ArrayBlockingQueue类结构
一、ArrayBlockingQueue类结构
先看一下ArrayBlockingQueue类里面有哪些属性:
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E>
extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/**
* 用来存放数据的数组
*/
final Object[] items;
/**
* 下次取数据的数组下标位置
*/
int takeIndex;
/**
* 下次放数据的数组下标位置
*/
int putIndex;
/**
* 元素个数
*/
int count;
/**
* 独占锁,用来保证存取数据安全
*/
final ReentrantLock lock;
/**
* 条件队列,如果数组为空,就一直阻塞 take 取数据的线程,直到被唤醒
*/
private final Condition notEmpty;
/**
* 条件队列,如果队列已满,就一直阻塞 put 存数据的线程,直到被唤醒
*/
private final Condition notFull;
}
根据成员变量的介绍可以得知:
-
ArrayBlockingQueue底层是基于数组实现的,使用对象数组 items 存储元素
-
takeIndex:表示下次取数据的位置,putIndex:表示下次放数据的位置
-
ArrayBlockingQueue 还使用 ReentrantLock 保证线程安全,并且定义了两个条件,当条件满足的时候才允许放数据 或 者取数据
二、初始化
ArrayBlockingQueue常用的初始化方法有两个:
-
指定容量大小
-
指定容量大小和是否是公平锁
/** * 指定容量大小的构造方法 */ BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingDeque1 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1); /** * 指定容量大小、公平锁的构造方法 */ BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingDeque1 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1, true);
再看一下对应的源码实现:
/**
* 指定容量大小的构造方法(默认是非公平锁)
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/**
* 指定容量大小、公平锁的构造方法
*
* @param capacity 数组容量
* @param fair 是否是公平锁
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
// 如果数组为空,就一直阻塞 take 取数据的线程,直到被唤醒
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
// 如果队列已满,就一直阻塞 put 存数据的线程,直到被唤醒
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
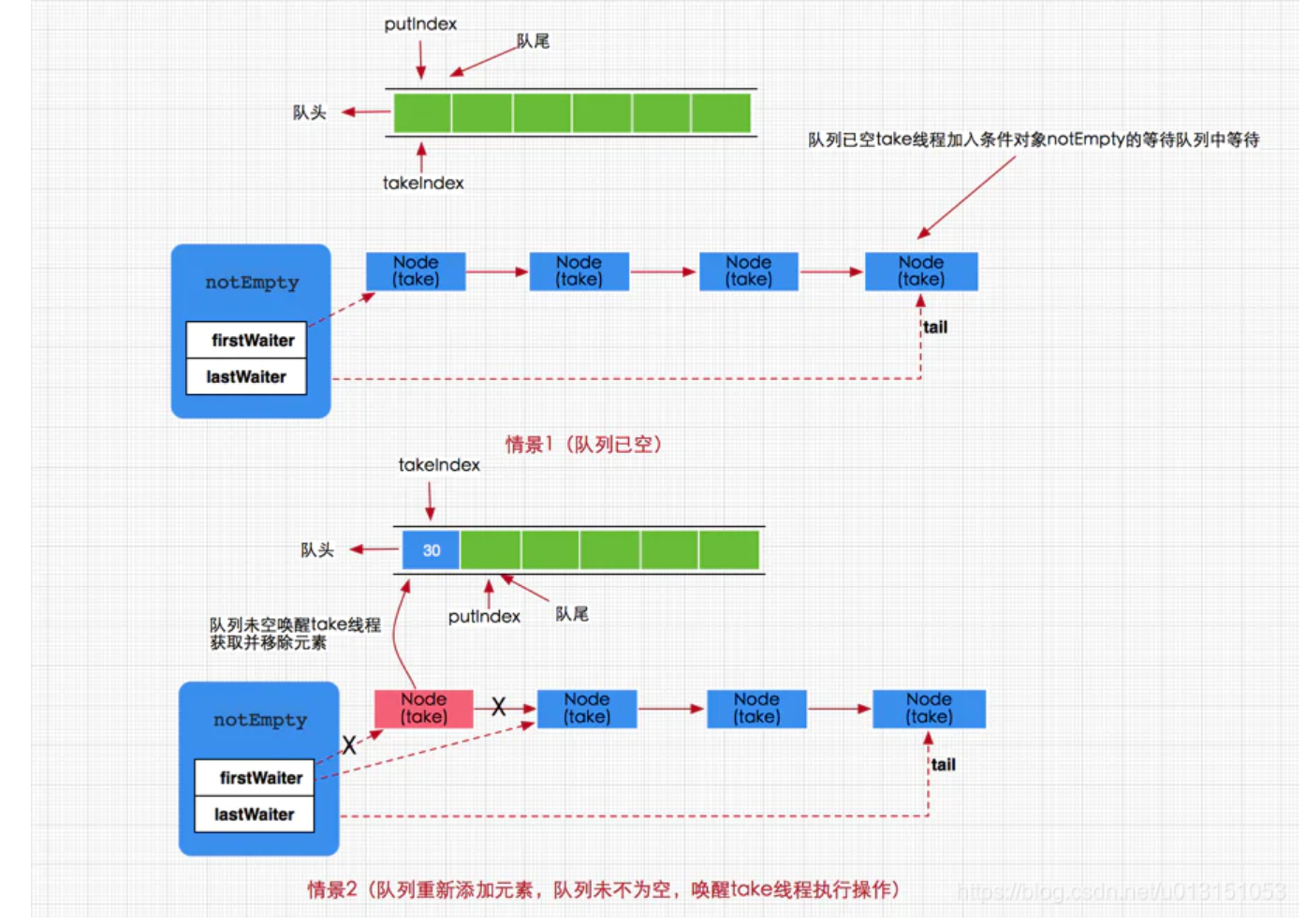
原理图流程分析:
三、放数据源码
放数据的方法有四个:

四、入队方法
1、boolean add(E e)
调用父类 add 方法,而父类 AbstractQueue add 方法实际调用的是 offer(E e) 方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return super.add(e);
}
// super.add 父类的add
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
2、boolean offer(E e)
加锁后判断容量大小,满了就不添加;没满执行共用的入队方法,入队成功返回 true
/**
* 插入成功返回 true,否则返回 false
* 插入元素为 NULL 返回空指针异常
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e); // 首先判断元素是否为 NULL,为 NULL 抛出异常
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false; // 若数组满,返回 false
else {
enqueue(e); // 添加元素并返回 true
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
3、 void put(E e) throws InterruptedException
put()方法在数组满的时候,会一直阻塞,直到有其他线程取走数据,空出位置,才能添加成功
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 判空,传参不允许为null
checkNotNull(e);
// 2. 加可中断的锁,防止一直阻塞
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 3. 如果队列已满,就一直阻塞,直到被唤醒
while (count == items.length) {
notFull.await();
}
// 4. 如果队列未满,直接入队
enqueue(e);
} finally {
// 5. 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
4、enqueue()
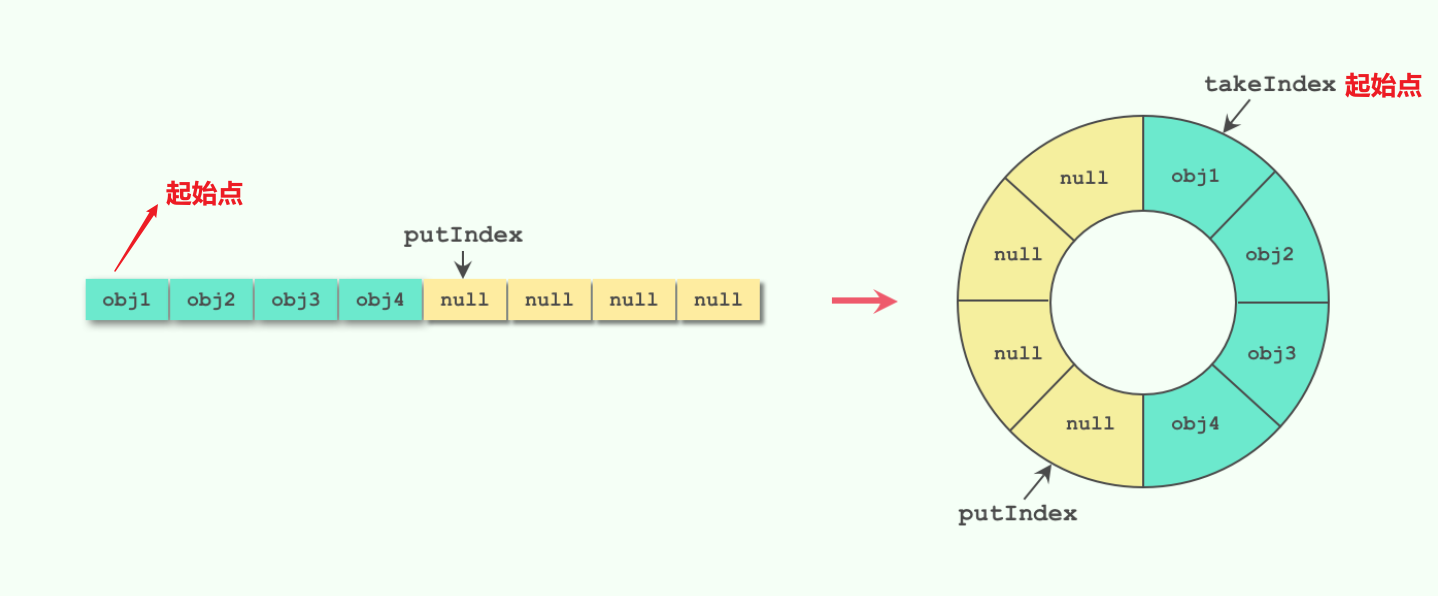
-
仅在同步方法块中调用
-
putIndex 的值一直在从 0 到 items.length 之间循环,添加元素进来就往后移动一位,移动到队尾就又回到了开头,像是在环形数组上面移动
private void enqueue(E x) { // 1. 获取数组 final Object[] items = this.items; // 2. 直接放入数组 items[putIndex] = x; // 3. 移动putIndex位置,如果到达数组的末尾就从头开始 if (++putIndex == items.length) { putIndex = 0; } // 4. 计数 count++; // 5. 唤醒因为队列为空,而阻塞等待take取数据的线程,表示当前数组有元素可取 notEmpty.signal(); }
四、取数据源码
取数据源(取出数据并删除)的方法有四个:
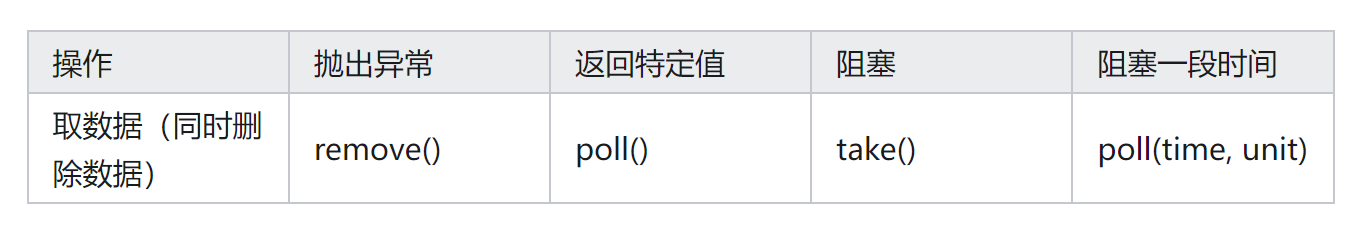
1、 remove方法源码
remove()方法源码,如果数组为空,remove()会抛出异常
/**
* remove方法入口
*/
public E remove() {
// 1. 直接调用poll方法
E x = poll();
// 2. 如果取到数据,直接返回,否则抛出异常
if (x != null) {
return x;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
2、 poll方法源码
poll()方法在弹出元素的时候,如果数组为空,则返回null,表示弹出失败
/**
* poll方法入口
*/
public E poll() {
// 1. 加锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 2. 如果数组为空,则返回null,否则返回队列头部元素
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
// 3. 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
3、take方法源码
take()方法源码,如果数组为空,take()方法就一直阻塞,直到被唤醒
/**
* take方法入口
*/
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 加可中断的锁,防止一直阻塞
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 2. 如果数组为空,就一直阻塞,直到被唤醒
while (count == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
// 3. 如果数组不为空,就从数组中取数据
return dequeue();
} finally {
// 4. 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
4、 dequeue 内部共用的出队操作
/**
* 出列
*/
private E dequeue() {
// 1. 取出队列头部元素
final Object[] items = this.items;
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
// 2. 取出元素后,把该位置置空
items[takeIndex] = null;
// 3. takeIndex 往后移动一位,如果到达数组的末尾,那么让他回到开头
if (++takeIndex == items.length) {
takeIndex = 0;
}
// 4. 元素个数减一
count--;
if (itrs != null) {
itrs.elementDequeued();
}
// 5. 唤醒因为队列已满,而被阻塞等待存放数据的线程
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
五、查看数据源码
再看一下查看数据源码,查看数据,并不删除数据
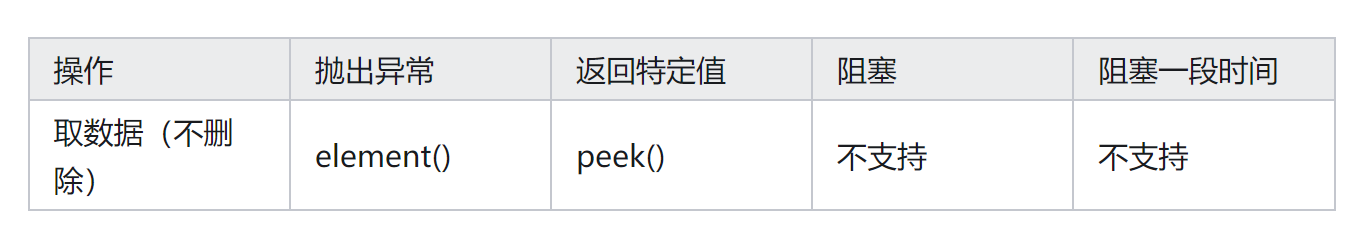
1、 peek方法源码
peek()方法源码,如果数组为空,就返回 null
/**
* peek方法入口
*/
public E peek() {
// 1. 加锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 2. 返回数组头部元素,如果数组为空,则返回null
return itemAt(takeIndex);
} finally {
// 3. 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 返回当前位置元素
*/
final E itemAt(int i) {
return (E) items[i];
}
2、element方法源码
element()方法源码,如果数组为空,则抛出异常
/**
* element方法入口
*/
public E element() {
// 1. 调用peek方法查询数据
E x = peek();
// 2. 如果查到数据,直接返回
if (x != null) {
return x;
} else {
// 3. 如果没找到,则抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
六、总结
ArrayBlockingQueue队列具有以下特点:
1、ArrayBlockingQueue实现了BlockingQueue接口,提供了四组放数据和读数据的方法,来满足不同的场景
2、ArrayBlockingQueue底层基于数组实现,采用循环数组,提升了数组的空间利用率
3、ArrayBlockingQueue初始化的时候,必须指定队列长度,是有界的阻塞队列,所以要预估好队列长度,保证生产者和消费者速率相匹配
4、ArrayBlockingQueue的方法是线程安全的,使用ReentrantLock在操作前后加锁来保证线程安全




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号