[Clickhouse] Clickhouse 函数
0 引言
如无特殊说明,ck版本为 21.3.4.25
1 数据类型的支持情况
查看当前受支持的数据类型
select * from system.data_type_families
-- select name,case_insensitive,alias_to from system.data_type_families;
output
name |case_insensitive|alias_to |
-------------------------------+----------------+-----------+
Polygon | 0| |
Ring | 0| |
MultiPolygon | 0| |
IPv6 | 0| |
IntervalSecond | 0| |
IPv4 | 0| |
UInt32 | 0| |
IntervalYear | 0| |
IntervalQuarter | 0| |
IntervalMonth | 0| |
Int64 | 0| |
IntervalDay | 0| |
IntervalHour | 0| |
UInt256 | 0| |
Int16 | 0| |
LowCardinality | 0| |
AggregateFunction | 0| |
Nothing | 0| |
Decimal256 | 1| |
Tuple | 0| |
Array | 0| |
Enum16 | 0| |
IntervalMinute | 0| |
FixedString | 0| |
String | 0| |
DateTime | 1| |
Map | 0| |
UUID | 0| |
Decimal64 | 1| |
Nullable | 0| |
Enum | 0| |
Int32 | 0| |
UInt8 | 0| |
Date | 1| |
Decimal32 | 1| |
Point | 0| |
Float64 | 0| |
DateTime64 | 1| |
Int128 | 0| |
Decimal128 | 1| |
Int8 | 0| |
SimpleAggregateFunction | 0| |
Nested | 0| |
Decimal | 1| |
Int256 | 0| |
IntervalWeek | 0| |
UInt64 | 0| |
Enum8 | 0| |
DateTime32 | 1| |
UInt16 | 0| |
Float32 | 0| |
INET6 | 1|IPv6 |
INET4 | 1|IPv4 |
BINARY | 1|FixedString|
NATIONAL CHAR VARYING | 1|String |
BINARY VARYING | 1|String |
NCHAR LARGE OBJECT | 1|String |
NATIONAL CHARACTER VARYING | 1|String |
NATIONAL CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT| 1|String |
NATIONAL CHARACTER | 1|String |
NATIONAL CHAR | 1|String |
CHARACTER VARYING | 1|String |
LONGBLOB | 1|String |
MEDIUMTEXT | 1|String |
TEXT | 1|String |
TINYBLOB | 1|String |
VARCHAR2 | 1|String |
CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT | 1|String |
DOUBLE PRECISION | 1|Float64 |
LONGTEXT | 1|String |
NVARCHAR | 1|String |
INT1 UNSIGNED | 1|UInt8 |
VARCHAR | 1|String |
CHAR VARYING | 1|String |
MEDIUMBLOB | 1|String |
NCHAR | 1|String |
CHAR | 1|String |
SMALLINT UNSIGNED | 1|UInt16 |
TIMESTAMP | 1|DateTime |
FIXED | 1|Decimal |
TINYTEXT | 1|String |
NUMERIC | 1|Decimal |
DEC | 1|Decimal |
TINYINT UNSIGNED | 1|UInt8 |
INTEGER UNSIGNED | 1|UInt32 |
INT UNSIGNED | 1|UInt32 |
CLOB | 1|String |
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | 1|UInt32 |
BOOL | 1|Int8 |
SMALLINT | 1|Int16 |
INTEGER SIGNED | 1|Int32 |
NCHAR VARYING | 1|String |
INT SIGNED | 1|Int32 |
TINYINT SIGNED | 1|Int8 |
BIGINT SIGNED | 1|Int64 |
BINARY LARGE OBJECT | 1|String |
SMALLINT SIGNED | 1|Int16 |
MEDIUMINT | 1|Int32 |
INTEGER | 1|Int32 |
INT1 SIGNED | 1|Int8 |
BIGINT UNSIGNED | 1|UInt64 |
BYTEA | 1|String |
INT | 1|Int32 |
SINGLE | 1|Float32 |
FLOAT | 1|Float32 |
MEDIUMINT SIGNED | 1|Int32 |
BOOLEAN | 1|Int8 |
DOUBLE | 1|Float64 |
INT1 | 1|Int8 |
CHAR LARGE OBJECT | 1|String |
TINYINT | 1|Int8 |
BIGINT | 1|Int64 |
CHARACTER | 1|String |
BYTE | 1|Int8 |
BLOB | 1|String |
REAL | 1|Float32 |
查看指定字段的数据类型
select toTypeName(now())
ClickHouse可以在数据表中存储多种数据类型。
Clickhouse所有的数据类型存储在system.data_type_families表中,可以检查数据类型名称是否区分大小写
2 字符串文本类型
String
String类型
https://clickhouse.com/docs/zh/sql-reference/functions/string-functions
字符串由String定义,长度不限————在使用String的时候无须声明大小。
它完全代替了传统意义上数据库的 Varchar、Text、Clob 和 Blob 等字符类型。
String类型不限定字符集,因为它根本就没有这个概念,所以可以将任意编码的字符串存入其中。
字符串拼接
> select concat('a', '#', 'C', 'D')
a#CD
字符串分割
substring函数
substring(要截取的字符串, 起始位置(从1开始计数), 要截取的长度)
如果起始位置或长度超出了字符串的实际范围,函数将返回从起始位置到字符串末尾的部分。
SELECT substring('ClickHouse', 1, 5) AS result; -- Click
SELECT
-- 1234567890123
'Hello, World!' as content -- 'Hello, World'
, substring(content, 0, 5) AS res -- ''
, substring(content, 1, 5) AS res1 -- 'Hello'
, substring(content, 8, 5) AS res2 -- 'World'
splitByChar函数
SELECT
splitByChar('-', totalMileagePeriod)
, arrayElement(splitByChar('-', totalMileagePeriod), 1)
FROM (
select '20-30' as totalMileagePeriod, 0 as vehicleCount
union all
select '30-40' as totalMileagePeriod, 0 as vehicleCount
union all
select '40-50' as totalMileagePeriod, 0 as vehicleCount
union all
select '50-' as totalMileagePeriod, 0 as vehicleCount
)
out
a | b
['30','40'] 30
['50',''] 50
['20','30'] 20
['40','50'] 40
字符串替换
replaceOne/replaceAll函数
select
replaceOne('≥50≥', '≥', '') as a
, replaceAll('≥50≥', '≥', '') as b
out
a , b
50≥ , 50
字符串查找
position函数
https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/sql-reference/functions/string-search-functions
position 函数起到了与 like 几乎等效的字符串模式匹配作用
select
position('hello world!', 'hello') as pos1 -- 1
, position('hello world!', 'world') as pos2 -- 7
, position('hello world!', 'word') as pos3 -- 0
文本格式化 : format
https://clickhouse.com/docs/zh/sql-reference/functions/string-functions
format(pattern, s0, s1, ...)
使用常量字符串pattern格式化其他参数。
pattern字符串中包含由大括号{}包围的«替换字段»。
未被包含在大括号中的任何内容都被视为文本内容,它将原样保留在返回值中。
如果你需要在文本内容中包含一个大括号字符,它可以通过加倍来转义:{{ '{{' }}和{{ '{{' }} '}}' }}。
字段名称可以是数字(从零开始)或空(然后将它们视为连续数字)
> SELECT format('{1} {0} {1}', 'World', 'Hello')
┌─format('{1} {0} {1}', 'World', 'Hello')─┐
│ Hello World Hello │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
> SELECT format('{} {}', 'Hello', 'World')
┌─format('{} {}', 'Hello', 'World')─┐
│ Hello World │
└───────────────────────────────────┘
文本格式化————文本左/右补齐、左/右填充
leftPad函数
使用空格或指定字符串(如果需要,多次)从左侧填充字符串,直到结果字符串达到指定的 length。
- 版本支持情况
21.3.4.25 不支持
自 21.10 开始支持
- 语法
leftPad(string, length[, pad_string])
- 别名:LPAD
- 参数
- string — 应填充的输入字符串。 字符串。
- length — 结果字符串的长度。 UInt 或 Int。如果该值小于输入字符串长度,则输入字符串会被缩短为 length 个字符。
- pad_string — 用于填充输入字符串的字符串。 String。可选。如果未指定,则输入字符串将用空格填充。
- 返回值
给定长度的左填充字符串。
类型: String。
- 示例
SELECT leftPad('abc', 7, '*'), leftPad('def', 7);
结果
┌─leftPad('abc', 7, '*')─┬─leftPad('def', 7)─┐
│ ****abc │ def │
rightPad函数
使用空格或指定字符串(如果需要,多次)从右侧填充字符串,直到结果字符串达到指定的 length。
- 版本支持情况
21.3.4.25 不支持
自 21.10 开始支持
- 语法
rightPad(string, length[, pad_string])
- 别名:RPAD
- 参数
- string — 应填充的输入字符串。 字符串。
- length — 结果字符串的长度。 UInt 或 Int。如果该值小于输入字符串长度,则输入字符串会被缩短为 length 个字符。
- pad_string — 用于填充输入字符串的字符串。 String。可选。如果未指定,则输入字符串将用空格填充。
- 返回值
给定长度的左填充字符串。
类型: String。
- 示例
SELECT rightPad('abc', 7, '*'), rightPad('abc', 7);
结果
┌─rightPad('abc', 7, '*')─┬─rightPad('abc', 7)─┐
│ abc**** │ abc │
└─────────────────────────┴────────────────────┘
hash 函数系列
SELECT
-- 计算字符串的MD5值。( 如果您不需要一定使用MD5,请使用‘sipHash64’函数。)
halfMD5('HELLO WORLD!'), -- 13086268085575473511
halfMD5(12); -- 6397527522938966646
SELECT
MD5('drew-zero,78967'); -- Y>�g��a����ʉ�i
SELECT
-- 为任何类型的整数计算32位的哈希。 这是相对高效的非加密Hash函数
intHash32(1221232132132) AS intHash32, -- 2973986010
-- 推荐:从任何类型的整数计算64位哈希码。 它的工作速度比intHash32函数快。
intHash64(1221232132132) AS intHash64, -- 5086150559331381349
-- 计算任意数量字符串的CityHash64或使用特定实现的Hash函数计算任意数量其他类型的Hash。
cityHash64('username') AS cityHash64, -- 15465004142654333059
-- 1.使用sha1或者sha224加密的话,只能用于字符串
-- 2.字符串 需使用单引号。
SHA1('1232131') AS sha1, -- ,tGX?��p���h�Ü\��
SHA224('1232131') AS sha224, -- Y��?)!LZ��8���]m-u
�5S@0r�
SHA256('DREW-ZERO') AS sha256; -- ��[�=vH�Rs�
u�
X�!R�8#��j�<
-- URLHash(url[, N]) 一种快速的非加密哈希函数,用于规范化的从URL获得的字符串
-- 从一个字符串计算一个哈希,如果结尾存在尾随符号/,?或#则忽略。 URLHash(s,N)
-- 计算URL层次结构中字符串到N级别的哈希值,如果末尾存在尾随符号/,?或#则忽略。 URL的层级与URLHierarchy中的层级相同
-- 用处:此函数被用于Yandex.Metrica。
SELECT
URLHash('www.baidu.com'), -- 11390370829909720855
URLHash('www.baidu.com', 0), -- 11390370829909720855
--
URLHash('www.baidu.com', 1); -- 11160318154034397263
-- farmHash64(s) 计算字符串的FarmHash64。 接受一个String类型的参数。返回UInt64。
SELECT
farmHash64('www.runoob.com'); -- 6668483584160323388
-- javaHash(s) 计算字符串的JavaHash。 接受一个String类型的参数。返回Int32。
SELECT javaHash('www.baidu.com'); -- 270263191
-- hiveHash(s) 计算字符串的HiveHash。 接受一个String类型的参数。返回Int32。 与JavaHash相同,但不会返回负数
SELECT hiveHash('www.baidu.com'); -- 270263191
比较两个文本串是否相同
select
concat('abc ', 'hello') as res
, 'abc hello' as res1
, (res == res1) as isEquals
out
abc hello abc hello 1
比较两个文本串的相似度 : ngramSimHash 、bitHammingDistance 函数
- 背景描述
在业务中我们经常会遇到查重的需求,例如给定一个文本字符串,判断在已有的文档中,是否存在与其相似的。
想要实现这类功能的方式有很多种:
- 一种高效的方式是先利用
SinHash, 将数据降维压缩成一串哈希值,再利用海明距离(Hamming Distance) 来比较两者之间的相似度。
- SinHash 是一种局部敏感性哈希算法,特别适合在海量数据下的场景使用。
- 恰好在
ClickHouse中现在已经内置了MinHash和 海明距离的相关函数,相关PR在此:
- demo : 计算 文本串的 hash 值
SELECT
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个签名值,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh1,
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个签名值,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh2,
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh3,
ngramSimHash('SimHash本身属于一种局部敏感哈希算法,它产生的Hash签名在一定程度上可以表征原内容的相似度。') AS sh4
Query id: 7cf4a1d1-266f-4638-a75c-88ab1d93dbdf
┌──────sh1─┬──────sh2─┬──────sh3─┬───────sh4─┐
│ 20645847 │ 20645847 │ 54200087 │ 957490773 │
└──────────┴──────────┴──────────┴───────────┘
1 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.004 sec.
从哈希值直观的来看,sh1 和 sh2 是两段完全相同的文本,而 sh3 和 sh4 与 sh1 是有差异的,但是直接通过哈希值我们并不能判断它们的相似程度,这个时候就需要利用海明距离了。
- demo : 计算海明距离
使用
bitHammingDistance函数计算哈希值之间的差异距离
SELECT
bitHammingDistance(sh1, sh2) AS `1and2`,
bitHammingDistance(sh1, sh3) AS `1and3`,
bitHammingDistance(sh1, sh4) AS `1and4`
FROM (
SELECT
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个签名值,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh1,
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个签名值,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh2,
ngramSimHash('传统的hash算法只负责将原始内容尽量均匀随机地映射为一个,原理上相当于伪随机数产生算法。') AS sh3,
ngramSimHash('SimHash本身属于一种局部敏感哈希算法,它产生的Hash签名在一定程度上可以表征原内容的相似度。') AS sh4
)
Query id: c5b24238-cf85-4eb0-a77c-0b82a888a439
┌─1and2─┬─1and3─┬─1and4─┐
│ 0 │ 3 │ 10 │
└───────┴───────┴───────┘
1 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.004 sec.
从结果可得知:
- sh1 和 sh2 的海明距离是0,所以它们没有差异;
- sh1 和 sh3 的距离是3,根据经验,距离在3以内的两段文本相似度就算很高了;
- sh1 和 sh4 的距离是10,远大于3,所以它们是不同的。
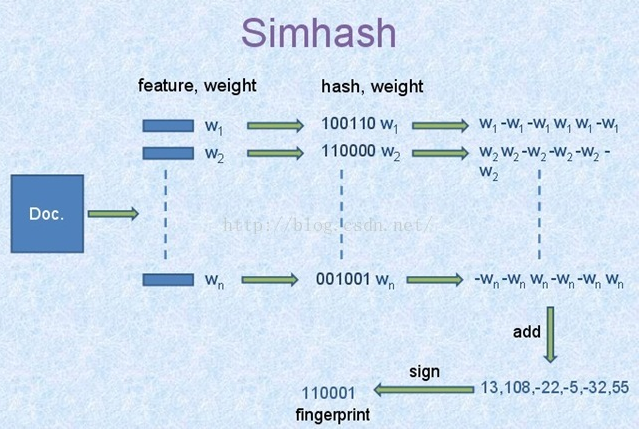
- 原理:sim hash (相似度hash算法)
这里feature可以指一篇文档分词后的某个词,即将文档中的某个词作为一个特征。
weight是这个词的权重,这里可以是这个词在这个句子中出现的次数。
图中的hash算法就是传统的hash算法,通过调用一个hash函数实现的。
simhash是为了计算一篇文档之间的相似度存在的,通过simhash算法可以计算出文档的simhash值,通过各个文档计算出的二进制值来计算文档之间的汉明距离,然后根据汉明距离来比较文档之间的相似度。
- 原理:汉明距离
- 汉明距离是指两个相同长度的字符串相同位置上不同的字符的个数。
- https://blog.csdn.net/chouisbo/article/details/54906909
- 原理: simhash 的 算法步骤:分词、hash、加权、合并、降维
具体过程如下所述:
- 分词
给定一段语句,进行分词,得到有效的特征向量,然后为每一个特征向量设置1-5等5个级别的权重(如果是给定一个文本,那么特征向量可以是文本中 的词,其权重可以是这个词出现的次数)。例如给定一段语句:“CSDN博客结构之法算法之道的作者July”,分词后为:“CSDN 博客 结构 之 法 算法 之 道 的 作者 July”,然后为每个特征向量赋予权值:CSDN(4) 博客(5) 结构(3) 之(1) 法(2) 算法(3) 之(1) 道(2) 的(1) 作者(5) July(5),其中括号里的数字代表这个单词在整条语句中的重要程度,数字越大代表越重要。
- hash
通过hash函数计算各个特征向量的hash值,hash值为二进制数01组成的n-bit签名。比如“CSDN”的hash值Hash(CSDN)为100101,“博客”的hash值Hash(博客)为“101011”。就这样,字符串就变成了一系列数字。
- 加权
在hash值的基础上,给所有特征向量进行加权,即W = Hash * weight,且遇到1则hash值和权值正相乘,遇到0则hash值和权值负相乘。例如给“CSDN”的hash值“100101”加权得 到:W(CSDN) = 1001014 = 4 -4 -4 4 -4 4,给“博客”的hash值“101011”加权得到:W(博客)=1010115 = 5 -5 5 -5 5 5,其余特征向量类似此般操作。
- 合并
将上述各个特征向量的加权结果累加,变成只有一个序列串。拿前两个特征向量举例,例如“CSDN”的“4 -4 -4 4 -4 4”和“博客”的“5 -5 5 -5 5 5”进行累加,得到“4+5 -4+-5 -4+5 4+-5 -4+5 4+5”,得到“9 -9 1 -1 1 9”。
- 降维
对于n-bit签名的累加结果,如果大于0则置1,否则置0,从而得到该语句的simhash值,最后我们便可以根据不同语句simhash的海 明距离来判断它们的相似度。例如把上面计算出来的“9 -9 1 -1 1 9”降维(某位大于0记为1,小于0记为0),得到的01串为:“1 0 1 0 1 1”,从而形成它们的simhash签名。
- 参考文献

FixedString
FixedString类型
和传统意义上的Char类型有些类似,对于一些字符有明确长度的场合,可以使用固定长度的字符串。
定长字符串通过 FixedString(N) 声明,其中N表示字符串长度。
但与Char不同的是,FixedString 使用null字节填充末尾字符,而Char通常使用空格填充。
比如在下面的例子中,字符串‘abc’虽然只有3位,但长度却是5,因为末尾有2位空字符填充。
- demo
SELECT
-- toFixedString 函数 : 用于将字符串或者数字转换为固定长度的字符串。如果原始数据的长度超过了目标长度,那么会截断超出的部分。如果原始数据的长度小于目标长度,那么会在原始数据的右侧填充 null。
toFixedString('abc ', 10) AS res1 -- 'abc <null><null><null><null><null>'
, concat( res1, 'hello' ) as res2 -- 'abc <null><null><null><null><null>hello'
, ngramSimHash( 'abc ' ) as hash
-- , ngramSimHash( res1 ) as hash2 -- 入参不支持 FixedString 类型 ,将报错 "DB::Exception: First argument of function ngramSimHash must be String, got FixedString(10) ..."
out
|res1 |res2 | hash |
|----------|---------------| ----- |
|abc <null><null><null><null><null>|abc <null><null><null><null><null>hello|568969805|
3 日期时间类型
DateTime64
时间字符串转 DateTime64
select
-- toDateTime64('2023-05-03 03:49:47.625000 +0000', 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') as dt0 -- 错误示范(需去除'+0000')
-- toDateTime64('2023-05-03 03:49:47.625000', 'Asia/Shanghai') as dt0 -- 错误示范(缺参数,如: 3)
toDateTime64('2023-05-03 03:49:47.625000', 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') as dt1
, toDateTime64('2023-05-03', 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') as dt2
, formatDateTime( dt2 , '%Y-%m' , 'Asia/Shanghai') as `month`
- out
dt1(DateTime64) |dt2(DateTime64) |month(String) |
-----------------------------+-----------------------------+---------------+
2023-05-03 03:49:47.625 +0800|2023-05-03 00:00:00.000 +0800|2023-05 |
UInt32(秒级时间戳) => DateTime64
select
-- 1726042010 : UInt32
toDateTime64( 1726042010 , 3) -- 2024-09-11 08:06:50
, toDateTime64( 1726042010 , 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') -- 2024-09-11 16:06:50.000 +0800
综合案例
-- 时间戳 转 DateTime64
select toDateTime64( toUInt32(0) , 3 ) -- 1970-01-01 00:00:00
-- DateTime 转 DateTime64
select toUnixTimestamp(now()) -- 172 604 201 0
select toDateTime64( 1726042010 , 3) -- 2024-09-11 08:06:50
注:
now()的 Type :DateTime
DateTime 类型
| 数据类型 | 是否大小写敏感 | 别名 | 取值范围 | 最小单位 | 备注说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DateTime | [1970-01-01 00:00:00, 2106-02-07 06:28:15] | 秒(s) |
非标准日期时间字符串转 DateTime : parseDateTimeBestEffort
select
parseDateTimeBestEffort('20220427') as t1
-- , parseDateTimeBestEffort('2022427') -- 报错,不支持
, parseDateTimeBestEffort('2022/4/27') as t2
, parseDateTimeBestEffort('04/27/2022') as t3
, parseDateTimeBestEffort('4-27-2022') as t4
t1 |t2 |t3 |t4 |
-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+
2022-04-26 16:00:00|2022-04-26 16:00:00|2022-04-26 16:00:00|2022-04-26 16:00:00|
DateTime => UInt64(秒级时间戳)
toUnixTimestamp( now() ) -- 1763094563 | DateTime => UInt64
Date32 类型
toDate(...) 函数
select
-- toDate('20240506') -- 将报错 : DB::Exception: Cannot parse date: value is too short: Cannot parse Date from String: While processing toDate('20240506') (version 21.3.4.25)
toDate('2022-10-22') as date0 -- 2022-10-22
, toTypeName(toDate('2022-10-22')) -- 'Date'
, toDate('2022-10-22 10:27:00') as date1 -- 2022-10-22
, toDateTime64(now(), 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') as date2 -- 2022-10-22 10:29:38.000 +0800
, toDate( toDateTime64(now(), 3, 'Asia/Shanghai') ) as date3 -- 2022-10-22
-- , toUInt16(toDate('1970-01-01')) -- 0
-- , toUInt16(toDate('2022-10-22')) -- 0
, toDate(19287) -- 2022-10-22
UnixTimestamp/时间戳类型
toUnixTimestamp(...)函数: 时间字符串/DateTime/DateTime64 => UInt64(秒级时间戳)
toUnixTimestamp是ck的一个内置函数,用于将日期或日期时间转换为Unix时间戳(自1970年1月1日00:00:00 UTC以来的秒数)
select
-- DateTime64 => UInt64 (10位,秒级时间戳)
toUnixTimestamp( toDateTime64('2025-11-14 12:25:34', 3,'Asia/Shanghai') ) as ut1 -- 1763094334
-- DateTime => UInt64 (10位,秒级时间戳)
, toUnixTimestamp( toDateTime('2025-11-14 12:25:34', 'Asia/Shanghai'), 'Asia/Shanghai') as ut2-- 1763094334
-- , toUnixTimestamp( now() ) AS ut2 DateTime => UInt64 (10位,秒级时间戳)
-- 日期字符串[String(DateTime)] 转 UInt64 (10位,秒级时间戳)
, toUnixTimestamp('2025-11-14 12:25:34', 'Asia/Shanghai') as ut3-- 1763094334 | String(DateTime) => UInt64 (10位,秒级时间戳)
, toUnixTimestamp('2025-11-14') AS ut4 -- 1763049600
, toUnixTimestamp('2025-11-14 12:25:34') AS ut5 -- 1763094334
- out
ut1 |ut2 |ut3 |ut4 |ut5 |
----------+----------+----------+----------+----------+
1763094334|1763094334|1763094334|1763049600|1763094334|
toUnixTimestamp64Milli(...) 函数 : DateTime64 => Int64 (13位,毫秒级时间戳)
select
toUnixTimestamp64Milli( toDateTime64('2025-11-14 12:25:34', 3,'Asia/Shanghai') ) as ut1-- 1763094334000 | DateTime64 => Int64 (13位,毫秒级时间戳)
时间戳(毫秒级) 转为指定时区的所在天的 00:00:00
-- 时间戳(毫秒级) 转为指定时区的所在天的 00:00:00
SELECT toDateTime( formatDateTime( toDateTime({{startTime}}/1000, 'Asia/Shanghai') , '%Y-%m-%d' , 'Asia/Shanghai') , 'Asia/Shanghai' ) as event_date
-- 典型用途: SELECT ... from ... WHERE d.event_date >= toDateTime( formatDateTime( toDateTime({{startTime}}/1000, 'Asia/Shanghai') , '%Y-%m-%d' , 'Asia/Shanghai') , 'Asia/Shanghai' )
综合案例
查询指定月份的天数
select toDayOfMonth(subtractDays(addMonths(toStartOfMonth(toDate('2022-10-25')), 1), 1))
-- 31
- 补充: MYSQL 实现
select DAYOFMONTH(last_day('2022-10-10'))
-- 31
统计每月每天都满勤的设备数(人员数)
-- 外层查询
SELECT
month -- 月份
, count(deviceId) as activeDevices -- 每个月内每天都活跃的设备
FROM (
-- 内层查询
select
*
FROM (
SELECT
deviceId
-- groupArray(deviceId) as deviceIdArray
--, groupArray(`month`) as month
, replace(month, '-', '') as month
-- , toDate( concat(month, '-01') ) as xx
, toDayOfMonth(subtractDays(addMonths(toStartOfMonth( toDate( concat(month, '-01') ) ), 1), 1) ) as totalMonthDays -- 当月总天数
-- , groupArray(month) as monthArray
--, groupArray(totalMonthDays) as totalMonthDaysArray
, groupArray(`date`) as dates
, length(dates) as realMonthDays -- 当月的实际活跃天数 (也可理解为:当月的实际上班天数)
FROM (
SELECT
deviceId
, formatDateTime( create_time , '%Y-%m' , 'Asia/Shanghai') as `month` -- 'yyyyMM' / '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
--, toDayOfMonth(subtractDays(addMonths(toStartOfMonth( create_time ), 1), 1) ) as totalMonthDays -- 当月总天数
, toDate(create_time, 'Asia/Shanghai' ) as `date` -- "yyyy-MM-dd"
FROM bdp_dwd.dwd_device_status_record_ri_d -- MergeTree
where
1 = 1
-- and create_time < toDateTime(toUInt64({{endTime}})/1000 ,'{{timeZone}}') -- [必填参数] 13位时间戳
-- and create_time <= toDateTime64('{{endTime}}', 3 ,'{{timeZone}}') -- [必填参数] 13位时间戳
group by
deviceId
, month
-- , monthTotalDays
, `date`
order by deviceId asc, `date` asc
)
group by
deviceId
, month
-- , monthTotalDays
order by deviceId
)
where 1 = 1
and realMonthDays = totalMonthDays -- 当月实际活跃天数 = 当月总天数
union all
select 'XXGERGREY001' as deviceId ,'202408' as month , toUInt8(31) as totalMonthDays , [] as dates , 31 as realMonthDays
union all
select 'XXGERGREY002' as deviceId ,'202408' as month , toUInt8(31) as totalMonthDays , [] as dates , 31 as realMonthDays
)
group by
month
order by month desc
- 内层查询结果
XXGERGREY002 202408 31 [] 31
XXGERGREY001 202408 31 [] 31
XXGERGREY003 202401 31 ['2024-01-01','2024-01-02','2024-01-03','2024-01-04','2024-01-05','2024-01-06','2024-01-07','2024-01-08','2024-01-09','2024-01-10','2024-01-11','2024-01-12','2024-01-13','2024-01-14','2024-01-15','2024-01-16','2024-01-17','2024-01-18','2024-01-19','2024-01-20','2024-01-21','2024-01-22','2024-01-23','2024-01-24','2024-01-25','2024-01-26','2024-01-27','2024-01-28','2024-01-29','2024-01-30','2024-01-31'] 31
XXGERGREY003 202309 30 ['2023-09-01','2023-09-02','2023-09-03','2023-09-04','2023-09-05','2023-09-06','2023-09-07','2023-09-08','2023-09-09','2023-09-10','2023-09-11','2023-09-12','2023-09-13','2023-09-14','2023-09-15','2023-09-16','2023-09-17','2023-09-18','2023-09-19','2023-09-20','2023-09-21','2023-09-22','2023-09-23','2023-09-24','2023-09-25','2023-09-26','2023-09-27','2023-09-28','2023-09-29','2023-09-30'] 30
- 外层统计结果
month / activeDevices
202408 3
202402 1
202401 1
202310 1
202309 1
202308 1
计算两个时间的时间差、相对日期数 : dateDiff 函数
dateDiff函数
- 解析:返回两个Date或DateTime类型之间的时差。
- 语法:
dateDiff('unit', startdate, enddate, [timezone]) - 参数:
- unit — 返回结果的时间单位。 类型 :String.
支持的时间单位: second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, year.- startdate — 第一个待比较值。 Date 或 DateTime.
- enddate — 第二个待比较值。 Date 或 DateTime.
- timezone — 可选参数。
如果指定了,则同时适用于startdate和enddate。
如果不指定,则使用startdate和enddate的时区。
如果两个时区不一致,则结果不可预料
- 返回值
以unit为单位的startdate和enddate之间的时差。
类型: int.
- DEMO
select dateDiff('month', toDate('1970-01-01'), toDate(now()) ) as relativeMonth
-- 656
select dateDiff('day', toDateTime('2021-01-01 22:00:00', 'Asia/Shanghai'), toDateTime('2021-01-13 23:00:00', 'Asia/Shanghai'), 'Asia/Shanghai');
-- 12
select dateDiff('year', toDate('2021-01-01', 'Asia/Shanghai'), toDateTime('2024-01-13', 'Asia/Shanghai') );
-- 3
相对月份数与真实月份的转换
- 获取自 1970-01-01 至 指定日期 的相对月份数
select dateDiff('month', toDateTime('1970-01-01 00:00:00'), toDateTime('2024-09-29 00:00:00'))
-- 或 select dateDiff('month', toDate('1970-01-01'), toDate('2024-09-29') )
-- 656
- 基于相对月份数,转换为 绝对月份首日 Date
SELECT
addMonths(toDate('1900-01-01'), 656) AS d1
, toStartOfMonth( addMonths(toDate('1900-01-01'), 656) ) as d2 -- 推荐做法
-- out
d1 |d2 |
----------+----------+
2024-09-01|2024-09-01|
- 特别注意
- clickhouse 21.3 的
toRelativeMonthNum函数 有 bug,不建议使用
-- 错误示范
select toRelativeMonthNum( toDate('2024-01-01') ) -- 24289
4 Array 类型
Array 类型
生成 Array
方式0:创建1个数组 :array()、[]
> SELECT array(1, 2) AS x, toTypeName(x)
┌─x─────┬─toTypeName(array(1, 2))┐
│ [1,2] │ Array(UInt8) │
└───────┴───────────┘
> SELECT array(1, 2, NULL) AS x, toTypeName(x)
┌─x──────────┬─toTypeName(array(1, 2, NULL))─┐
│ [1,2,NULL] │ Array(Nullable(UInt8)) │
└────────────┴──────────────┘
> SELECT [1, 2] AS x, toTypeName(x)
┌─x─────┬─toTypeName([1, 2])─┐
│ [1,2] │ Array(UInt8) │
└───────┴─────────┘
注意事项:不允许1个数组内的数据类型不同。
> SELECT array(1, 'a')
Received exception from server (version 1.1.54388):
Code: 386. DB::Exception: Received from localhost:9000, 127.0.0.1. DB::Exception: There is no supertype for types UInt8, String because some of them are String/FixedString and some of them are not.
方式1:范围内生成Array:range
select
range(
toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')), toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-10')) + 1
)
-- out
range(toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')), plus(toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-10')), 1))|
------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637] |
方式3:元素映射与转换:arrayMap
select
arrayMap(
x -> toDate(x), -- toUInt32 转 toDate
range( toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')),toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-10')) + 1 )
)
arrayMap(lambda(tuple(x), toDate(x)), range(toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')), plus(toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-10')), 1))) |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05','2021-01-06','2021-01-07','2021-01-08','2021-01-09','2021-01-10']|
获取指定下标的数组元素:arrayElement(array, index)
- demo1
select
arrayElement(['a', 'b', 'c'], 1) as a1 -- 正常下标范围
, arrayElement(['a', 'b', 'c'], -1) as a2 -- 负数: 反向
, arrayElement(['a', 'b', 'c'], -3) as a3 -- 负数: 反向
, arrayElement(['a', 'b', 'c'], 5) as a4 -- 下标超界: <空>
out
a1|a2|a3|a4|
--+--+--+--+
a |c |a | |
- demo2
select
toDate('2022-11-03') as `date`
, [toDate('2022-10-27'), toDate('2022-10-28'),toDate('2022-10-29'),toDate('2022-10-31'),toDate('2022-11-01'),toDate('2022-11-02'),toDate('2022-11-03')] as datesA
, length(datesA) as `length`
, arrayElement(datesA, -7) as `date2` -- 负数:反向数(从1开始)
, `date` - INTERVAL 6 day `date3`
, `date2` = `date3` as resultA -- 1: true / 0: false
, [toDate('2022-10-28'), toDate('2022-10-29'),toDate('2022-10-30'),toDate('2022-10-31'),toDate('2022-11-01'),toDate('2022-11-02'),toDate('2022-11-03')] as datesB
, arrayElement(datesB, -7) as `date4`
, `date4` = `date3` as resultB
out
date |datesA |length|date2 |date3 |resultA|datesB |date4 |resultB|
----------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+----------+----------+-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+----------+-------+
2022-11-03|['2022-10-27','2022-10-28','2022-10-29','2022-10-31','2022-11-01','2022-11-02','2022-11-03']| 7|2022-10-27|2022-10-28| 0|['2022-10-28','2022-10-29','2022-10-30','2022-10-31','2022-11-01','2022-11-02','2022-11-03']|2022-10-28| 1|
获取指定元素的下标:indexOf(array, element)
select
indexOf(['a', 'b', 'c'], 'a') -- 正常数据类型 [命中]
,indexOf(['a', 'b', 'c'], 'd') -- 正常数据类型 [未命中] 0
-- , indexOf(['a', 'b', 'c'], 1) -- 异常数据类型: 报错
indexOf(['a', 'b', 'c'], 'a')|indexOf(['a', 'b', 'c'], 'd')|
-----------------------------+-----------------------------+
1| 0|
获得数组元素个数/长度:arrayCount | length
- 方式1 arrayCount(array)
select arrayCount([1,2,3,4,5]) -- arrayCount(Array(UInt8)) : arrayCount 函数 仅支持 元素为 UInt8 的数组
-- 5
select arrayCount(
lambda(
tuple(x),
x
)
, [1, 2, 3, 4]
)
-- 4
-- 也可自己定义列名: SELECT arrayCount(x -> x, [1, 2, 3, 4]) AS arrayLength;
- 方式2 length(array)
select length(['1', '2', '3', '4', '9'])
-- 5
数组元素值求和:arraySum(array)
select
arraySum([1,2,3]) -- 6
, arraySum([1.1, 2.4, 3.6]) -- 7.1
-- , arraySum(['1','2','3']) -- 不支持 非数值型的元素(将报错)
-- , arraySum([toDate(1664553600), toDate(1665158399)]) -- -- 不支持 非数值型的元素(将报错)
WHERE 子句中按条件过滤 Array 字段
select
scores, name
from (
select [2, 3, 5] as scores, 'johnny' as name
union all
select [2, 7, 9] as scores, 'jane' as name
) x
where 1 = 1
and arrayExists(x -> x > 2, scores)
遍历元素并转为下标:arrayEnumerate(array)
- 函数说明 :
arrayEnumerate(array)
- 作用:类比Oracle、Hive的开窗函数
row_number()- 用途:Query SQL 中 生成排序序号、组内序号等
- 关联函数:arrayEnumerateDense、arrayEnumerateUniq
- 函数
arrayEnumerate(arr): 类比开窗函数: ROW_NUMBER()
- return: array(1,2,3,..., length(arr))
- 该函数通常跟
ARRAY JOIN关键字一起试用,在应用ARRAY JOIN后为每个数组进行计算一次
- 函数
arrayEnumerateDense(arr): 类比开窗函数: DENSE_RANK()- 函数
arrayEnumerateUniq(arr)
- return: 与源数组大小相同的数组,其中每个元素表示与其下标对应的源数组元素在源数组中出现的次数。
- 例如:arrayEnumerateUniq( [10,20,10,30 ])= [1,1,2,1 ]
- demo1
select
range(
toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')),toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-10')) + 1
) as arr1
, arrayEnumerate( arr1 ) as arr2
out
arr1 |arr2 |
-------------------------------------------------------------+----------------------+
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]|
- demo2
SELECT
[ '2020-05-01','2020-05-02','2020-05-03', '2020-05-01','2020-05-01', '2020-05-02' ] as time,
arrayEnumerate(time) as row_number,
arrayEnumerateDense(time) as dense_rank,
arrayEnumerateUniq(time) as uniq_rank; -- 每个数元素出现的次数
-- 响应结果:
time / row_number / dense_rank / uniq_rank
['2020-05-01','2020-05-02','2020-05-03','2020-05-01','2020-05-01','2020-05-02'] [1,2,3,4,5,6] [1,2,3,1,1,2] [1,1,1,2,3,2]
- demo3 实现开窗函数的效果
实现开窗函数
row_number()的效果
SELECT
problemLevel
-- ,arrayJoin_array_ecuComponent
-- ,arrayJoin_array_faultCount
, array_ecuComponent
, array_faultCount
, arrayEnumerate(array_faultCount)
, arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount
FROM (
SELECT 'A' as problemLevel , ['BLE', 'VCU'] as array_ecuComponent , [2, 9] as array_faultCount
union all
SELECT 'B' as problemLevel , ['ABM','AC'] as array_ecuComponent , [6, 5] as array_faultCount
)
ARRAY JOIN
arrayEnumerate(array_faultCount) as arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount -- 类似于 开窗函数: row_number()
;
out
problemLevel|array_ecuComponent|array_faultCount|arrayEnumerate(array_faultCount)|arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount|
------------+------------------+----------------+--------------------------------+-------------------------------+
B |['ABM','AC'] |[6,5] |[1,2] | 1|
B |['ABM','AC'] |[6,5] |[1,2] | 2|
A |['BLE','VCU'] |[2,9] |[1,2] | 1|
A |['BLE','VCU'] |[2,9] |[1,2] | 2|
- demo4 M个数组(每个数组含N个元素)个数组转为N行M列记录+不重复的排序序号(row_number())
SELECT
problemLevel
,arrayJoin_array_ecuComponent
,arrayJoin_array_faultCount
,arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount
FROM (
SELECT 'A' as problemLevel , ['BLE', 'VCU'] as array_ecuComponent , [2, 9] as array_faultCount
union all
SELECT 'B' as problemLevel , ['ABM','AC'] as array_ecuComponent , [6, 5] as array_faultCount
)
ARRAY JOIN
array_ecuComponent as arrayJoin_array_ecuComponent -- 从 array 恢复回: ecuComponent
,array_faultCount as arrayJoin_array_faultCount -- 从 array 恢复回: faultCount
,arrayEnumerate(array_faultCount) as arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount -- 类似于 开窗函数: row_number()
;
out
problemLevel|arrayJoin_array_ecuComponent|arrayJoin_array_faultCount|arrayEnumerate_array_faultCount|
------------+----------------------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------+
B |ABM | 6| 1|
B |AC | 5| 2|
A |BLE | 2| 1|
A |VCU | 9| 2|
数组元素过滤:arrayFilter(lambdaExpression, array)
- 语法格式
arrayFilter(func, arr1, …)
func是一个lambda表达式,通过作用于数组中每一个元素后,只留下结果为非0的部分。
- demo
SELECT
arrayFilter(
x -> x LIKE '%World%'
, ['Hello', 'abc World']
) AS res
┌─res─────────——————————————──┐
│ ['abc World'] │
└─————————————————────────────┘
SELECT
arrayFilter(
(i, x) -> (x LIKE '%World%'),
arrayEnumerate(arr),
['Hello', 'abc World'] AS arr
) AS res
┌─res─——┐
│ [2] │
└───————┘
- demo 过滤获取大于6的数值
SELECT
arrayFilter(x -> (x > 6), [2, 5, 7, 8, 9]) as arr1
, arrayJoin( arr1 ) AS arrayFilter
arr1 |arrayFilter|
-------+-----------+
[7,8,9]| 7|
[7,8,9]| 8|
[7,8,9]| 9|
数组 JOIN : array join 、 arrayJoin(...)
- demo1
with cityRankInfo as (
select * from (
select 'hubei' as province , ['wuhan','xiangyang'] as cityArray, [1,2] as rankArray
union all
select 'guangdong' as province , ['guangzhou','shenzhen','zhuhai'] as cityArray, [1,2,3] as rankArray
union all
select 'beijing' as province , [] as cityArray, [10] as rankArray
union all
select 'shanghai' as province , [] as cityArray, [20] as rankArray
union all
select 'hongkong' as province , [] as cityArray, [] as rankArray
)
)
-- select * from cityRankInfo
SELECT
province
, cityArray
, city
FROM cityRankInfo
ARRAY JOIN cityArray as city;
out
province |cityArray |city |
---------+---------------------------------+---------+
hubei |['wuhan','xiangyang'] |wuhan |
hubei |['wuhan','xiangyang'] |xiangyang|
guangdong|['guangzhou','shenzhen','zhuhai']|guangzhou|
guangdong|['guangzhou','shenzhen','zhuhai']|shenzhen |
guangdong|['guangzhou','shenzhen','zhuhai']|zhuhai |
- demo2 arrayJoin 函数
select
range( toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-02')) , toUInt32( toDate('2021-01-10') ) + 1 ) as arr1
, arrayJoin( arr1 ) as arr2
-- out:
arr1 |arr2 |
-------------------------------------------------------+-----+
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18629|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18630|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18631|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18632|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18633|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18634|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18635|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18636|
[18629,18630,18631,18632,18633,18634,18635,18636,18637]|18637|
- demo3
select
range( toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-01')),toUInt32(toDate('2021-01-05')) + 1 ) as arr1
, arrayMap( x -> toDate(x), arr1 ) as arr2
, arrayJoin( arr2 ) as day1;
-- out:
arr1 |arr2 |day1 |
-------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------+----------+
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632]|['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05']|2021-01-01|
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632]|['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05']|2021-01-02|
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632]|['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05']|2021-01-03|
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632]|['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05']|2021-01-04|
[18628,18629,18630,18631,18632]|['2021-01-01','2021-01-02','2021-01-03','2021-01-04','2021-01-05']|2021-01-05|
分组聚合/分组的数组 :groupArray(columnName)
- demo1 全部元素合为一组
select
groupArray(user_id) as tags
from (
select 1 as user_id, 'A' as tag
union all
select 2 as user_id, 'B' as tag
union all
select 3 as user_id, 'A' as tag
union all
select 4 as user_id, 'B' as tag
union all
select 5 as user_id, 'C' as tag
) user_tag
out
tags |
-----------+
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]|
- demo2 按照指定维度(tag)对指定字段(userId)分组
select
tag
, groupArray(user_id) as tags
from (
select 1 as user_id, 'A' as tag
union all
select 2 as user_id, 'B' as tag
union all
select 3 as user_id, 'A' as tag
union all
select 4 as user_id, 'B' as tag
union all
select 5 as user_id, 'C' as tag
) user_tag
group by tag
out
tag|tags |
---+-----+
B |[2,4]|
C |[5] |
A |[1,3]|
- demo3 N行M列记录 转为 M个数组(每个数组含N个元素)
按照 problemLevel 对 ecuComponent 和 faultCount 分组聚合
SELECT
problemLevel
,groupArray(ecuComponent) as array_ecuComponent
,groupArray(faultCount) as array_faultCount
FROM (
( SELECT 'ABM' as ecuComponent, 6 AS faultCount, 'A' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'BLE' as ecuComponent, 2 AS faultCount, 'B' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'AC' as ecuComponent, 5 AS faultCount, 'A' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'VCU' as ecuComponent, 9 AS faultCount, 'B' as problemLevel)
)
group by problemLevel;
-- out:
problemLevel|array_ecuComponent|array_faultCount|
------------+------------------+----------------+
B |['BLE','VCU'] |[2,9] |
A |['ABM','AC'] |[6,5] |
分组去重的数组:groupUniqArray(columnName)
SELECT
problemLevel
,groupUniqArray(ecuComponent) as array_ecuComponent -- 组内元素去重的数组
,groupUniqArray(faultCount) as array_faultCount -- 组内元素去重的数组
FROM (
( SELECT 'ABM' as ecuComponent, 6 AS faultCount, 'A' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'BLE' as ecuComponent, 2 AS faultCount, 'B' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'AC' as ecuComponent, 5 AS faultCount, 'A' as problemLevel )
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'VCU' as ecuComponent, 9 AS faultCount, 'B' as problemLevel)
UNION ALL
( SELECT 'VCU' as ecuComponent, 7 AS faultCount, 'B' as problemLevel)
)
group by problemLevel;
out
problemLevel|array_ecuComponent|array_faultCount|
------------+------------------+----------------+
B |['BLE','VCU'] |[9,2,7] |
A |['AC','ABM'] |[6,5] |
数组元素去重:arrayDistinct(columnName)
截取部分元素:arraySlice
- 语法
arraySlice(array, offset[, length])
-
作用:返回一个子数组,包含从指定位置的指定长度的元素。
-
参数
array– 数组。offset– 数组的偏移。正值表示左侧的偏移量,负值表示右侧的缩进值。数组下标从1开始。length- 子数组的长度。如果指定负值,则该函数返回[offset,array_length - length]。如果省略该值,则该函数返回[offset,the_end_of_array]。
- demo
select
[9,2,3,7,5,6] as arr
, arraySlice(arr , 1, 3) as a -- [9, 2, 3]
, arraySlice(arr , 0, 3) as b -- [ ] (说明: 下标offset从1开始)
-- out:
arr |a |b |
-------------+-------+--+
[9,2,3,7,5,6]|[9,2,3]|[]|
数组中的指定元素的存在性判断 : arrayExists(x -> condition, column) = 1
- 语法
arrayExists([func,] arr1, ...)
判断数组里是否含有元素,第一个参数是表达式,表示x经过运算是否=元素,第二个参数即是数组,可用ck列名代替,如果含有即是1,不含即为0。
搭配>0或=1使用。
- 案例
select
ids
, names
from (
SELECT array(1, 2, -1) AS ids, array('jack', 'jane', null) as names -- record 1
union all
SELECT array(1, 4, null) AS ids, array('jack', 'pony') as names -- record 2
union all
SELECT array(10, 99, null) AS ids, array('mike', 'bill') as names -- record 3
) x
where 1 = 1
and (
-- 利用 arrayExists + coalesce(NumberColumn, NullTransToOtherValue) 实现对数组列记录的过滤搜索
arrayExists(x -> coalesce(x, 0) > 5, ids) > 0 -- 筛选 record 3
-- 利用 arrayExists + coalesce(StringColumn, NullTransToOtherValue) + like 实现对数组列记录的模糊搜索
or arrayExists(x -> coalesce(x, '####') like '%##%', names) > 0 -- 筛选 record 1
)
out
ids |names |
--------+------------------+
[1,2,-1]|['jack','jane','']|
[10,99,]|['mike','bill'] |
- [补充] coalesce 函数
coalesce可将NULL值替换成空字符串或0,常用于空值的填充处理
SELECT COALESCE(column_name, '') FROM table_name;
SELECT COALESCE(column_name, 0) FROM table_name;
5 数值型
进制转换场景:16进制与10进制间的转换
- 综合案例
select
-- 17990 = 0x4646 = [52, 54, 52, 54] (ASCII码,10进制) = [0x34, 0x36, 0x34 , 0x36] (ASCII码,16进制)
hex('4646') -- out : String ASCII值 16进制拼接 = '34363436' | String 16进制字符串 = '4646'
, hex(17990) -- out : String 16进制字符串 = '4646' | in : Int 10进制 = 17990
, unhex('34363436') -- out : String 16进制字符串 = '4646' | in : String ASCII值 16进制拼接 = '34363436'
- hex(String|unsigned integer|Date|DateTime) : String
- 接受
String,unsigned integer,Date或DateTime类型的参数。- 返回:包含参数的十六进制表示的字符串。
- 使用大写字母A-F。不使用0x前缀或h后缀。
- 对于字符串,所有字节都简单地编码为两个十六进制数字。
- 数字转换为大端(«易阅读»)格式。
- 对于数字,去除其中较旧的零,但仅限整个字节。例如,hex(1)='01'。
- Date被编码为自Unix时间开始以来的天数。
- DateTime编码为自Unix时间开始以来的秒数。
- unhex(String)
- 接受包含任意数量的十六进制数字的字符串,并返回包含相应字节的字符串。
- 支持大写和小写字母A-F。
- 十六进制数字的数量不必是偶数。
如果是奇数,则最后一位数被解释为00-0F字节的低位。
- 如果参数字符串包含除十六进制数字以外的任何内容,则返回一些实现定义的结果(不抛出异常)。
- 如果要将结果转换为数字,可以使用«reverse»和«reinterpretAsType»函数。
K 通用综合场景
数据类型转换
查询时 Nullable(Xxx) 类型 转 Xxx 类型 : ifNull 或 coalesce 函数
- 在 ClickHouse 中,如果你有一个可为空的日期类型(
Nullable(Date)),你可以使用ifNull函数或者coalesce函数来处理NULL值,并将其转换成一个普通的Date类型。
尤其是针对 Clickhouse 某些特性不允许数据类型为 Nullable 类型
比如:WITH FILL特性 : DB::Exception: Incompatible types of WITH FILL expression values with column type Nullable(Date) (version 21.3.4.25)
select
-- create_time : Nullable(DateTime64) 类型,样例值: "2023-01-17 18:27:18"
toDate( formatDateTime( ifnull(create_time, toDateTime64( now() , 3)) , '%Y-%m-01' , 'Asia/Shanghai') ) as `monthFirstDay` -- monthFirstDay 的类型因 ifNull 函数 而转为了 toDate 类型;否则,还是 Nullable 类型
from dwd_device_status_ri_d
或者使用coalesce函数:
coalesce函数的作用是: 返回参数列表中的第1个非空值。如果所有参数都是NULL,则返回NULL。COALESCE函数用于将多个列中的空值中最小的非空值作为结果返回。
https://clickhouse.ac.cn/docs/en/sql-reference/functions/functions-for-nulls#coalesce
SELECT
coalesce(your_column, '1970-01-01') AS date_without_nulls
FROM your_table;
select COALESCE(column1, column2, column3, ...); -- column1、column2、column3等是要检查的列名
- demo
select
coalesce(create_time, toDateTime64( now() , 3)) as dt
from (
select toDateTime64('2023-01-17 18:27:18', 3) as create_time
union all
select toDateTime64('2024-11-17 18:33:18', 3) as create_time
union all
select null as create_time
)
dt |
-------------------+
2023-01-17 18:27:18|
2024-11-26 17:56:07|
2024-11-17 18:33:18|
Y 自定义函数
- 参考文献
- 自定义函数/UDF
- UDF通常通过SQL扩展数据库的能力,大多数采用SQL语句,但有些数据库还支持UDAF(user-defined aggregate function) 和UDTF(user defined table-generating function)。
- ClickHouse UDF通过lambda表达式定义,有参数、常量、操作符或其他函数调用组成。
- 版本支持情况
- ClickHouse v21.10 版本开始支持期待已久的特性————UDF(User defined function)。
- 简单 DEMO
CREATE FUNCTION linear_equation AS (x, k, b) -> k*x + b;
SELECT number, linear_equation(number, 2, 1) FROM numbers(3);
X 参考文献

本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen
关于博文:评论和私信会在第一时间回复,或直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
日常交流:大数据与软件开发-QQ交流群: 774386015 【入群二维码】参见左下角。您的支持、鼓励是博主技术写作的重要动力!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号