AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
一、定义
postProcessBeforeInstantiation 是 Spring AOP 动态代理的核心扩展点,通过提前创建代理对象优化性能,并支持丰富的自定义逻辑(如事务、安全)
二、代码分析
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
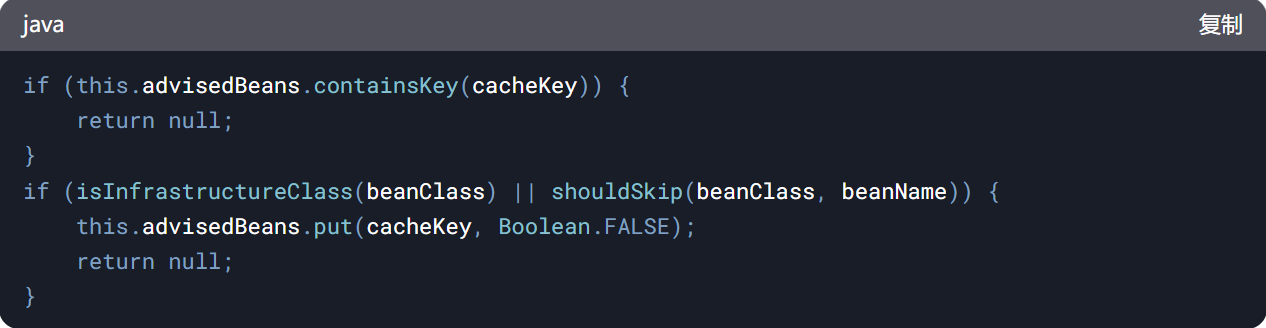
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
if (beanName != null) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
1、生成缓存键

- 作用: 根据 Bean 的类名或 Bean 名称生成唯一的缓存键,用于后续缓存操作
2、检查是否需要处理当前 Bean

-
作用: 确定当前 Bean 是否已经被处理过
-
条件解释:
-
beanName == null: 处理匿名 Bean。
-
!targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName): 确保 Bean 未被标记为已处理。
-
-
集合说明: targetSourcedBeans: 记录已通过自定义 TargetSource 处理的 Bean,避免重复代理
3、查是否已处理 或 需跳过
-
分支 1: 如果缓存键已经存在于
advisedBeans中,直接返回null。这说明这个Bean已经被处理过,不需要再次处理,直接跳过 -
分支 2:
-
isInfrastructureClass(beanClass): 判断是否为 Spring 内部类(如 Advisor, Advice),实现逻辑: 检查类是否实现 Advice、Advisor 等接口
-
shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName): 根据用户配置或注解(如 @SkipAop)决定跳过代理
-
标记为不代理: 将 cacheKey 对应值设为 FALSE,避免重复检查
-
4、处理自定义 TargetSource
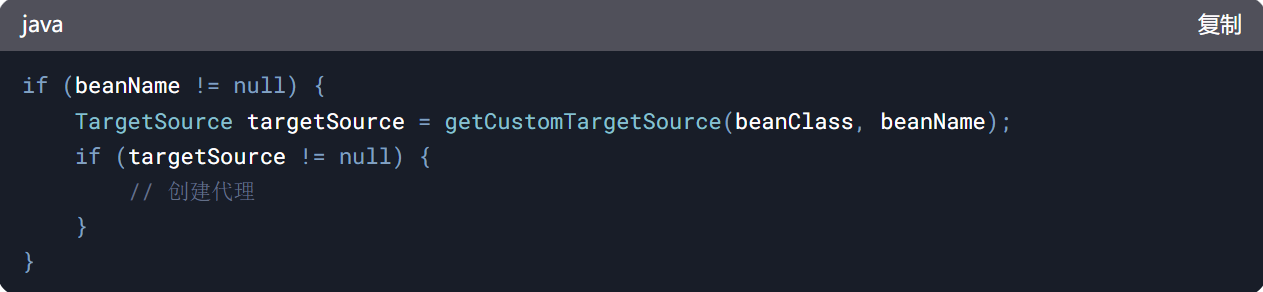
-
作用: 检查是否有自定义的 TargetSource,若有则创建代理。
-
getCustomTargetSource 逻辑:
-
查找 Bean 定义中是否指定了 TargetSource。
-
示例:通过 @Scope 配置 proxyMode 或 XML 中定义 target-source 属性。
-
-
示例场景:
- 动态数据源切换: 根据请求上下文动态选择数据源实现。
5、创建代理对象
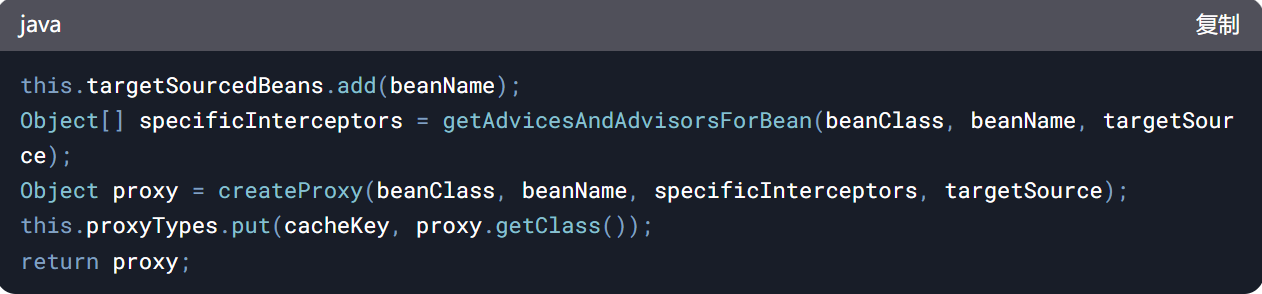
-
步骤详解:
-
1、标记为已处理: 将 beanName 加入 targetSourcedBeans。
-
2、获取拦截器:
-
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean: 收集匹配该 Bean 的所有拦截器(如事务、日志 Advice)。
-
匹配逻辑: 根据切点表达式(Pointcut)判断拦截器是否适用
-
-
3、生成代理:
-
createProxy: 根据配置选择 JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB。
-
JDK 代理: Bean 实现至少一个接口。
-
CGLIB 代理: Bean 无接口或强制使用 CGLIB。
-
-
参数 SingletonTargetSource: 确保代理持有单例目标对象
-
-
6、默认返回 null

-
作用: 若无自定义 TargetSource 或无需代理,返回 null,触发 Spring 默认实例化流程。
-
后续流程: Spring 将调用构造器创建 Bean,进行属性注入和初始化。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号