线程池
三大方法,七大参数,四种拒绝策略
三大方法
- ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单个线程
- ExecutorService threadPool2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //创建一个固定的线程池的大小
- ExecutorService threadPool3 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //可伸缩的
//工具类 Executors 三大方法;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool1 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单个线程
ExecutorService threadPool2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //创建一个固定的线程池的大小
ExecutorService threadPool3 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //可伸缩的 (主要看电脑能支持几条线程同时运行了)
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool1.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
threadPool1.shutdown();
threadPool2.shutdown();
threadPool3.shutdown();
}
}
七大参数
源码分析
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
本质:都是通过new ThreadPoolExecutor()创建的
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,//核心线程数 核心线程一直存活,及使没有任务需要执行
int maximumPoolSize,//最大线程数
long keepAliveTime,//存活时间
TimeUnit unit,//存活时间单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//线程池(阻塞)队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory,//线程池工厂
//任务拒绝处理器
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
阿里巴巴开发规范:
Exectors会造成oom,不建议使用

理解的业务图:
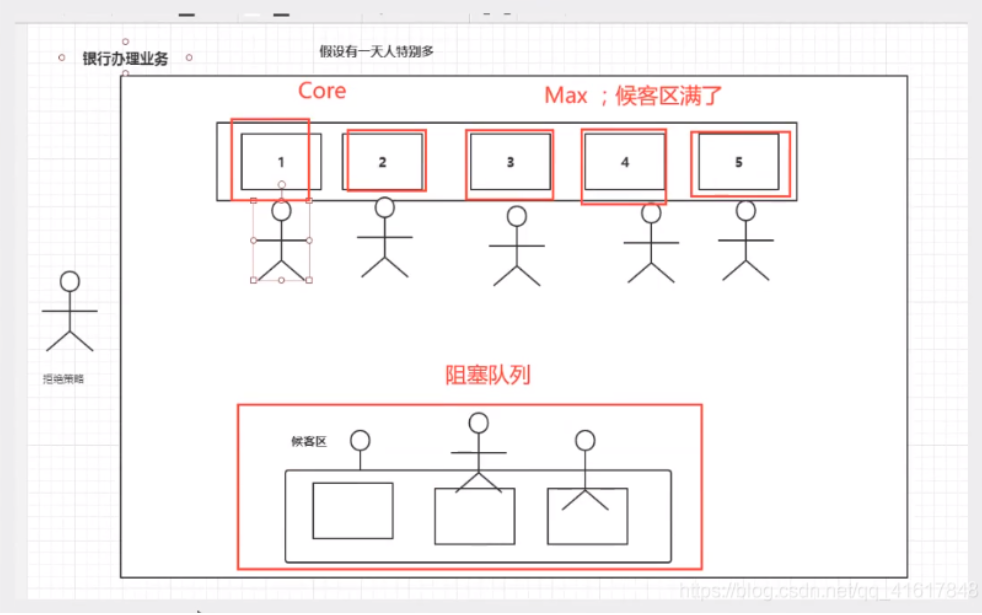
四种拒绝策略
-
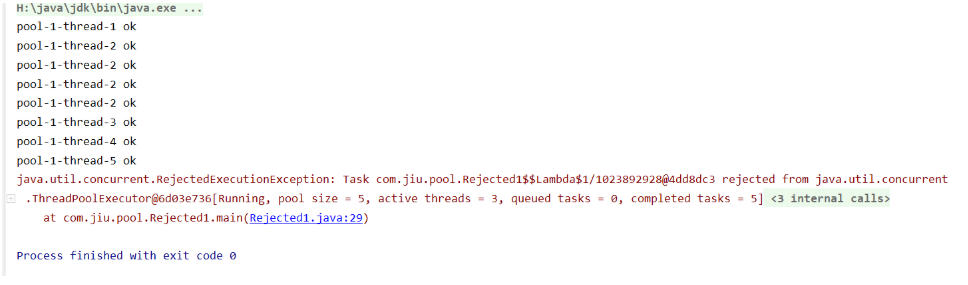
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(): 默认策略 //该拒绝策略为:银行满了,还有人(线程)进来,不处理这个人的,并抛出异常
超出最大承载,就会抛出异常:队列容量大小+maxPoolSize
public class Rejected1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // int corePoolSize, 核心线程数量 一直在服务 // int maximumPoolSize, 池子的最大线程数 // long keepAliveTime, // TimeUnit unit, // BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, 阻塞队列 当线程增加最后占用这个队列 // ThreadFactory threadFactory, // RejectedExecutionHandler handler ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() ); try { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { threadPool.execute(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok"); }); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown(); } } }![]()
-
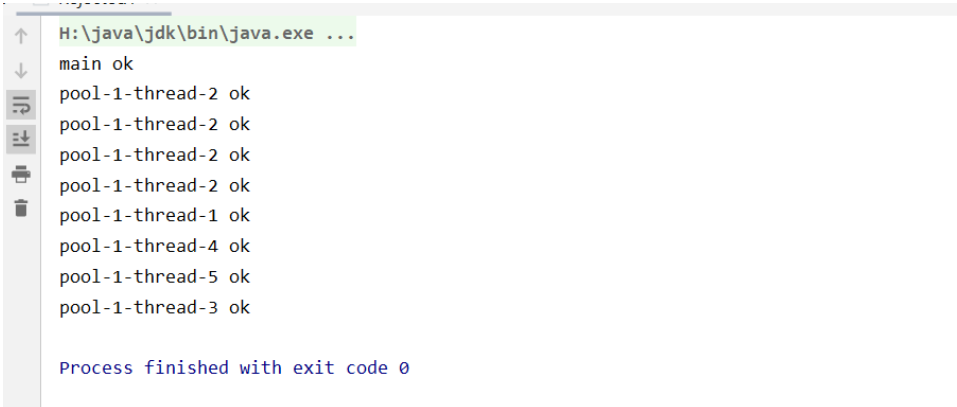
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy(): //该拒绝策略为:哪来的去哪里 main线程进行处理
将对应的拒绝策略实例换了就ok
![]()
-
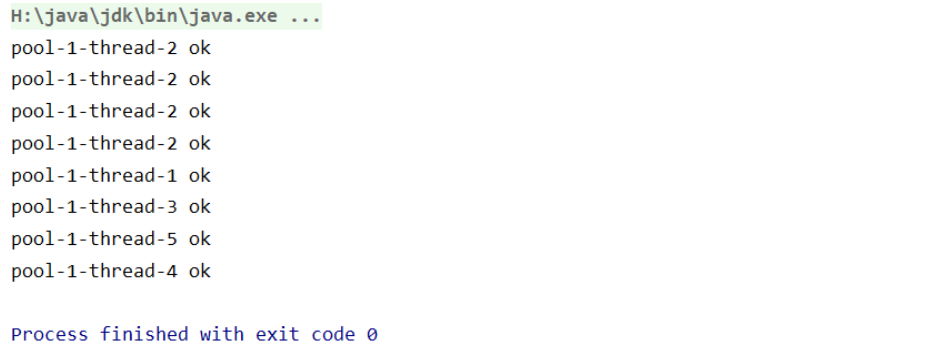
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy(): //该拒绝策略为:队列满了,丢掉多的线程,不会抛出异常。
![]()
-
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy(): //该拒绝策略为:队列满了,尝试去和最早的进程竞争,竞争失败就丢掉多的线程,不会抛出异常
![]()
线程池大小设置方式方式
-
CPU密集型:电脑的核数是几核就选择几;选择maximunPoolSize的大小
-
I/O密集型:
在程序中有15个大型任务,io十分占用资源;I/O密集型就是判断我们程序中十分耗I/O的线程数量,大约是最大I/O数的一倍到两倍之间。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号