粤嵌学习记录第二十二天链地址法哈希表
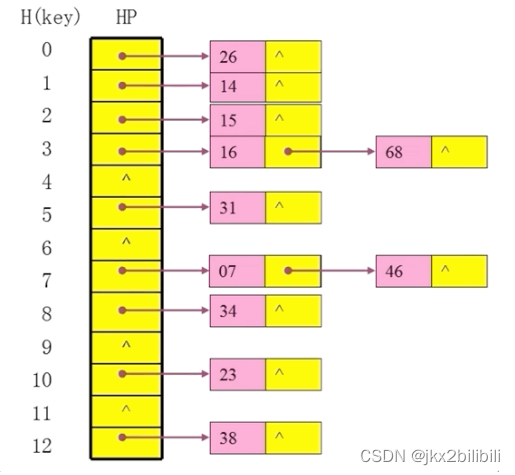
用链地址法哈希表存储11个整数23,34,14,38,46,16,68,15,7,31,26
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} node;
typedef struct
{
node *data[13]; // 存储某种数据的哈希表(数组)
int capacity; // 哈希表总容量
int size; // 哈希表当前元素个数
} hashTable;
定义哈希表和单链表管理结构体。
node *inilist(int data)
{
node *head = malloc(sizeof(node));
head->next = NULL;
head->data = data;
return head;
}
hashTable *inihash(int capacity)
{
hashTable *list = malloc(sizeof(hashTable));
list->capacity = capacity;
list->size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++)
{
list->data[i] = inilist(0);
}
return list;
}
初始化链表与哈希表。
node *insert(node *head,node *new)
{
new->next = head->next;
head->next = new;
return new;
}
hashTable *inserthash(int data,int prime,hashTable *list)
{
if(list->size==list->capacity)
{
printf("表已满");
}
int sub=data%prime;
node *tail = list->data[sub];
if (tail->next!=NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
insert(tail,inilist(data));
list->size += 1;
}
链表插入节点与哈希表插入数据。
void forlist(node *head)
{
node *tmp=head->next;
while (tmp)
{
printf("%d\n",tmp->data);
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
总结
哈希表是一种为了提高查找效率的数据存储方式,其核心思想就是将节点的存储位置与节点本身对应起来,让我们在查找数据时无需通过比对就能直接计算得到它的位置。
要想使用哈希值来查找数据,就必须先造表,造表的过程主要解决以下两个问题:
哈希函数
解决冲突
造表完成后,按照完全一样的哈希函数和解决冲突的办法,就可以查表,这种方式下查找的效率平均是O(1)O(1),也就是常数级,即查找所需时间与节点个数无关。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号