Elasticsearch
一、核心术语概念
- ES与数据库类比
| ES | 数据库 |
|---|---|
| 索引 index | 表 |
| 文档 doucment | 行(记录) |
| 字段 fields | 列 |
- 集群相关
- 分片(shard):把索引库拆分为多份,分别放在不同的节点上,比如有3个节点,3个节点的所有数据内容加在一起是一个完整的索引库。分别保存到三个节点上,目的为了水平扩展,提高吞吐量。
- 备份(replica):每个shard的备份。
shard = primary shard(主分片)
replica = replica shard(备份节点)
二、查看集群健康
文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/_cluster_health.html#_cluster_health
请求
GET /_cluster/health
三、索引操作
1、创建索引
PUT /index_test # 直接跟索引名称
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "2", # 主分片数
"number_of_replicas": "0" # 副本数
}
}
}
2、查看索引
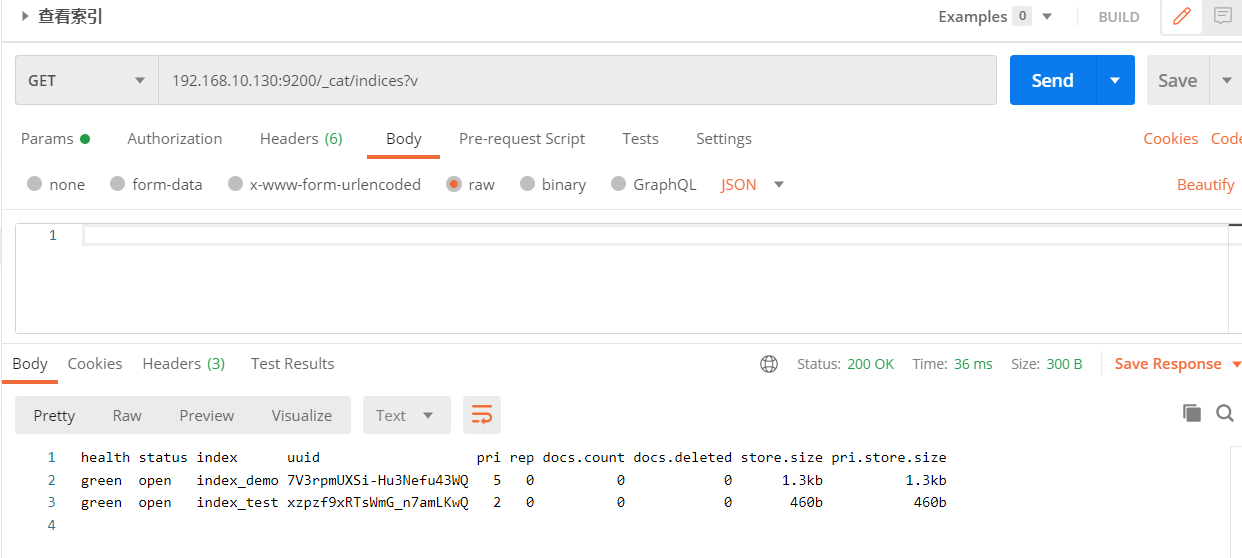
GET /index_test # 查看单个
GET _cat/indices?v # 查看所有
3、删除索引
DELETE /index_test
四、索引的mappings映射
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-params.html
1、创建索引同时创建mappings
PUT /index_test
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "2",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"realname": {
"type": "text",
"index": true
},
"username": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
}
}
}
}
注:index:默认true,设置为false的话,那么这个字段就不会被索引
2、查看分词效果
GET /index_test/_analyze
{
"field": "realname",
"text": "imooc is good"
}
3、为已存在的索引新增mappings
POST /index_test/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"nickname": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"money1": {
"type": "float"
},
"money2": {
"type": "double"
},
"sex": {
"type": "byte"
},
"score": {
"type": "short"
},
"is_teenager": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"birthday": {
"type": "date"
},
"relationship": {
"type": "object"
}
}
}
注:某个属性一旦被建立,就不能修改了,但是可以新增额外属性
映射的数据类型
- text, keyword,
string - long, integer, short, byte
- double, float
- boolean
- date
- object
- 数组不能混,类型一致
字符串:
text:文字类需要被分词被倒排索引的内容,比如 商品名称、商品详情、商品介绍,使用text。
keyword:不会被分词,不会被倒排索引,直接匹配搜索,比如 订单状态、微信号、用户qq、手机号等,这些精确匹配,无需分词。
五、文档的操作
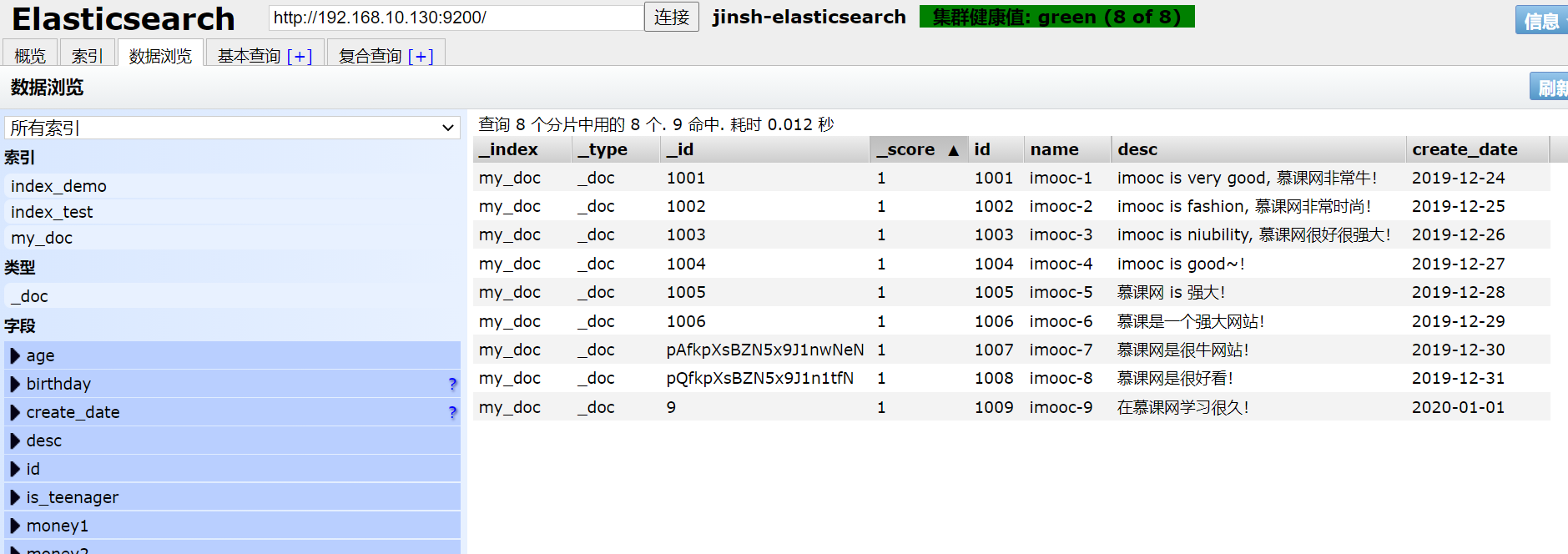
1、添加文档数据
我先添加了个my_doc索引
POST /my_doc/_doc/1 # 索引名/_doc/索引ID(是指索引在es中的id,而不是这条记录的id,比如记录的id从数据库来是1001,并不是这个。如果不写,则自动生成一个字符串。建议和数据id保持一致> )
参数,添加9次
{
"id": 1001,
"name": "imooc-1",
"desc": "imooc is very good, 慕课网非常牛!",
"create_date": "2019-12-24"
}
{
"id": 1002,
"name": "imooc-2",
"desc": "imooc is fashion, 慕课网非常时尚!",
"create_date": "2019-12-25"
}
{
"id": 1003,
"name": "imooc-3",
"desc": "imooc is niubility, 慕课网很好很强大!",
"create_date": "2019-12-26"
}
{
"id": 1004,
"name": "imooc-4",
"desc": "imooc is good~!",
"create_date": "2019-12-27"
}
{
"id": 1005,
"name": "imooc-5",
"desc": "慕课网 is 强大!",
"create_date": "2019-12-28"
}
{
"id": 1006,
"name": "imooc-6",
"desc": "慕课是一个强大网站!",
"create_date": "2019-12-29"
}
{
"id": 1007,
"name": "imooc-7",
"desc": "慕课网是很牛网站!",
"create_date": "2019-12-30"
}
{
"id": 1008,
"name": "imooc-8",
"desc": "慕课网是很好看!",
"create_date": "2019-12-31"
}
{
"id": 1009,
"name": "imooc-9",
"desc": "在慕课网学习很久!",
"create_date": "2020-01-01"
}
注:
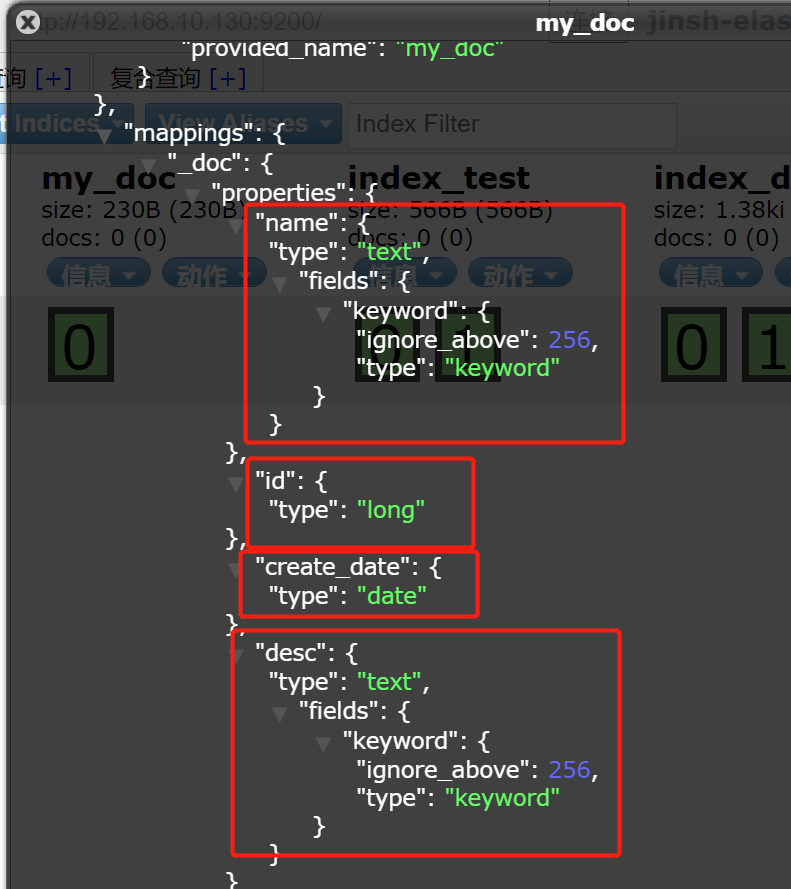
- 如果索引没有手动建立mappings,那么当插入文档数据的时候,会根据文档类型自动设置属性类型。这个就是es的动态映射,帮我们在index索引库中去建立数据结构的相关配置信息。
- "fields": {"type": "keyword"}
对一个字段设置多种索引模式,使用text类型做全文检索,也可使用keyword类型做聚合和排序 - "ignore_above" : 256
设置字段索引和存储的长度最大值,超过则被忽略
2、删除文档数据
DELETE /my_doc/_doc/pQfkpXsBZN5x9J1n1tfN # 最后面跟的是_id
注:文档删除不是立即删除,文档还是保存在磁盘上,索引增长越来越多,才会把那些曾经标识过删除的,进行清理,从磁盘上移出去。
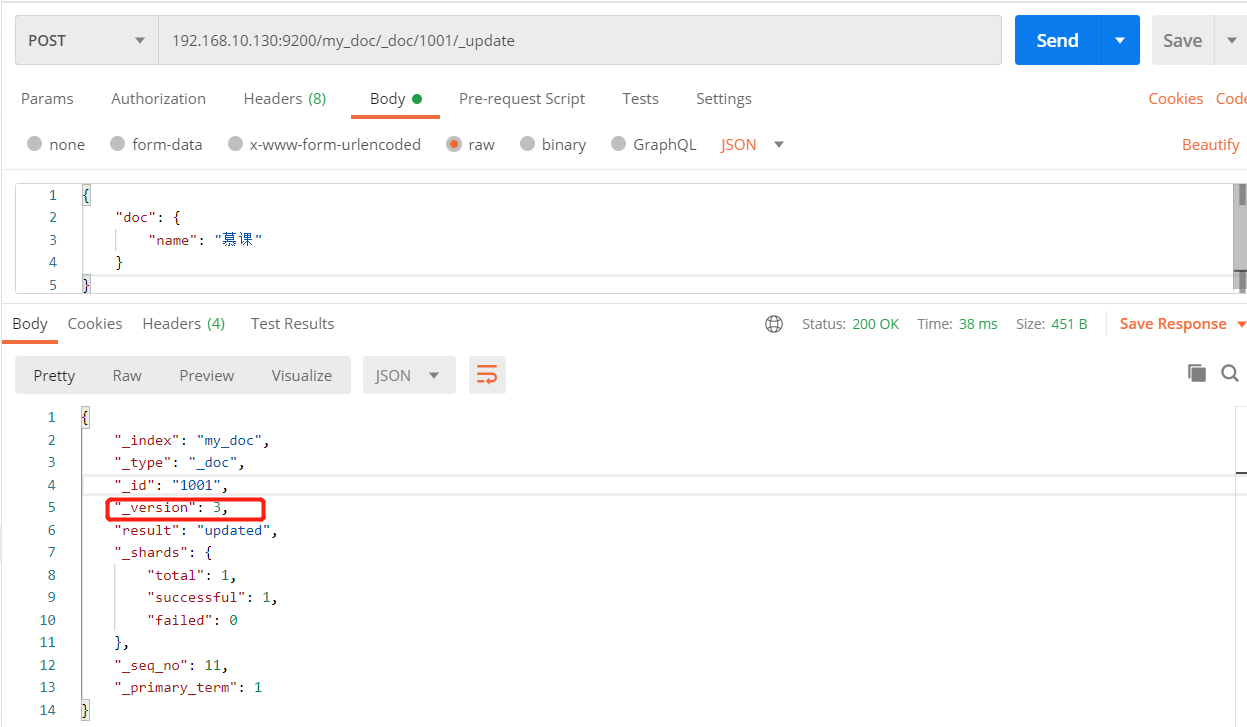
3、修改文档数据
- 只修改单个文档里的单个属性
POST /my_doc/_doc/pQfkpXsBZN5x9J1n1tfN/_update
{
"doc": {
"name": "慕课"
}
}
- 修改整个文档
PUT /my_doc/_doc/1001
{
"id": 1001,
"name": "imooc-1",
"desc": "imooc is very good, 慕课网非常牛!",
"create_date": "2019-12-24"
}
注:每次修改后,version会更改
4、查询
常规查询
GET /index_demo/_doc/2 # 根据_id查询单个
GET /index_demo/_doc/_search # 查询所有
查询结果
{
"_index": "my_doc",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1.0,
"_version": 9,
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "imooc-2",
"desc": "imooc is fashion",
"create_date": "2019-12-25"
}
}
_index:文档数据所属那个索引,理解为数据库的某张表即可。
_type:文档数据属于哪个类型,新版本使用 _doc。
_id:文档数据的唯一标识,类似数据库中某张表的主键。可以自动生成或者手动指定。
_score:查询相关度,是否契合用户匹配,分数越高用户的搜索体验越高。
_version:版本号。
_source:文档数据,json格式。
下面两个新版本里才有,用于文档的乐观锁控制
_seq_no:文档版本号,作用同_version。
_primary_term:文档所在位置(相当于班级)
POST /my_doc/_doc/{_id}/_update?if_seq_no={数值}&if_primary_term={数值}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/optimistic-concurrency-control.html
定制结果集
GET /index_demo/_doc/1?_source=id,name
GET /index_demo/_doc/_search?_source=id,name
查询结果中_source中的属性只查看id和name。
判断文档是否存在
HEAD /index_demo/_doc/1
返回200即存在,404不存在。
六、分词与内置分词器
什么是分词?
把文本转换为一个个的单词,分词称之为 analysis。ES默认只对英文语句做分词,中文不支持,每个中文字都会被拆分为独立的个体。
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "text文本"
}
内置分词器
- standard:默认分词,单词会被拆分,大小会转换为小写。
- simple:按照非字母分词。大写转为小写。
- whitespace:按照空格分词。忽略大小写。
- stop:去除无意义单词,比如 the/a/an/is...
- keyword:不做分词。把整个文本作为一个单独的关键词。
例:
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "My name is Peter Parker,I am a Super Hero. I don't like the Criminals."
}
结果:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "my",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "name",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 7,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "is",
"start_offset": 8,
"end_offset": 10,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "peter",
"start_offset": 11,
"end_offset": 16,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "parker",
"start_offset": 17,
"end_offset": 23,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "i",
"start_offset": 24,
"end_offset": 25,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 5
},
{
"token": "am",
"start_offset": 26,
"end_offset": 28,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 6
},
{
"token": "a",
"start_offset": 29,
"end_offset": 30,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 7
},
{
"token": "super",
"start_offset": 31,
"end_offset": 36,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 8
},
{
"token": "hero",
"start_offset": 37,
"end_offset": 41,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 9
},
{
"token": "i",
"start_offset": 43,
"end_offset": 44,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 10
},
{
"token": "don't",
"start_offset": 45,
"end_offset": 50,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 11
},
{
"token": "like",
"start_offset": 51,
"end_offset": 55,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 12
},
{
"token": "the",
"start_offset": 56,
"end_offset": 59,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 13
},
{
"token": "criminals",
"start_offset": 60,
"end_offset": 69,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 14
}
]
}
IK中文分词器插件
安装:
zip解压后再放到 /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.4.2/plugins/ik 目录下
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip -d /usr/local/elasticsearch-7.4.2/plugins/ik
重启ES。
测试效果:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "上下班车流量很大"
}
返回
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "上下班",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 3,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "上下",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "下班",
"start_offset": 1,
"end_offset": 3,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "班车",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 4,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "车流量",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 4
},
{
"token": "车流",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 5
},
{
"token": "流量",
"start_offset": 4,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 6
},
{
"token": "很大",
"start_offset": 6,
"end_offset": 8,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 7
}
]
}
-
ik_max_word: 会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,中华人民,中华,华人,人民共和国,人民,人,民,共和国,共和,和,国国,国歌”,会穷尽各种可能的组合,适合 Term Query;
-
ik_smart: 会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,国歌”,适合 Phrase 查询。
自定义词库扩展
有些词语IK词库中没有,比如一些新的网络用语和专有名词等,我们可以手动给他添加进词库,进行一个扩展。
/usr/local/elasticsearch-7.4.2/plugins/ik/config/ 目录下 IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml 文件,进行一个修改

然后在config目录下添加一个自定义的 custom.dic文件,文件中输入扩展词汇,一个词一行,然后保存,最后重启ES就可以了。
7、DSL搜索
先准备一些数据
自定义下词库custom.dic
慕课网
慕课
课网
慕
课
网
创建一个shop索引
建立mappings
POST /shop/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"username": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"nickname": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"money": {
"type": "float"
},
"desc": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"sex": {
"type": "byte"
},
"birthday": {
"type": "date"
},
"face": {
"type": "text",
"index": false
}
}
}
录入数据
POST /shop/_doc/1001
{
"id": 1001,
"age": 18,
"username": "imoocAmazing",
"nickname": "慕课网",
"money": 88.8,
"desc": "我在慕课网学习java和前端,学习到了很多知识",
"sex": 0,
"birthday": "1992-12-24",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1002,
"age": 19,
"username": "justbuy",
"nickname": "周杰棍",
"money": 77.8,
"desc": "今天上下班都很堵,车流量很大",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1993-01-24",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1003,
"age": 20,
"username": "bigFace",
"nickname": "飞翔的巨鹰",
"money": 66.8,
"desc": "慕课网团队和导游坐飞机去海外旅游,去了新马泰和欧洲",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1996-01-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1004,
"age": 22,
"username": "flyfish",
"nickname": "水中鱼",
"money": 55.8,
"desc": "昨天在学校的池塘里,看到有很多鱼在游泳,然后就去慕课网上课了",
"sex": 0,
"birthday": "1988-02-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1005,
"age": 25,
"username": "gotoplay",
"nickname": "ps游戏机",
"money": 155.8,
"desc": "今年生日,女友送了我一台play station游戏机,非常好玩,非常不错",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1989-03-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1006,
"age": 19,
"username": "missimooc",
"nickname": "我叫小慕",
"money": 156.8,
"desc": "我叫凌云慕,今年20岁,是一名律师,我在琦䯲星球做演讲",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1993-04-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1007,
"age": 19,
"username": "msgame",
"nickname": "gamexbox",
"money": 1056.8,
"desc": "明天去进货,最近微软处理很多游戏机,还要买xbox游戏卡带",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1985-05-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1008,
"age": 19,
"username": "muke",
"nickname": "慕学习",
"money": 1056.8,
"desc": "大学毕业后,可以到imooc.com进修",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1995-06-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1009,
"age": 22,
"username": "shaonian",
"nickname": "骚年轮",
"money": 96.8,
"desc": "骚年在大学毕业后,考研究生去了",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1998-07-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1010,
"age": 30,
"username": "tata",
"nickname": "隔壁老王",
"money": 100.8,
"desc": "隔壁老外去国外出差,带给我很多好吃的",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1988-07-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1011,
"age": 31,
"username": "sprder",
"nickname": "皮特帕克",
"money": 180.8,
"desc": "它是一个超级英雄",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1989-08-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
{
"id": 1012,
"age": 31,
"username": "super hero",
"nickname": "super hero",
"money": 188.8,
"desc": "BatMan, GreenArrow, SpiderMan, IronMan... are all Super Hero",
"sex": 1,
"birthday": "1980-08-14",
"face": "https://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo.png"
}
请求参数查询(query shtring)
查询某字段包含某内容的文档
GET /shop/_doc/_search?q=desc:慕课网
GET /shop/_doc/_search?q=nickname:慕&q=age:25
这种方式称之为QueryString查询方式,参数都是放在url中作为请求参数的。
DSL查询
QueryString用的很少,一旦参数复杂就难以构建,所以大多查询都会使用dsl来进行查询更好。
- Domain Specific Language
- 特定领域语言
- 基于JSON格式的数据查询
- 查询更灵活,有利于复杂查询
DSL基本语法
# 查询
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网"
}
}
}
# 判断某个字段是否存在
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "desc"
}
}
}
- 语法格式为一个json object,内容都是key-value键值对,json可以嵌套。
match_all
在索引中查询所有的文档
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ["id", "nickname", "age"]
}
_source 限制查询结果显示的字段,只显示"id", "nickname", "age"
分页查询
from:从第几条开始
size:每页显示几条
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10
}
-
深度分页
ES分页from最多只能到9999,我们在获取第9999条到10009条数据的时候,其实每个分片都会拿到10009条数据,然后集合在一起,总共是10009*3=30027条数据,针对30027数据再次做排序处理,最终会获取最后10条数据。如此一来,搜索得太深,就会造成性能问题,会耗费内存和占用cpu。而且es为了性能,他不支持超过一万条数据以上的分页查询。那么如何解决深度分页带来的性能呢?其实我们应该避免深度分页操作(限制分页页数),比如最多只能提供100页的展示,从第101页开始就没了,毕竟用户也不会搜的那么深,我们平时搜索淘宝或者百度,一般也就看个10来页就顶多了。 -
分页的from限制也是可以更改的
GET /shop/_settings # 查询
PUT /shop/_settings # 修改
{
"index.max_result_window": "20000"
}
term/match
- term精确搜索
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"desc": "慕课网"
}
}
}
term 就是精确匹配,”慕课网“作为一整个词去匹配
- match分词搜索
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网"
}
}
}
match 会对”慕课网“进行分词,”慕课网“、”慕课“、”课网“、”慕“、”课“、”网“,然后根据分词去匹配
- terms 多个词语匹配
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"desc": ["慕课网", "学习", "骚年"]
}
}
}
match扩展
- operator:
- or:搜索内容分词后,只要存在一个词语匹配就展示结果
- and:搜索内容分词后,都要满足词语匹配
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网"
}
}
}
# 等同于
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": {
"query": "xbox游戏机",
"operator": "or"
}
}
}
}
# 相当于 select * from shop where desc='xbox' or|and desc='游戏机'
- minimum_should_match: 最低匹配精度,至少有[分词后的词语个数]x百分百,得出一个数据值取整。举个例子:当前属性设置为70,若一个用户查询检索内容分词后有10个词语,那么匹配度按照 10x70%=7,则desc中至少需要有7个词语匹配,就展示;若分词后有8个,则 8x70%=5.6,则desc中至少需要有5个词语匹配,就展示。
- minimum_should_match 也能设置具体的数字,表示个数
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": {
"query": "女友生日送我好玩的xbox游戏机",
"minimum_should_match": "60%"
}
}
}
}
match_phrase 短语匹配
match:分词后只要有匹配就返回,match_phrase:分词结果必须在text字段分词中都包含,而且顺序必须相同,而且必须都是连续的。(搜索比较严格)
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"desc": {
"query": "大学 毕业 研究生",
"slop": 2
}
}
}
}
slop:表示允许词语间跳过的词的数量
根据文档主键ids搜索
GET /shop/_doc/1001
# 查询多个
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"type": "_doc",
"values": ["1001", "1010", "1008"]
}
}
}
multi_match
满足使用match在多个字段中进行查询的需求
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "皮特帕克慕课网",
"fields": ["desc", "nickname"]
}
}
}
boost:权重,为某个字段设置权重,权重越高,文档相关性得分就越高。通畅来说搜索商品名称要比商品简介的权重更高。
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "皮特帕克慕课网",
"fields": ["desc", "nickname^10"]
}
}
}
nickname^10 代表搜索提升10倍相关性,也就是说用户搜索的时候其实以这个nickname为主,desc为辅,nickname的匹配相关度当然要提高权重比例了。
布尔查询
可以组合多重查询
- must:查询必须匹配搜索条件,譬如 and
- should:查询匹配满足1个以上条件,譬如 or
- must_not:不匹配搜索条件,一个都不要满足
例1:
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "慕课网",
"fields": ["desc", "nickname"]
}
},
{
"term": {
"sex": 1
}
},
{
"term": {
"birthday": "1996-01-14"
}
}
]
}
}
}
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should(must_not)": [
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "学习",
"fields": ["desc", "nickname"]
}
},
{
"match": {
"desc": "游戏"
}
},
{
"term": {
"sex": 0
}
}
]
}
}
}
例2:
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"desc": "慕"
}
},
{
"match": {
"nickname": "慕"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"sex": "0"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"birthday": "1992-12-24"
}
}
]
}
}
}
Head 可视化组合查询

为指定词语加权
特殊场景下,某些词语可以单独加权,这样可以排得更加靠前。
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"desc": {
"query": "律师",
"boost": 18
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"desc": {
"query": "进修",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
过滤器
对搜索出来的结果进行数据过滤。不会到es库里去搜,不会去计算文档的相关度分数,所以过滤的性能会比较高,过滤器可以和全文搜索结合在一起使用。
post_filter元素是一个顶层元素,只会对搜索结果进行过滤。不会计算数据的匹配度相关性分数,不会根据分数去排序,query则相反,会计算分数,也会按照分数去排序。
使用场景:
- query:根据用户搜索条件检索匹配记录
- post_filter:用于查询后,对结果数据的筛选
实操:查询账户金额大于80元,小于160元的用户。并且描述包含”慕课网游戏“的文档。
- gte:大于等于
- lte:小于等于
- gt:大于
- lt:小于
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网游戏"
}
},
"post_filter": {
"range": {
"money": {
"gt": 80,
"lt": 160
}
}
}
}
排序
- 数字类型排序
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网游戏"
}
},
"post_filter": {
"range": {
"money": {
"gt": 55.8,
"lte": 155.8
}
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": "desc"
},
{
"money": "desc"
}
]
}
- 文本型排序
由于文本会被分词,所以往往要去做排序会报错,通常我们可以为这个字段增加额外的一个附属属性,类型为keyword,用于做排序。
例:先创建个新索引和mappings
POST /shop2/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"nickname": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"fields": {
"keyword": { # 这个keyword是自定义的,可以改
"type": "keyword" # 附属属性的type必须为keyword,这个text类型字段才能排序
}
}
}
}
}
添加一些数据
POST /shop2/_doc
{
"id": 1001,
"nickname": "美丽的风景"
}
{
"id": 1002,
"nickname": "漂亮的小哥哥"
}
{
"id": 1003,
"nickname": "飞翔的巨鹰"
}
{
"id": 1004,
"nickname": "完美的天空"
}
{
"id": 1005,
"nickname": "广阔的海域"
}
排序:
{
"sort": [
{
"nickname.keyword": "desc" # 这里的.keyword是取上面自定义的名称
}
]
}
高亮highlight
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"desc": "慕课网"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": ["<tag>"],
"post_tags": ["</tag>"],
"fields": {
"desc": {}
}
}
}
pre_tags和post_tags,自定义高亮现实的标签,不写的话默认标签是<em>。
模糊匹配
- prefix
根据前缀去查询
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"desc": "imo"
}
}
}
- fuzzy
模糊搜索,用户在进行搜索的时候的打字错误现象,搜索引擎会自动纠正,然后尝试匹配索引库中的数据。
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"desc": "imoov.coom"
}
}
}
# 或多字段搜索
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": [ "desc", "nickname"],
"query": "imcoc supor",
"fuzziness": "AUTO"
}
}
}
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"fields": [ "desc", "nickname"],
"query": "演说",
"fuzziness": "1"
}
}
}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/fuzzy-match-query.html
- wildcard
占位符查询- ?:1个字符
- *:1个或多个字符
POST /shop/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"desc": "*oo?"
}
}
}
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"desc": "演*"
}
}
}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-wildcard-query.html
滚动搜索
一次性查询1万+数据,往往会造成性能影响,因为数据量太多了。这个时候可以使用滚动搜索,也就是 scroll。
滚动搜索可以先查询出一些数据,然后再紧接着依次往下查询。在第一次查询的时候会有一个滚动id,相当于一个锚标记,随后再次滚动搜索会需要上一次搜索的锚标记,根据这个进行下一次的搜索请求。每次搜索都是基于一个历史的数据快照,查询数据的期间,如果有数据变更,那么和搜索是没有关系的,搜索的内容还是快照中的数据。
POST /shop/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
},
"sort" : ["_doc"],
"size": 5
}
POST /_search/scroll
{
"scroll": "1m",
"scroll_id" : "your last scroll_id"
}
- scroll=1m,相当于是一个session会话时间,搜索保持的上下文时间为1分钟。
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/scroll.html
批量查询 mget
POST /shop/_doc/_mget
{
"ids": ["1001","1002","1003", "1111"]
}
批量操作 bulk
基本语法
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
...
bulk操作和以往的普通请求格式有区别。不要格式化json,不然就不在同一行了,这个需要注意。
- { action: { metadata }} 代表批量操作的类型,可以是新增、删除或修改
- \n 是每行结尾必须填写的一个规范,每一行包括最后一行都要写,用于es的解析
- { request body } 是请求body,增加和修改操作需要,删除操作则不需要
批量操作类型
action 必须是以下选项之一:
- create:如果文档不存在,那么就创建它。存在会报错。发生异常报错不会影响其他操作。
- index:创建一个新文档或者替换一个现有的文档。
- update:部分更新一个文档。
- delete:删除一个文档。
实操
- create新增文档数据,在metadata中指定index以及type
POST /_bulk
{"create": {"_index": "shop2", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "2001"}}
{"id": "2001", "nickname": "name2001"}
{"create": {"_index": "shop2", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "2002"}}
{"id": "2002", "nickname": "name2002"}
{"create": {"_index": "shop2", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "2003"}}
{"id": "2003", "nickname": "name2003"}
- create创建已有id文档,在url中指定index和type
POST /shop/_doc/_bulk
{"create": {"_id": "2003"}}
{"id": "2003", "nickname": "name2003"}
{"create": {"_id": "2004"}}
{"id": "2004", "nickname": "name2004"}
{"create": {"_id": "2005"}}
{"id": "2005", "nickname": "name2005"}
- index创建,已有文档id会被覆盖,不存在的id则新增
POST /shop/_doc/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": "2004"}}
{"id": "2004", "nickname": "index2004"}
{"index": {"_id": "2007"}}
{"id": "2007", "nickname": "name2007"}
{"index": {"_id": "2008"}}
{"id": "2008", "nickname": "name2008"}
- update跟新部分文档数据
POST /shop/_doc/_bulk
{"update": {"_id": "2004"}}
{"doc":{ "id": "3004"}}
{"update": {"_id": "2007"}}
{"doc":{ "nickname": "nameupdate"}}
- delete批量删除
POST /shop/_doc/_bulk
{"delete": {"_id": "2004"}}
{"delete": {"_id": "2007"}}
- 综合批量各种操作
POST /shop/_doc/_bulk
{"create": {"_id": "8001"}}
{"id": "8001", "nickname": "name8001"}
{"update": {"_id": "2001"}}
{"doc":{ "id": "20010"}}
{"delete": {"_id": "2003"}}
{"delete": {"_id": "2005"}}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/bulk.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号