题目集4~6总结
一.前言:
题目集四:
题量较小,2,3题难度适中,但由于第一题需要使用正则表达式,所以当时对我较为困难,很多测试点很难过,所以题目集四虽然题量小,但所花时间还是不会少的。
题目集五:
相较题目集四,题量有较小提升,但难度差异不大,题目集五的第四题与题目集四的第一题都要用到正则表达式,但这次的第四题测试点更加难过。这次的第五题又让我们以另一种类间关系完成题目,感觉这次方法比上次更加好用。
题目集六;
题目集六虽然题量较大,但总体难度低,更偏向让我们练练手,熟悉一下正则表达式,接口等操作。唯一要花些时间的可能是第五题,需要思考的测试点较多。
二.设计与分析
一.题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较:
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
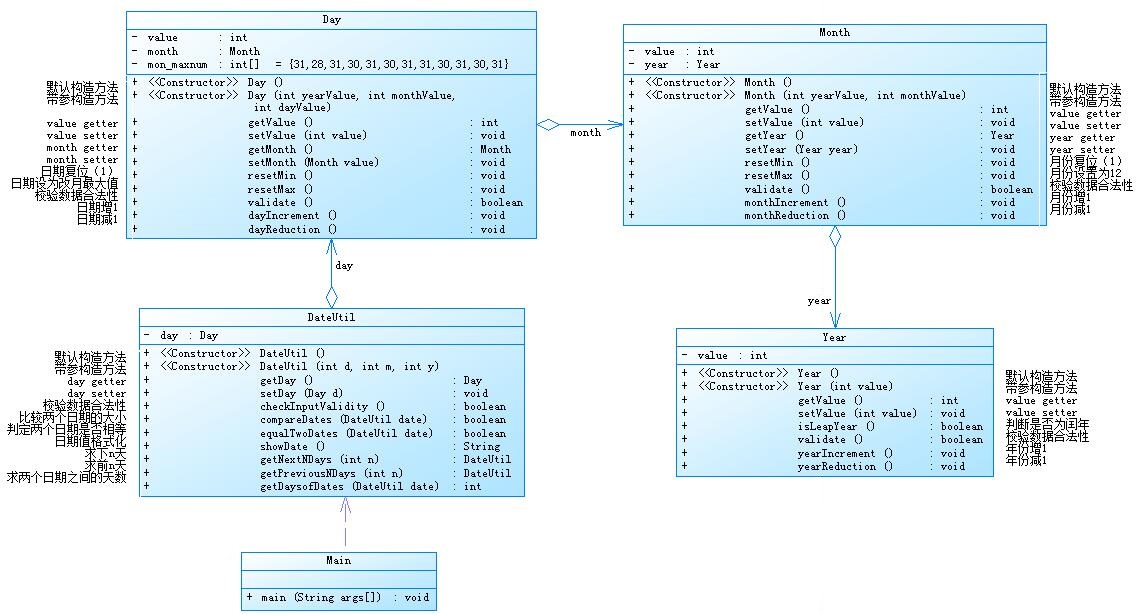
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { // test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println(" " +fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return ;
}
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
Day day;
public DateUtil(){
}
public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y){
this.day = new Day(d,m,y);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day d) {
this.day = d;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&day.validate())
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())
return false;
else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getValue())
return false;
if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getValue()<this.getDay().getValue())
return false;
return true;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){//判断两个日期是否相等
if (this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()
&& this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&& this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue())
return true;
return false;
}
public String showDate(){//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue();
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = restday(this);
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int mday = arr[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()];
if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==2) {
mday++;
}
mday-=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>=n) { //本月
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
day = n+this.getDay().getValue();
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
month++;
k++;
}
day = n;
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year++;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 1;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
k++;
}
month = k;
day = n;
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" next "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int restday(DateUtil d) {
int n = 0;
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for (int i = d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1; i <=12; i++) {
n+=arr[i];
}
n+=arr[d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-d.getDay().getValue();
if(d.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
n++;
return n;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = 365-restday(this);
if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
rest++;
}
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int mday=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>n) { //本月
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
day = mday-n;
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;
if (month==0) {
month = 12;
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-1;
}
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
month--;
k--;
}
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year--;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 12;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
k--;
}
month = k;
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" previous "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
DateUtil pred = this;
DateUtil nextd = date;
if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
}
else if (!this.compareDates(date)) {
pred = date;
nextd = this;
}
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int i,j,d = 0;
for(i=pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;i<nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();i++) {
d=d+365;
if(new Year(i).isLeapYear())
d++;
}
if (pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()!=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
for(j=pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++)
d=d+arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
for(j=1;j<nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue();j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
if (nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) {
d++;
}
}
else if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
for(j=pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
}
else if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
d=nextd.getDay().getValue()-pred.getDay().getValue();
}
return d;
}
}
class Day{
int value;
Month month;
int mon_maxnum[]= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Day() {
}
public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) {
this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
this.value = dayValue;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month value) {
this.month = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())
mon_maxnum[1]++;
if(1<=value&&mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]>=value)
return true;
return false;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Month{
int value;
Year year;
public Month() {
}
public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) {
this.year = new Year(yearValue);
this.value = monthValue;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(1<=value&&12>=value)
return true;
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Year{
int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断year是否为闰年
boolean y1 = value%4 == 0;
boolean y2 = value%100 != 0;
boolean y3 = value%400 == 0;
if((y1&&y2)||y3)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value<=2020&&value>=1820)
return true;
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value--;
}
}
题目集四7-2,采用层层调用,使用时较为麻烦,而且类与类之间的关系过于紧密,会增加处理bug时的难度',写代码时也较为繁琐,代码长度感觉也太长了
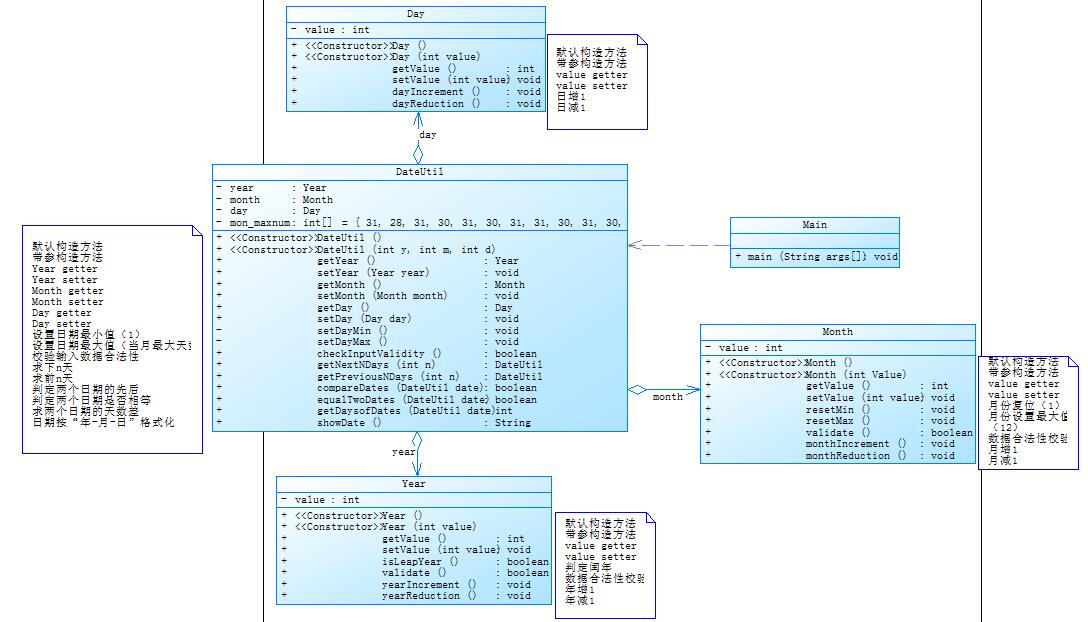
这是题目集五7-4的类图,类与类之间的耦合度相对于上个题目有着明显降低,不但使程序变得更具有可读性,而且在编写代码时也更简洁,降低了类与类之间的关联性。
总的来说,我觉得题目集五7-4的类图设计比题目集四7-2的类图设计要好,降低了类与类直接的依赖性。
二.题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
题目集4(7-3):
编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
- 类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法
public double getArea();//求图形面积 - 类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
- 类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
- 类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求球体积 - 类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求立方体体积 - 注意:
- 每个类均有构造方法,且构造方法内必须输出如下内容:
Constructing 类名 - 每个类属性均为私有,且必须有getter和setter方法(可用Eclipse自动生成)
- 输出的数值均保留两位小数
主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
import java.util.Scanner;
class Shape{
Shape(){
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
}
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
private double radius;
Circle() {
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
public double getArea() {
return radius*radius*Math.PI ;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width,length;
Rectangle() {
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
Ball(){
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
public double getArea() {
return super.getArea()*4;
}
public double getVolume() {
return getArea()/3*getRadius();
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle{
private double height;
Box(){
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
}
public double getArea() {
return 2*(getWidth()*getLength()+getWidth()*getHeight()+getLength()*getHeight());
}
public double getVolume() {
return super.getArea()*height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
switch(n) {
case 1:
double r;
r=in.nextDouble();
if(r<0)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else
{
Circle circle=new Circle() ;
circle.setRadius(r);
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f\n",circle.getArea());
}
break;
case 2:
double a,b;
a=in.nextDouble();
b=in.nextDouble();
if(a<=0||b<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else
{
Rectangle f=new Rectangle();
f.setWidth(a);
f.setLength(b);
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f\n",f.getArea());
}
break;
case 3:
double c;
c=in.nextDouble();
if(c>=0) {
Ball ball=new Ball();
ball.setRadius(c);
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",ball.getArea());
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f\n",ball.getVolume());}
else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");}
break;
case 4:
double e,f,g;
e=in.nextDouble();
f=in.nextDouble();
g=in.nextDouble();
if(e<=0||f<=0||g<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else
{
Box box=new Box();
box.setWidth(e);
box.setLength(f);
box.setHeight(g);
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",box.getArea());
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f\n",box.getVolume());
}
break;
default :
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
类图如下:
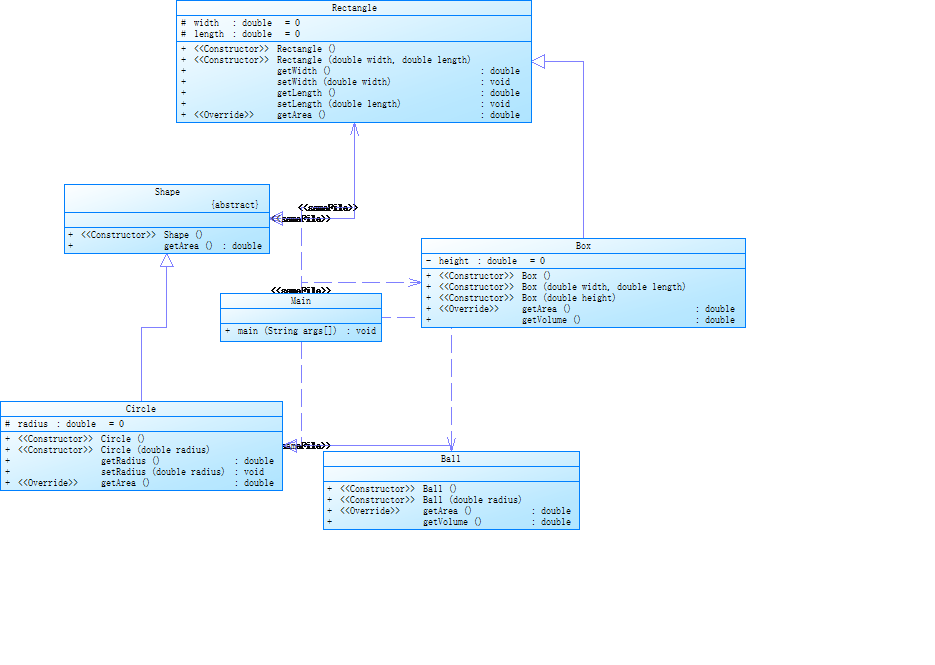
题目较简单,让Circle,Ball,Box,Rectangle继承自Shape,Shape是父类,Circle,Ball,Box,Rectangle是子类,其中Shape类还是一个抽象的类,其中有getArea()方法,在子类中分别重写该方法。
题目集6(7-5)
输入格式:
从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数),数与数之间可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 如果图形数量非法(小于0)或图形属性值非法(数值小于0以及三角形三边关系),则输出
Wrong Format。 - 如果输入合法,则正常输出,输出内容如下(输出格式见输入输出示例):
- 各个图形的面积;
- 所有图形的面积总和;
- 排序后的各个图形面积;
- 再次所有图形的面积总和。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String []args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
if(a<0||b<0||c<0) {
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Circle []s=new Circle[a];
Rectangle []d=new Rectangle[b];
Triangle []f=new Triangle[c];
double[] area=new double [a+b+c];
int []k = new int [3];
int o = 0;
double sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
double radius=in.nextDouble();
s[i]=new Circle(radius);
area[o++] = s[i].getArea();
if(s[i].validate()) {
k [0]= 0;
}
else k [0]= 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<b;i++){
double width=in.nextDouble();
double length=in.nextDouble();
d[i] = new Rectangle(width,length);
area[o++] = d[i].getArea();
if(d[i].validate()) {
k [1]= 0;
}
else k [1]= 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
double l=in.nextDouble(),w=in.nextDouble(),h=in.nextDouble();
f[i] = new Triangle(l,w,h);
area[o++] = f[i].getArea();
if(f[i].validate()) {
k [2]= 0;
}
else k [2]= 1;
}
if(k[0] == 1 || k[1] == 1 ||k[2] == 1) {
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
else {
System.out.println("Original area:");
for(int i=0;i<a+b+c;i++){
System.out.printf("%.2f ",area[i]);
sum+=area[i];
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Sum of area:");
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",sum);
System.out.println("Sorted area:");
Arrays.sort(area);
for(int i=0;i<a+b+c;i++){
System.out.printf("%.2f ",area[i]);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f",sum);
}}
}
abstract class Shape{
boolean validate() {
return false;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
Circle() {
}
public double getArea() {
return radius*radius*Math.PI ;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public Circle(double radius) {
super();
this.radius = radius;
}
boolean validate() {
if(radius >0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width,length;
Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
super();
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
boolean validate() {
if( width > 0 && length > 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
private double l,w,h;
public Triangle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Triangle(double l, double w, double h) {
super();
this.l = l;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
public double getL() {
return l;
}
public void setL(double l) {
this.l = l;
}
public double getW() {
return w;
}
public void setW(double w) {
this.w = w;
}
public double getH() {
return h;
}
public void setH(double h) {
this.h = h;
}
public double getArea() {
double p = (l+ w + h) / 2;
return Math.sqrt(p * (p - l) * (p - w) * (p - h));
}
boolean validate() {
if (l<=0 || w <=0 || h <= 0||l+w<=h||w+h<=l||l+h<=w)
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
类图如下:
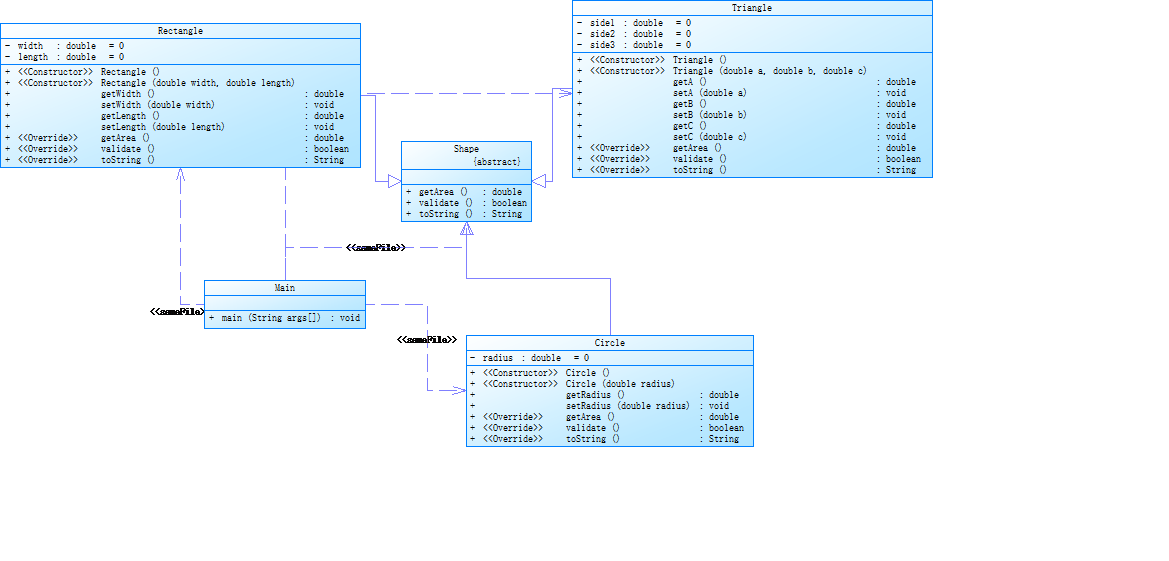
。该题将类中的属性都是私有属性,这样就保证了各个类属性的封装性。还设计了一个抽象的Shape类,Circle,Rectangle,Triangle类均是继承自Shape类,Shape类中写了getArea(),validate(),toString()三个抽象方法,三个子类均从父类中继承各个方法,并且在各自的类中对三个方法进行复写,实现代码的多态。
题目集6(7-6)
输入格式:
从键盘分别输入圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值,用空格分开。
输出格式:
- 如果输入的圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值非法(≤0),则输出
Wrong Format - 如果输入合法,则分别输出圆的面积和矩形的面积值(各占一行),保留两位小数。
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
interface GetArea {
public double getArea();
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String []args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = in.nextDouble();
double b = in.nextDouble();
double o = in.nextDouble();
double c = 0;
double u = 0;
int []k = new int[100];
Circle d = new Circle();
Rectangle e = new Rectangle();
d = new Circle(a);
u = d.getArea();
e = new Rectangle(b,o);
c = e.getArea();
if(d.validate()) {
k[1] = 1;
}
else
k[1] = 0;
if(e.validate()) {
k[2] = 1;
}
else
k[2] = 0;
if(k[1] == 1&&k[2] == 1) {
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", u));
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", c));
}
else
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
class Circle implements GetArea{
private double radius;
Circle() {
}
public double getArea() {
return radius*radius*Math.PI ;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public Circle(double radius) {
super();
this.radius = radius;
}
boolean validate() {
if(radius >0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
class Rectangle implements GetArea{
private double width,length;
Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
super();
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
boolean validate() {
if( width > 0 && length > 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
}
类图如下:
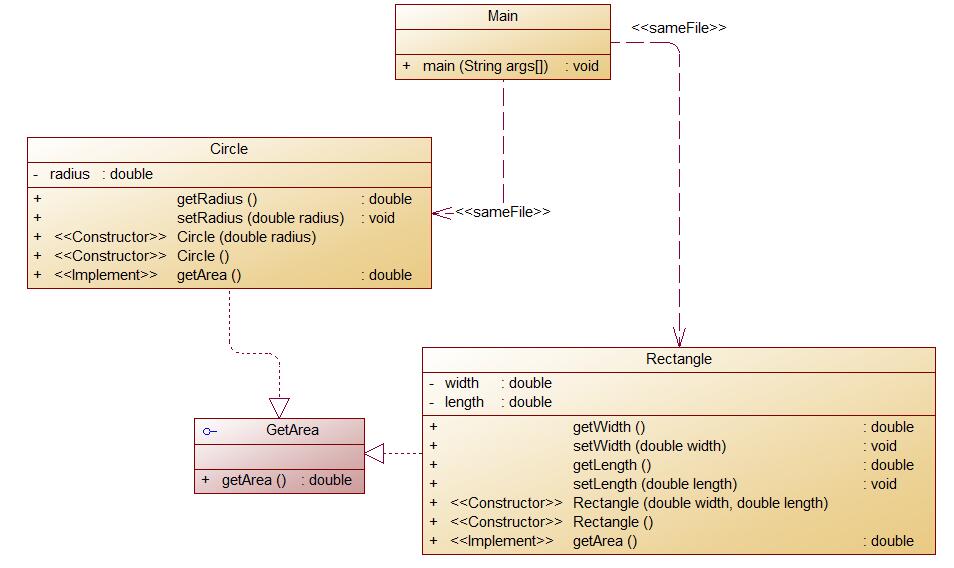
这次使用了一个接口GetArea,和类有些不同,接口是公开的,不能有私有的方法或变量,接口中的所有方法都没有方法体,通过关键字interface实现。抽象类是可以有私有方法或私有变量的,通过把类或者类中的方法声明为abstract来表示一个类是抽象类,被声明为抽象的方法不能包含方法体。子类实现方法必须含有相同的或者更低的访问级别(public->protected->private)。抽象类的子类为父类中所有抽象方法的具体实现,否则也是抽象类。该题也实现了封装性与多态。
③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
题目集四:7-1
这一题的重点是正则表达式的匹配还有分组。经过前三次的作业,对正则表达式已经有一点熟悉了,而这次则是对数字和日期的匹配进行练习。在编写代码的过程中,首先遇到了对小数点后几位的匹配出现问题,因为有的是一位小数,有的是两位或者是三位,没有办法去确定。后来我通过 对数字进行 ( ?) 加上问号的处理,这样位数就可以出现0次或多次。首先是对输入的数据一行一行的读入处理,对输入的数据判断之后就是对数据进行分组,在这里我采用的是group()的方法,将一行中的数据分为五部分:测量时间、目标水位、实际水位、开度(包含目标开度和实际开度,以“/” 分隔)、流量,然后挨个对数据进行处理并且记录下行与列。
题目集六中
7-1是匹配QQ号,算是最简单的一道题,直接对数字挨个进行匹配,只需注意QQ号的位数是5-15位不等,所以需要用 ? 去判断。
7-3是匹配验证码,在这就存在一个出现的字符可以是数字也可以是字母,所以使用了 [0-9a-zA-Z] 这样的匹配方式,代码的意思就是出现0-9数字或者a-z,A-Z的字母即可匹配,这样就可以解决这个问题。其次是验证码刚好是四位数的验证码,所以就存在一个出现次数的问题,[0-9a-zA-Z]{4} 这样就代表可以出现四次。
7-4是学号校验,一共是八位数,均是数字,首先是班级的问题,只存在固定的几个班,,将班级的部分用括号括起来中间,将三个不同的方向班级用 | 分开,再用括号将学号的两位数括起来,将学号分为个位数匹配 0[1-9] 和10-39的两位数匹配 [1-3][0-9] 和 40 三个类型用 | 去隔开就可以匹配01-40的学号。
④题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
首先说说集合与数组的区别
数组的长度是固定的,如果想增加长度,只能创建新的数组。
集合的长度是可变的,数据理论可以无限添加,自动扩容。
数组元素的类型必须是同一种类型,比如 String[] arr = ["aaa","bbb"];
集合元素可以是不同的类型 ArrayList



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号