("3");
add("3");
add("4");
}};
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (list.get(i).equals("3")) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
答:不能删除干净,最终删除的结果是 2、3、4,有一个 3 删除不掉,原因我们看下图:
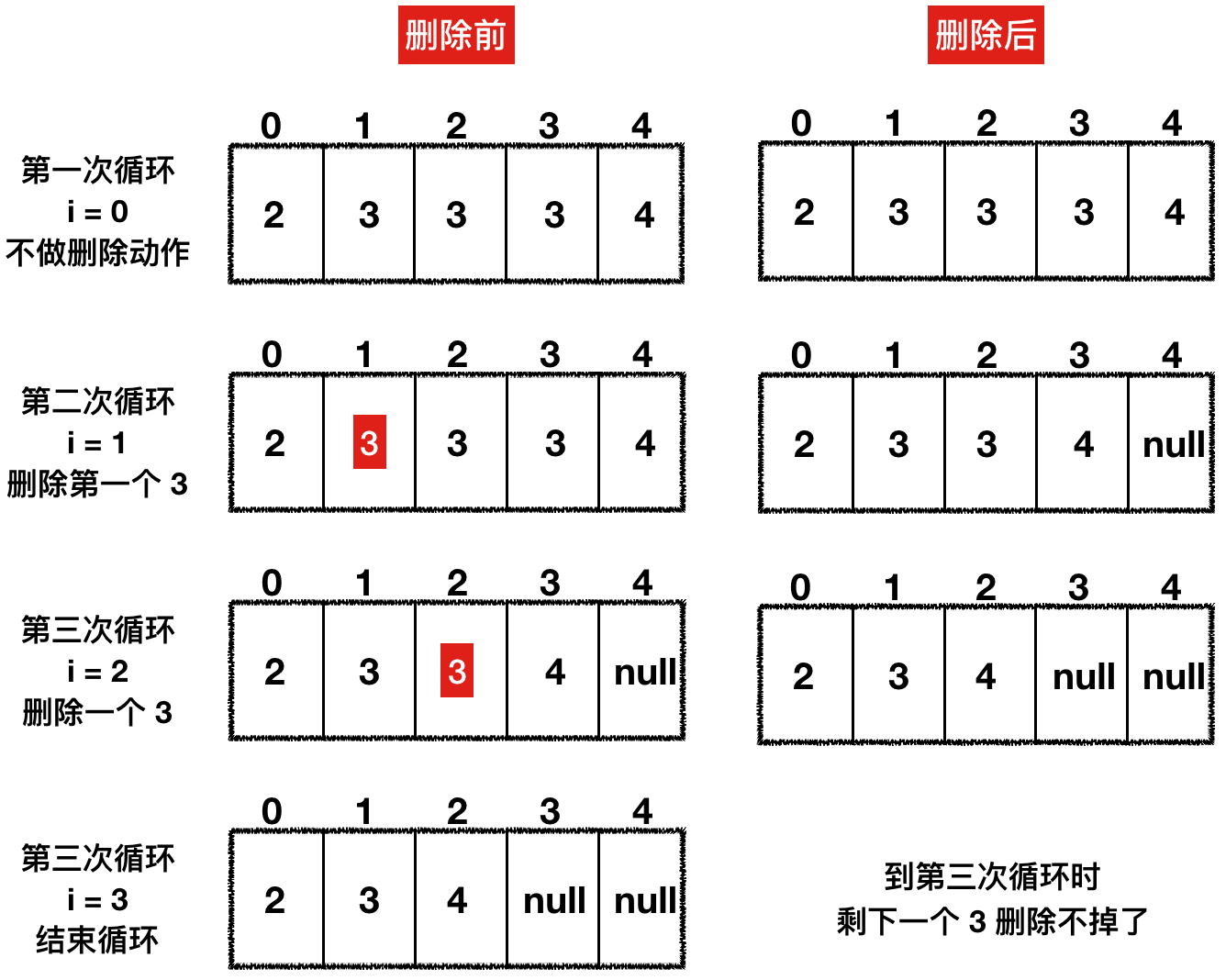
图片描述从图中我们可以看到,每次删除一个元素后,该元素后面的元素就会往前移动,而此时循环的 i 在不断地增长,最终会使每次删除 3 的后一个 3 被遗漏,导致删除不掉。
Q:还是上面的 ArrayList 数组,我们通过增强 for 循环进行删除,可以么?
答:不可以,会报错。因为增强 for 循环过程其实调用的就是迭代器的 next () 方法,当你调用 list#remove () 方法进行删除时,modCount 的值会 +1,而这时候迭代器中的 expectedModCount 的值却没有变,导致在迭代器下次执行 next () 方法时,expectedModCount != modCount 就会报 ConcurrentModificationException 的错误。
Q:还是上面的数组,如果删除时使用 Iterator.remove () 方法可以删除么,为什么?
答:可以的,因为 Iterator.remove () 方法在执行的过程中,会把最新的 modCount 赋值给 expectedModCount,这样在下次循环过程中,modCount 和 expectedModCount 两者就会相等。
Q:以上三个问题对于 LinkedList 也是同样的结果么?
答:是的,虽然 LinkedList 底层结构是双向链表,但对于上述三个问题,结果和 ArrayList 是一致的。
Q:对比类问题
Q:ArrayList 和 LinkedList 有何不同?
答:可以先从底层数据结构开始说起,然后以某一个方法为突破口深入,比如:最大的不同是两者底层的数据结构不同,ArrayList 底层是数组,LinkedList 底层是双向链表,两者的数据结构不同也导致了操作的 API 实现有所差异,拿新增实现来说,ArrayList 会先计算并决定是否扩容,然后把新增的数据直接赋值到数组上,而 LinkedList 仅仅只需要改变插入节点和其前后节点的指向位置关系即可。
Q:ArrayList 和 LinkedList 应用场景有何不同
答:ArrayList 更适合于快速的查找匹配,不适合频繁新增删除,像工作中经常会对元素进行匹配查询的场景比较合适,LinkedList 更适合于经常新增和删除,对查询反而很少的场景。
Q:ArrayList 和 LinkedList 两者有没有最大容量
答:ArrayList 有最大容量的,为 Integer 的最大值,大于这个值 JVM 是不会为数组分配内存空间的,LinkedList 底层是双向链表,理论上可以无限大。但源码中,LinkedList 实际大小用的是 int 类型,这也说明了 LinkedList 不能超过 Integer 的最大值,不然会溢出。
Q:ArrayList 和 LinkedList 是如何对 null 值进行处理的
答:ArrayList 允许 null 值新增,也允许 null 值删除。删除 null 值时,是从头开始,找到第一值是 null 的元素删除;LinkedList 新增删除时对 null 值没有特殊校验,是允许新增和删除的。
Q:ArrayList 和 LinedList 是线程安全的么,为什么?
答:当两者作为非共享变量时,比如说仅仅是在方法里面的局部变量时,是没有线程安全问题的,只有当两者是共享变量时,才会有线程安全问题。主要的问题点在于多线程环境下,所有线程任何时刻都可对数组和链表进行操作,这会导致值被覆盖,甚至混乱的情况。
如果有线程安全问题,在迭代的过程中,会频繁报 ConcurrentModificationException 的错误,意思是在我当前循环的过程中,数组或链表的结构被其它线程修改了。
Q:如何解决线程安全问题?
Java 源码中推荐使用 Collections#synchronizedList 进行解决,Collections#synchronizedList 的返回值是 List 的每个方法都加了 synchronized 锁,保证了在同一时刻,数组和链表只会被一个线程所修改,或者采用 CopyOnWriteArrayList 并发 List 来解决,这个类我们后面会说。
Q:其它类型题目
Q:你能描述下双向链表么?
答:如果和面试官面对面沟通的话,你可以去画一下,可以把 《LinkedList 源码解析》中的 LinkedList 的结构画出来,如果是电话面试,可以这么描述:双向链表中双向的意思是说前后节点之间互相有引用,链表的节点我们称为 Node。Node 有三个属性组成:其前一个节点,本身节点的值,其下一个节点,假设 A、B 节点相邻,A 节点的下一个节点就是 B,B 节点的上一个节点就是 A,两者互相引用,在链表的头部节点,我们称为头节点。头节点的前一个节点是 null,尾部称为尾节点,尾节点的后一个节点是 null,如果链表数据为空的话,头尾节点是同一个节点,本身是 null,指向前后节点的值也是 null。
Q:描述下双向链表的新增和删除?
答:如果是面对面沟通,最好可以直接画图,如果是电话面试,可以这么描述:
新增:我们可以选择从链表头新增,也可以选择从链表尾新增,如果是从链表尾新增的话,直接把当前节点追加到尾节点之后,本身节点自动变为尾节点。
删除:把删除节点的后一个节点的 prev 指向其前一个节点,把删除节点的前一个节点的 next 指向其后一个节点,最后把删除的节点置为 null 即可。
F 案例实践
CASE 深入比对:ArrayList vs. LinkedList
- ArrayList 基于数组实现,适合随机访问;LinkedList 基于双向链表实现,适合频繁的插入和删除操作。
存储结构
ArrayList
- 基于动态数组实现,内存连续,支持快速随机访问。
LinkedList
- 基于双向链表实现,每个节点包含前后指针,插入和删除效率较高,但随机访问性能较差。
插入与删除效率
ArrayList
- 在插入或删除时需要移动元素,效率较低,尤其是头部和中间位置操作。
LinkedList
- 通过调整指针即可完成插入和删除,效率较高,尤其在头部操作时表现优异。
随机访问效率
ArrayList
- 由于底层是数组,支持 O(1) 的随机访问。
LinkedList
- 需要从头或尾遍历链表,随机访问效率为 O(n),性能远低于 ArrayList。
迭代性能
ArrayList的连续存储特性使其在迭代时性能更优,得益于 CPU 缓存优化。LinkedList由于需要频繁跳转指针,迭代性能稍逊。
内存占用
ArrayList仅存储元素本身,内存占用较低。LinkedList每个节点需额外存储两个指针(前驱和后继),内存占用更高。
有序性
- ArrayList 和 LinkedList 都是 有序集合,它们的主要区别在于底层实现和性能特点,而不是存储顺序是否有序。
/**
* 验证 array list 的有序性: 有序
*/
@Test
public void arrayListTest(){
String [] numbers = {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10"};
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList();
Arrays.stream(numbers).forEach( element -> {
list.add(element);
});
list.stream().forEach( element -> {
log.info( "{}", element );
});//"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10"
}
- 【延申】 Map 集合
- HashMap: 无序
- TreeMap: 有序
- LinkedHashMap: 有序
最佳实践
- 当需要频繁随机访问或存储大量数据时,推荐使用 ArrayList。
ArrayList 在随机访问和迭代性能上表现优异,适合读多写少的场景
- 若需要频繁在头部插入或删除元素,LinkedList 更为适合。
LinkedList 在插入和删除操作上更高效,适合写多读少或需要频繁头部操作的场景。
根据具体需求选择合适的数据结构是关键。
CASE List数据结构的增强设计:循环队列(FixedArrayList)
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
/**
* 循环队列实现
* 主要功能:
* 1.固定队列长度
* 2.队列先进先出,当写入时队列已满则移除第一次写入的数据
* 3.可以通过下标获取或更新指定队列的数据
* 4.当队列为空队列时重新开始计算
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class FixedArrayList<T> {
private int currentWritePos = 0;
private int currentReadPos = 0;
private int length = 5;
private ArrayList<T> arr;
/**
* 初始长度队列
*
* @param length
*/
public FixedArrayList(int length) {
this.length = length;
this.arr = new ArrayList<>(length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
this.arr.add(null);
}
}
/**
* 默认长度队列
*/
public FixedArrayList() {
this.arr = new ArrayList<>(this.length);
for (int i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
this.arr.add(null);
}
}
/**
* 获取位置
*
* @param pos
* @return
*/
private int getRealPosition(int pos) {
return pos % this.length;
}
/**
* 入队列
*
* @param obj
*/
public void push(T obj) {
if (isFull()) {
this.currentReadPos = this.currentWritePos + 1 - this.length;
}
this.arr.set(this.getRealPosition(this.currentWritePos), obj);
this.currentWritePos++;
}
/**
* 出队列
*/
public boolean pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
this.currentWritePos = 0;
this.currentReadPos = 0;
return false;
} else {
this.arr.set(this.getRealPosition(this.currentReadPos), null);
this.currentReadPos++;
return true;
}
}
/**
* 获取队列指定位置元素
*
* @param i
* @return
*/
public T get(int i) {
return this.arr.get(this.getRealPosition(this.currentReadPos + i));
}
/**
* 更新队列指定位置元素
*
* @param i
* @param obj
*/
public void set(int i, T obj) {
this.arr.set(this.getRealPosition(this.currentReadPos + i), obj);
}
/**
* 检测队列是否已满
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return this.currentWritePos == this.currentReadPos + this.length;
}
/**
* 检测队列是否全部不为null
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isAllNotNull() {
for (T t : this.arr) {
if (t == null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 检测队列是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.currentReadPos == this.currentWritePos;
}
/**
* 清空队列
*/
public void clean() {
this.currentWritePos = 0;
this.currentReadPos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
this.arr.set(i, null);
}
}
/**
* 获取当队列满时的队列最后一个元素
*/
public T getLastElement() {
return this.arr.get(this.arr.size() - 1);
}
/**
* 获取队列长度
*/
public int getLength() {
return this.arr.size();
}
/**
* 获取队列元素个数
*/
public int getElementLength() {
int i = 0;
for (T t : this.arr) {
if (t != null) {
i++;
}
}
return i;
}
}
CASE 基于 List<Double/Float> 对象,计算 Max/MaxIndex/Min/MinIndex/Avg 统计指标
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author johnnyzen
* @version v1.0
* @create-time 2025/10/16 19:21
* @update-time 2025/10/18 11:49
* @description ...
* @refrence-doc
* @gpt-promt
* ListUtils Java 工具类的作用:
* 1. 基于 List<Float> list 对象,分别计算出最小值、最小值的下标、最大值、最大值的下标、平均值。
* 2. 若列表为 null 或空,则 min/max/average 返回 Float.NaN,下标返回 -1。
* 请输出 ListUtils.java 的源代码文件
*/
public final class ListUtils {
/**
* 统计 List<Float>
* @note
* 1. 基于 List<Float> list 对象,分别计算出最小值、最小值的下标、最大值、最大值的下标、平均值。
* 2. 若列表为 null 或空,则 min/max/average 返回 Float.NaN,下标返回 -1。
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static Stat stat(List<Float> list) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return new Stat(null, -1, null, -1, null);
}
float min = Float.MAX_VALUE;
int minIndex = -1;
float max = -Float.MAX_VALUE;
int maxIndex = -1;
double sum = 0; // 用 double 累加,减小误差
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Float v = list.get(i);
if (v == null) {
continue; // 跳过 null 元素
}
float val = v;
if (val < min) {
min = val;
minIndex = i;
}
if (val > max) {
max = val;
maxIndex = i;
}
sum += val;
}
// 全是 null 时,认为无有效数据
if (minIndex == -1) {
return new Stat(null, -1, null, -1, null);
}
float average = (float) (sum / list.size());
return new Stat(min, minIndex, max, maxIndex, average);
}
public static float min(List<Float> list) {
return stat(list).min;
}
public static int minIndex(List<Float> list) {
return stat(list).minIndex;
}
public static float max(List<Float> list) {
return stat(list).max;
}
public static int maxIndex(List<Float> list) {
return stat(list).maxIndex;
}
public static float average(List<Float> list) {
return stat(list).average;
}
/**
* 统计结果封装
*/
public static final class Stat {
public final Float min;
public final int minIndex;
public final Float max;
public final int maxIndex;
public final Float average;
private Stat(Float min, int minIndex, Float max, int maxIndex, Float average) {
this.min = min;
this.minIndex = minIndex;
this.max = max;
this.maxIndex = maxIndex;
this.average = average;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stat{" +
"min=" + min +
", minIndex=" + minIndex +
", max=" + max +
", maxIndex=" + maxIndex +
", average=" + average +
'}';
}
}
}
CASE 基于 List<Map<String, Object>> : list对象,根据 Map 的指定 key 字段做排序
假定指定key的名称为 collectTimestamp (Long)
- 方案1: 使用 Stream API 排序(不修改原集合)
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
// 原集合:List<Map<String, Object>> list
List<Map<String, Object>> sortedList = list.stream()
// 按 collectTimestamp 降序排序
.sorted((map1, map2) -> {
// 从 Map 中获取 collectTimestamp 的值(强制转换为 Long)
Long time1 = (Long) map1.get("collectTimestamp");
Long time2 = (Long) map2.get("collectTimestamp");
// 降序排序:time2 - time1(若为升序则是 time1 - time2)
return Long.compare(time2, time1);
})
// 收集为新的 List
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 方案2: 使用 Collections.sort () 排序(直接修改原集合)
如果希望直接修改原集合(而非生成新集合),可以使用
Collections.sort():
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
// 原集合:List<Map<String, Object>> list
Collections.sort(list, (map1, map2) -> {
Long time1 = (Long) map1.get("collectTimestamp");
Long time2 = (Long) map2.get("collectTimestamp");
return Long.compare(time2, time1); // 降序
});
Y 推荐文献
X 参考文献

本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen
关于博文:评论和私信会在第一时间回复,或直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
日常交流:大数据与软件开发-QQ交流群: 774386015 【入群二维码】参见左下角。您的支持、鼓励是博主技术写作的重要动力!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号