多线程
操作系统是控制计算机的操作运行和硬件软件资源的系统软件程序,用于提供公共服务来组织用户交互。
操作系统根据运行环境,可以分为桌面操作系统、手机操作系统、服务器操作系统、嵌入式操作系统等等
2. 进程进程是计算机中程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动,是系统进行资源分配的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础。
3. 线程
线程是操作系统进行运算调度的最小单位,包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。
4. 线程的三种实现方式和线程池
(1).自定义Thread类型,重写run()方法
1 public class ThreadDemo01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Thread t1 = new ThreadDemo02(); 4 ThreadDemo02 t2 = new ThreadDemo02(); 5 Thread t3 = new Thread(t2); 6 Thread t4 = new Thread(){ 7 @Override 8 public void run() { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 10 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " "); 11 System.out.println(i); 12 } 13 } 14 }; 15 t1.start(); 16 t2.start(); 17 t3.start(); 18 t4.start(); 19 } 20 }
1 public class ThreadDemo02 extends Thread { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { 5 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " "); 6 System.out.println(i); 7 } 8 } 9
(2).自定义类实现Callable接口,重写call()方法,FutureTask
1 public class ThreadDemo03 implements Callable { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 ThreadDemo03 t1 = new ThreadDemo03(); 4 FutureTask ft = new FutureTask(t1); 5 new Thread(ft).start(); 6 System.out.println(ft.get()); 7 } 8 public String call() throws Exception { 9 Thread.sleep(1000); 10 return "hello"; 11 }; 12 }
(3).自定义类实现Runnable接口,重写run()方法
1 public class ThreadDemo04 implements Runnable{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 ThreadDemo04 t1 = new ThreadDemo04(); 4 new Thread(t1).start(); 5 6 for(int i = 0;i<100;i++){ 7 System.out.println("这是main方法 "+i); 8 } 9 } 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){ 13 System.out.println("这是run方法 "+i); 14 } 15 } 16 }
(4). 线程池
1 public class ThreadPoolExecutorDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 /* 4 * int corePoolSize 核心线程数 5 * int maximumPoolSize 最大线程数 6 * long keepAliveTime 有效时间 7 * TimeUnit unit 时间单位 8 * BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue 队列 9 * RejectedExecutionHandler handler 拒绝策略 10 **/ 11 12 ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 13 20, 14 30, 15 TimeUnit.SECONDS, 16 new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5)); 17 for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++){ 18 poolExecutor.submit(new Runnable(){ 19 @Override 20 public void run(){ 21 for(int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++){ 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + i); 23 } 24 } 25 }); 26 } 27 } 28 }
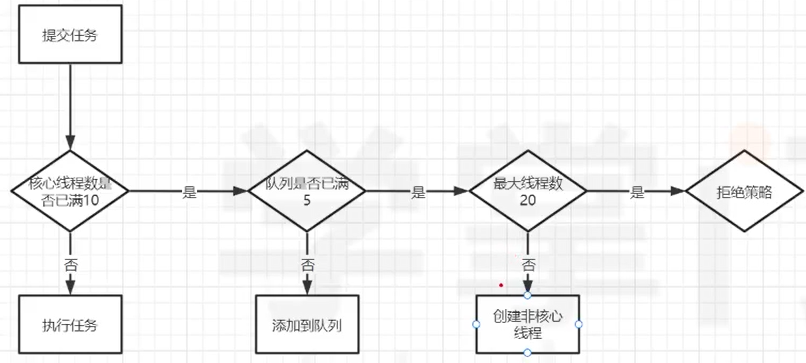
拒绝策略: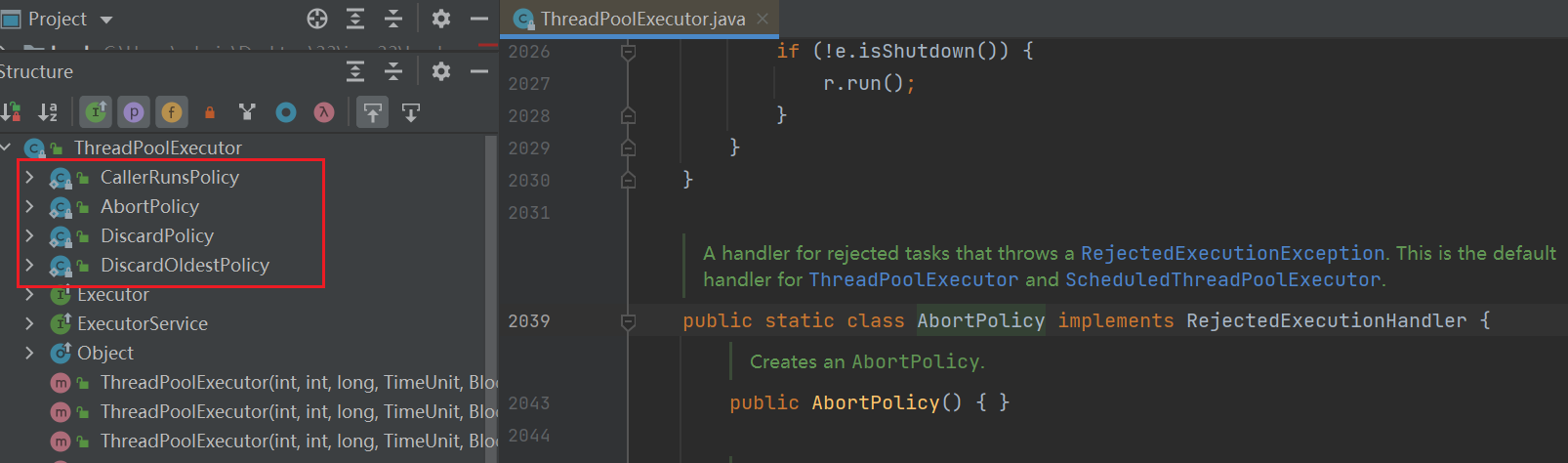
5. 线程状态
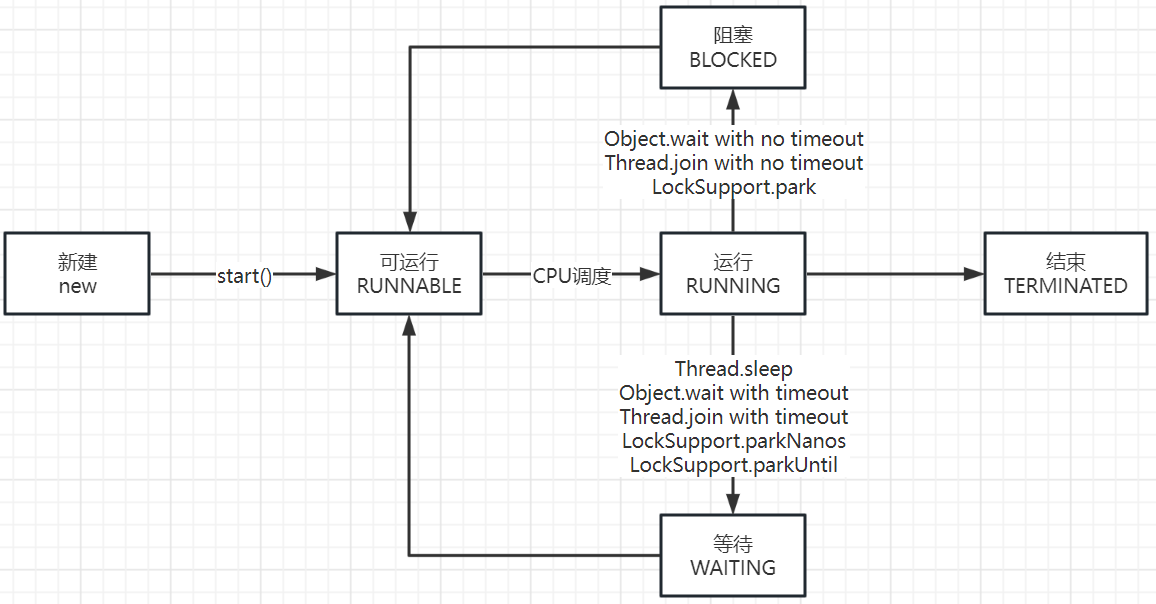
6. 线程安全
线程安全(Thread-Safe)是指在多线程环境下,对共享资源的访问不会导致不正确的结果。在并发编程中,多个线程同时访问共享资源可能会导致数据竞争(Data Race)和死锁(Deadlock)等问题,因此保证线程安全是非常重要的。
一个线程安全的程序,不仅在单线程环境下能够正确地执行,而且在多线程环境下也能够正确地执行。为了保证线程安全,程序需要采取一些同步措施,例如使用线程锁(Thread Lock)、原子操作(Atomic Operation)、线程安全的数据结构等。
7. 线程锁
线程锁是一种同步机制,用于协调多个线程之间对共享资源的访问。在并发编程中,多个线程可以同时访问共享资源,但同时进行的读写操作可能会导致数据不一致的情况发生。线程锁的作用就是确保在任何时刻只有一个线程可以访问共享资源,从而避免数据竞争和死锁等并发编程中常见的问题。
线程锁的基本原理是,在多个线程竞争访问同一共享资源的时候,只有一个线程能够获取到锁,其他线程需要等待锁被释放后才能进入临界区执行相应的操作。一旦线程完成了对共享资源的访问,它就会释放锁,让其他线程能够获取到锁并访问共享资源。
(1). synchronized同步代码块
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread); 5 Thread t2 = new Thread(myThread); 6 t1.start(); 7 t2.start(); 8 9 } 10 }
1 public class MyThread extends Thread{ 2 public int num = 100; 3 public Object obj = new Object(); 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 while(true) { 7 synchronized(obj) { 8 if(this.num > 0) { 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep(50); 11 } catch (Exception e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + num--); 15 } else { 16 break; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }
(2). synchronized同步方法
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread); 5 Thread t2 = new Thread(myThread); 6 t1.start(); 7 t2.start(); 8 9 } 10 }
1 public class MyThread extends Thread{ 2 public int num = 100; 3 public boolean flag = false; 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 while (!flag) { 7 sale(); 8 } 9 } 10 11 public synchronized void sale() { 12 if (this.num > 0) { 13 try { 14 Thread.sleep(50); 15 } catch (Exception e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + num--); 19 } else { 20 flag = true; 21 } 22 } 23 }
(3). Lock锁
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 2 3 public class LockDemo implements Runnable{ 4 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 5 public int num = 100; 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 while (true) { 9 lock.lock(); 10 if (this.num > 0) { 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(50); 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + num--); 17 } else { 18 break; 19 } 20 lock.unlock(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 LockDemo l1 = new LockDemo(); 26 Thread t1 = new Thread(l1); 27 Thread t2 = new Thread(l1); 28 t1.start(); 29 t2.start(); 30 } 31 }
(4).加锁对于对象的影响(JOL查看对象的内存情况)
1 import org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout; 2 3 public class Student { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Student st = new Student(); 6 st.age = 20; 7 st.name = "ZhangSan"; 8 System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(st).toPrintable()); 9 System.out.println("============================"); 10 synchronized (st) { 11 System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(st).toPrintable()); 12 } 13 14 } 15 public int age; 16 public String name; 17 }
结果:在对象的标记处做了修改
Demo14.Student object internals: OFF SZ TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 8 (object header: mark) 0x0000000000000005 (biasable; age: 0) 8 4 (object header: class) 0x2000ce08 12 4 int Student.age 20 16 4 java.lang.String Student.name (object) 20 4 (object alignment gap) Instance size: 24 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total ============================ Demo14.Student object internals: OFF SZ TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE 0 8 (object header: mark) 0x0000022e1671d005 (biased: 0x000000008b859c74; epoch: 0; age: 0) 8 4 (object header: class) 0x2000ce08 12 4 int Student.age 20 16 4 java.lang.String Student.name (object) 20 4 (object alignment gap) Instance size: 24 bytes Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
锁一共有4种状态,级别从低到高依次是:无锁、偏向锁、轻量级锁和重量级锁,锁状态只能升级不能降级
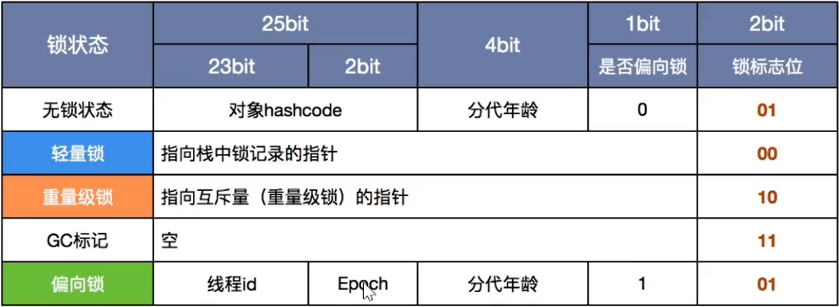
8. wait和notify
wait() --- 阻塞; notify() --- 释放
1 public class WaitDemo { 2 public static Object obj1 = new Object(); 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 4 new Thread(() -> { 5 synchronized(obj1) { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": A"); 7 try { 8 obj1.wait(); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) {} 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": B"); 11 } 12 }).start(); 13 14 Thread.sleep(1000); 15 synchronized(obj1) { 16 obj1.notify(); 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": C"); 18 } 19 } 20 }
9. LockSupport
part() --- 阻塞; unpart() --- 释放
1 public class LockSupportDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{ 3 Thread t0 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": A"); 7 LockSupport.park(); //阻塞 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": B"); 9 } 10 }); 11 t0.start(); 12 Thread.sleep(1000); 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": C"); 14 LockSupport.unpark(t0); 15 16 } 17 }
10. Join
join() --- 等待该线程终止(先让此线程运行至终止)
1 public class JoinDemo extends Thread{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); 6 } 7 } 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 10 JoinDemo j1 = new JoinDemo(); 11 j1.start(); 12 j1.join(); //等待该线程终止 13 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); 15 } 16 } 17 }
11. Daemon
当所有线程都是Daemon守护线程时,jvm会自动终止
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 3 public class DaemonDemo extends Thread { 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 7 try { 8 Thread.sleep(2000); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i); 13 } 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException { 17 DaemonDemo d1 = new DaemonDemo(); 18 d1.setDaemon(true); 19 d1.start(); 20 21 System.in.read(); //阻塞, 等待用户输入 22 } 23 }
12. ThreadLocal --- 线程局部变量
1 public class ThreadLocalDemo { 2 public static ThreadLocal<Integer> local = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(){ 3 @Override 4 protected Integer initialValue() { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 }; 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 new Thread(() -> { 11 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 12 local.set(local.get()+ 1); 13 } 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": " + local.get()); 15 }).start(); 16 17 new Thread(() -> { 18 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 19 local.set(local.get()+ 1); 20 } 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": " + local.get()); 22 }).start(); 23 } 24 }
结果: 由于变量是局部变量,所以结果不是一个3一个4,而是两个都是3
Thread-1: 3
Thread-0: 3



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号