django html页面开发总结
HTML页面 实现时钟效果
效果展示:
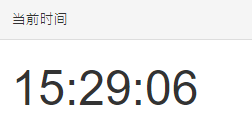
主题:(纯文字版)
<div id="clock" style="font-size: xxx-large;">12:00:00</div>
<script>
let oClock = document.querySelector('#clock');
let addZero = (num) => {
if (num >= 10) {
return num;
} else {
return `0${num}`;
}
}
let updateTime = () => {
let now = new Date();
let time = addZero(now.getHours()) + ":" + addZero(now.getMinutes()) + ":" + addZero(now.getSeconds());
oClock.innerText = time;
}
updateTime();
setInterval(updateTime, 1000);
</script>
HTML页面定时刷新
部署爬虫舆情监测系统时,需要时不时进行爬虫爬取和数据更新
只需要在里设置
20000:每20秒刷新一次页面
<body onload="setInterval('refreshPage()', 20000);">
....
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function refreshPage() {
location.reload();
}
</script>
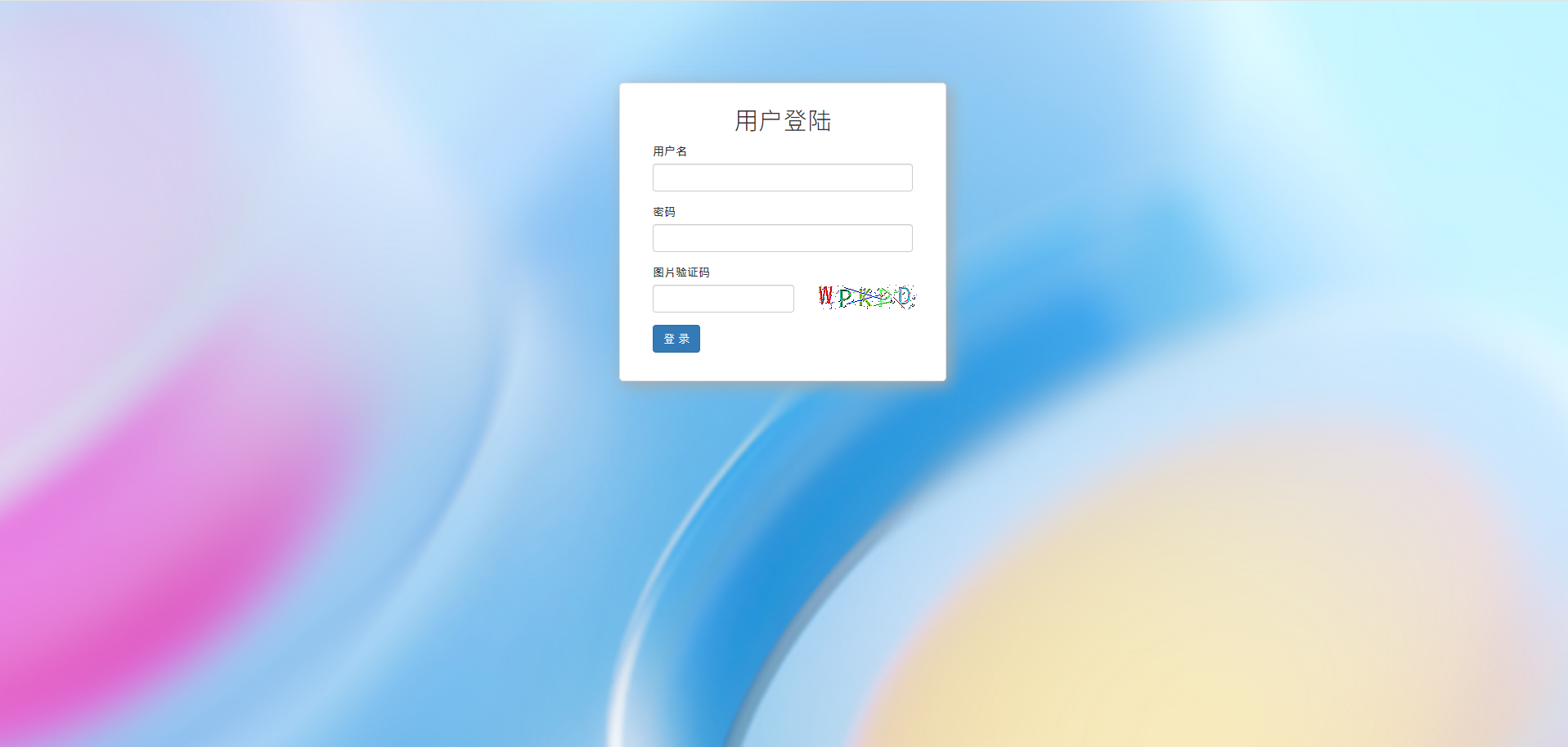
管理系统用户登陆页面模板
{% load static %}
{% csrf_token %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}">
<script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script>
<style>
.account {
width: 400px;
border: 1px solid #dddddd;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 5px 5px 20px #aaa;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
margin-top: 100px;
padding: 20px 40px;
}
.account h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
body {
background-image: url("{% static '/img/background.jpg'%}");background-repeat: no-repeat; /* 不重复 */
background-position: center center; /* 居中 */
background-size: cover; /* 覆盖整个元素 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="account" style="background-color: white">
<h2>用户登陆</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label>用户名</label>
{{ form.username }}
<span style="color: red">{{ form.username.errors.0 }}</span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>密码</label>
{{ form.password }}
<span style="color: red">{{ form.password.errors.0 }}</span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_code">图片验证码</label>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-7">
{{ form.code }}
<span style="color: red">{{ form.code.errors.0 }}</span>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-5">
<img id="image_code" src="/image/code/" href="/login/">
</div>
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="登 录" class="btn btn-primary">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
在django【views.py】中
(check_code函数在下面)
def image_code(request):
""" 生成图片验证码"""
img,code_string = check_code()
# print(code_string)
request.session['image_code'] = code_string
request.session.set_expiry(60) #60s超时
stream = BytesIO()
img.save(stream, 'png')
return HttpResponse(stream.getvalue())
python生成自动验证码
需要ttf文件(字体文件)
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont,ImageFilter
import random
def check_code(width=120, height=30, char_length=5, font_file='Monaco.ttf', font_size=28):
code = []
img = Image.new(mode='RGB', size=(width, height), color=(255, 255, 255))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img, mode='RGB')
def rndChar():
"""
生成随机字母
:return:
"""
return chr(random.randint(65, 90))
def rndColor():
"""
生成随机颜色
:return:
"""
return (random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(10, 255), random.randint(64, 255))
# 写文字
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_file, font_size)
for i in range(char_length):
char = rndChar()
code.append(char)
h = random.randint(0, 4)
draw.text([i * width / char_length, h], char, font=font, fill=rndColor())
# 写干扰点
for i in range(40):
draw.point([random.randint(0, width), random.randint(0, height)], fill=rndColor())
# 写干扰圆圈
for i in range(40):
draw.point([random.randint(0, width), random.randint(0, height)], fill=rndColor())
x = random.randint(0, width)
y = random.randint(0, height)
draw.arc((x, y, x + 4, y + 4), 0, 90, fill=rndColor())
# 画干扰线
for i in range(5):
x1 = random.randint(0, width)
y1 = random.randint(0, height)
x2 = random.randint(0, width)
y2 = random.randint(0, height)
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y2), fill=rndColor())
img = img.filter(ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE)
return img, ''.join(code)
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# img,code_str=check_code()
# print(code_str)
# with open('code.png','wb') as f:
# img.save(f,format='png')
# 1. 直接打开
# img,code = check_code()
# img.show()
# 2. 写入文件
# img,code = check_code()
# with open(r'D:/111实习项目实训/pachongsystem/code.png','wb') as f:
# img.save(f,format='png')
# 3. 写入内存(Python3)
# from io import BytesIO
# stream = BytesIO()
# img.save(stream, 'png')
# stream.getvalue()
# 4. 写入内存(Python2)
# import StringIO
# stream = StringIO.StringIO()
# img.save(stream, 'png')
# stream.getvalue()
python将文件放入内存操作
#写入内存(Python3)
from io import BytesIO
stream = BytesIO()
img.save(stream, 'png')
stream.getvalue()
django利用html模板语法制作echarts图
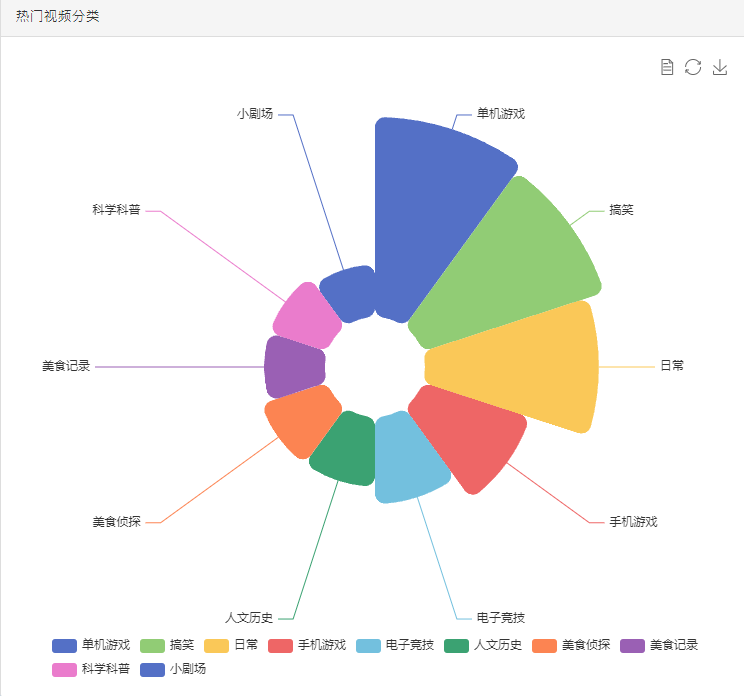
数据均来源于后台
【图片名为g_1_1】只需要把getElementById('g_1_1')修改即可
只需将数据转化成字典或者列表
用 django的模板语法 {% for %} 循环置入数据
{% for obj in topcatagory %}
{value: {{ obj.1}}, name: '{{ obj.0 }}'},
{% endfor %}
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-heading">热门视频分类</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<div id="g_1_1" style="width: 100%; height: 630px;user-select: none; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);" _echarts_instance_="ec_1705386174880">
<div style="position: relative; width: 1101px; height: 919px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; border-width: 0px; cursor: default;">
<canvas data-zr-dom-id="zr_0" width="1101" height="919" style="position: absolute; left: 0px; top: 0px; width: 1101px; height: 919px; user-select: none; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0); padding: 0px; margin: 0px; border-width: 0px;"></canvas>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var dom = document.getElementById('g_1_1');
var myChart = echarts.init(dom, null, {
renderer: 'canvas',
useDirtyRect: false
});
var app = {};
var option;
option = {
legend: {
top: 'bottom'
},
toolbox: {
show: true,
feature: {
mark: {show: true},
dataView: {show: true, readOnly: false},
restore: {show: true},
saveAsImage: {show: true}
}
},
series: [
{
name: 'Nightingale Chart',
type: 'pie',
radius: [50, 250],
center: ['50%', '50%'],
roseType: 'area',
itemStyle: {
borderRadius: 10
},
data: [
{% for obj in topcatagory %}
{value: {{ obj.1}}, name: '{{ obj.0 }}'},
{% endfor %}
]
}
]
};
if (option && typeof option === 'object') {
myChart.setOption(option);
}
window.addEventListener('resize', myChart.resize);
</script>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号