rest-assured对接口返回的不同格式的数据进行解析
由于要模拟接口返回的不同格式的数据,这里使用node.js搭建一个简单的服务
node.js教程:https://www.runoob.com/nodejs/nodejs-tutorial.html
一、node.js的下载安装: 下载地址:https://nodejs.org/en/download/
安装双击程序,直接下一步安装即可
验证是否安装成功:cmd命令窗口-->node --version
编写第一个应用:
新建一个helloword.js文件,编辑文件,代码如下:
var http = require('http');
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
// 发送 HTTP 头部
// HTTP 状态值: 200 : OK
// 内容类型: text/plain
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
// 发送响应数据 "Hello World"
response.end('Hello World\n');
}).listen(8888);
// 终端打印如下信息
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8888/');
将此文件放到根目录下,如cmd窗口进入的跟目录为: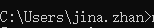 ,就将此文件放到C:\Users\jina.zhan目录下
,就将此文件放到C:\Users\jina.zhan目录下
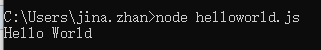
cmd窗口输入命令:node helloword.js,可启动服务:
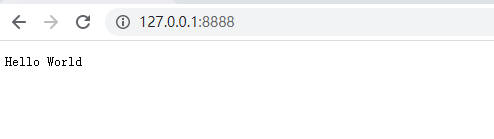
在浏览器中输入:http://127.0.0.1:8888/
二、利用node.js编写一个应用返回xml格式的数据,使用rest-assured对xml数据进行校验:
node.js代码:
var http = require('http');
const urlib = require("url");
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
var myobj = urlib.parse(request.url,true);
var firstName = myobj.query.firstName;
var lastName = myobj.query.lastName;
// 发送 HTTP 头部
// HTTP 状态值: 200 : OK
// 内容类型: text/plain
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'application/xml'});
// 发送响应数据 "Hello World"
response.end('<greeting><firstName>'+firstName+'</firstName><lastName>'+lastName+'</lastName></greeting> ');
}).listen(8888);
// 终端打印如下信息
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8888/?firstName=abc&lastName=aaa');
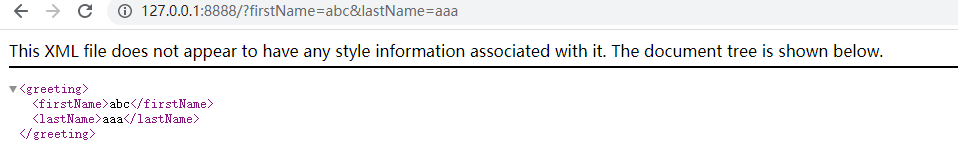
浏览器返回结果如下:
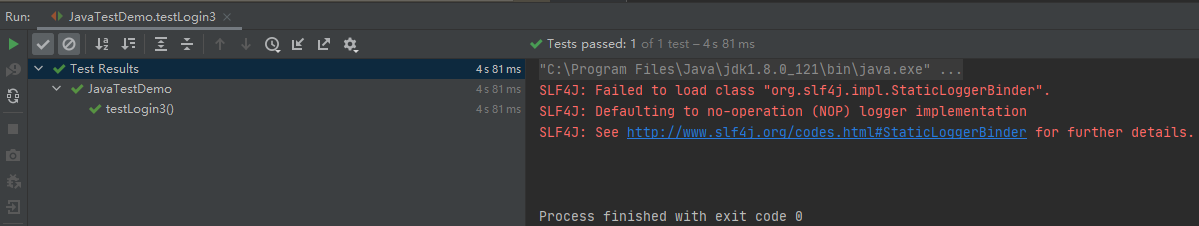
rest-assured对应代码:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
given()
.contentType("application/xml")
.post("http://127.0.0.1:8888/?firstName=abc&lastName=aaa")
.then()
.body("greeting.firstName",equalTo("abc"))
.body("greeting.lastName",equalTo("aaa"));
}
运行结果:
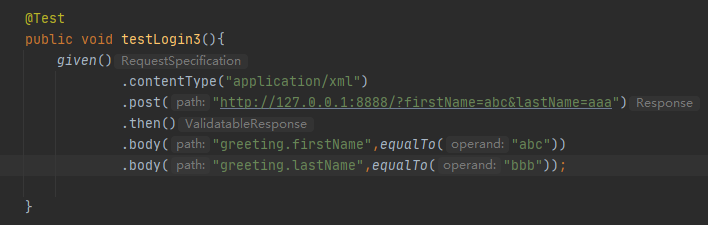
如果将lastName故意写错,再校验:
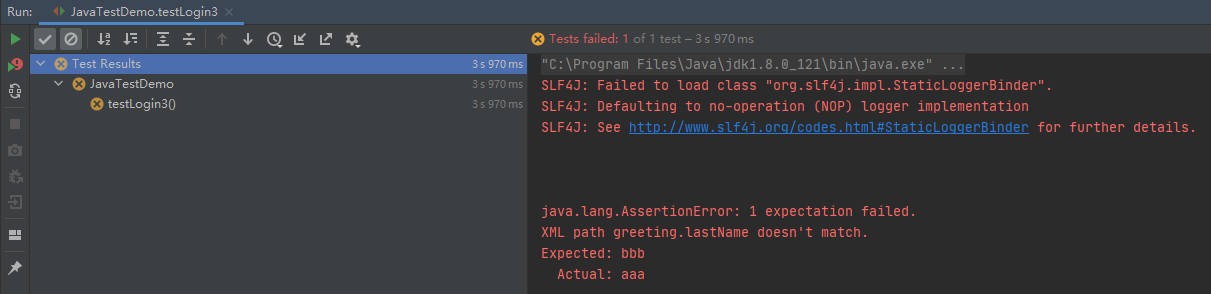
运行结果:
或者写成这样也是可以的:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
with().when().post("http://127.0.0.1:8888/?firstName=abc&lastName=aaa").then().body("greeting.firstName", equalTo("abc"), "greeting.lastName", equalTo("aaa"));
}
二、rest-assured对json数据进行断言
node.js代码:
先创建一个json文件lotto.json,内容如下:
{
"lotto": {
"lottoId": 5,
"winning-numbers": [2, 45, 34, 23, 7, 5, 3],
"winners": [{
"winnerId": 23,
"numbers": [2, 45, 34, 23, 3, 5]
}, {
"winnerId": 54,
"numbers": [52, 3, 12, 11, 18, 22]
}]
}
}
再创建一个js文件server2.js,代码如下:
var http = require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'application/json'});
fs.readFile( "lotto.json", 'utf8', function (err, data) {
console.log( data );
response.end( data );
});
}).listen(8888);
// 终端打印如下信息
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto');
再浏览器中访问地址:http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto
响应结果如下:
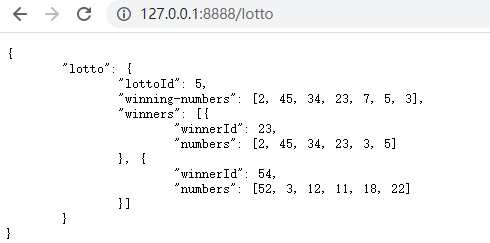
1.如果想要判断 lottoId 的值是否等于 5
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto").then().body("lotto.lottoId", equalTo(5));
}
2.想要检查 winnerId 的取值包括23 和 54
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto").then().body("lotto.winners.winnerId", hasItems(23, 54));
}
注意: equalTo 和 hasItems 是 Hamcrest matchers 的方法,所以需要静态导入 org.hamcrest.Matchers
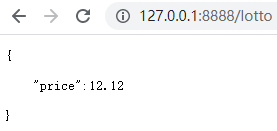
3.验证 price 字段是否等于 float 类型的 12.12
修改lotto.json文件内容为:
{
"price":12.12
}
刷新页面:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto").then().body("price", is(12.12f));
}
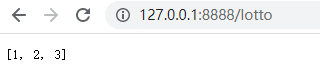
4.一个 JSON 文本并不总是有一个命名好的根属性。这里有个验证这种 JSON 的例子:
修改lotto.json文件内容为:
[1, 2, 3]
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
when().
get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto").
then().
body("$", hasItems(1, 2, 3));
}
5.比方说我们有个资源返回如下的 XML:
<shopping>
<category type="groceries">
<item>Chocolate</item>
<item>Coffee</item>
</category>
<category type="supplies">
<item>Paper</item>
<item quantity="4">Pens</item>
</category>
<category type="present">
<item when="Aug 10">Kathryn's Birthday</item>
</category>
</shopping>
比如我们想写一个测试来检验类型为 groceries 的 category 节点有 Chocolate 和 Coffee 这两个项目。在 rest-assured 可以这样做:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
given()
.when()
.get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto")
.then()
.body("shopping.category.find { it.@type == 'groceries' }.item", hasItems("Chocolate", "Coffee"));
//或者写成
//.body("**.find { it.@type == 'groceries' }.item", hasItems("Chocolate", "Coffee"));
}
如果只想获取到类型为 groceries 的 category 节点下的值不做校验,可写为:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
String response = get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto").asString();
List<String> groceries = from(response).getList("shopping.category.find { it.@type == 'groceries' }.item");
for(String i:groceries){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
6.假设返回如下的 JSON:
{
"store":{
"book":[
{
"author":"Nigel Rees",
"category":"reference",
"price":8.95,
"title":"Sayings of the Century"
},
{
"author":"Evelyn Waugh",
"category":"fiction",
"price":12.99,
"title":"Sword of Honour"
},
{
"author":"Herman Melville",
"category":"fiction",
"isbn":"0-553-21311-3",
"price":8.99,
"title":"Moby Dick"
},
{
"author":"J. R. R. Tolkien",
"category":"fiction",
"isbn":"0-395-19395-8",
"price":22.99,
"title":"The Lord of the Rings"
}
]
}
}
断言:搜集满足 price 字段值小于 10 的所有 book 数组里的 title 字段,得到了"Sayings of the Century"和"Moby Dick"这两个结果:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
given()
.when()
.get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto")
.then()
.body("store.book.findAll { it.price < 10 }.title", hasItems("Sayings of the Century", "Moby Dick"));
}
断言所有 author 字段值长度总和是否大于 50 的结果
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
given()
.when()
.get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto")
.then()
.body("store.book.author.collect { it.length() }.sum()", greaterThan(50));
}
7.假设返回的数据:
{
"title" : "My Title",
"_links": {
"self": { "href": "/title" },
"next": { "href": "/title?page=2" }
}
}
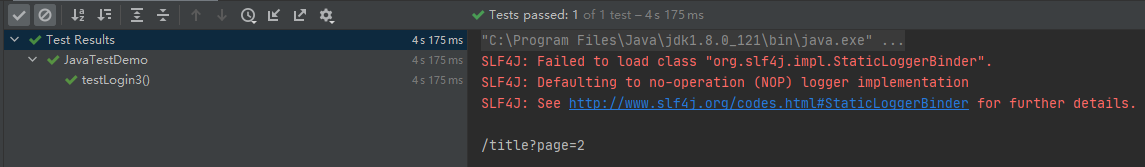
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
String link= given()
.when()
.get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto")
.then()
.body("title", equalTo("My Title"))
.extract()
.path("_links.next.href");
System.out.println(link);
}
运行结果:
如果想提取多个值,也可以考虑返回整个响应体:
@Test
public void testLogin3(){
Response re= given()
.when()
.get("http://127.0.0.1:8888/lotto")
.then()
.body("title", equalTo("My Title"))
.extract()
.response();
String nextTitleLink = re.path("_links.next.href");
System.out.println(nextTitleLink);
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号