Spring Security 身份认证流程讲解
这里有个简化版的图:
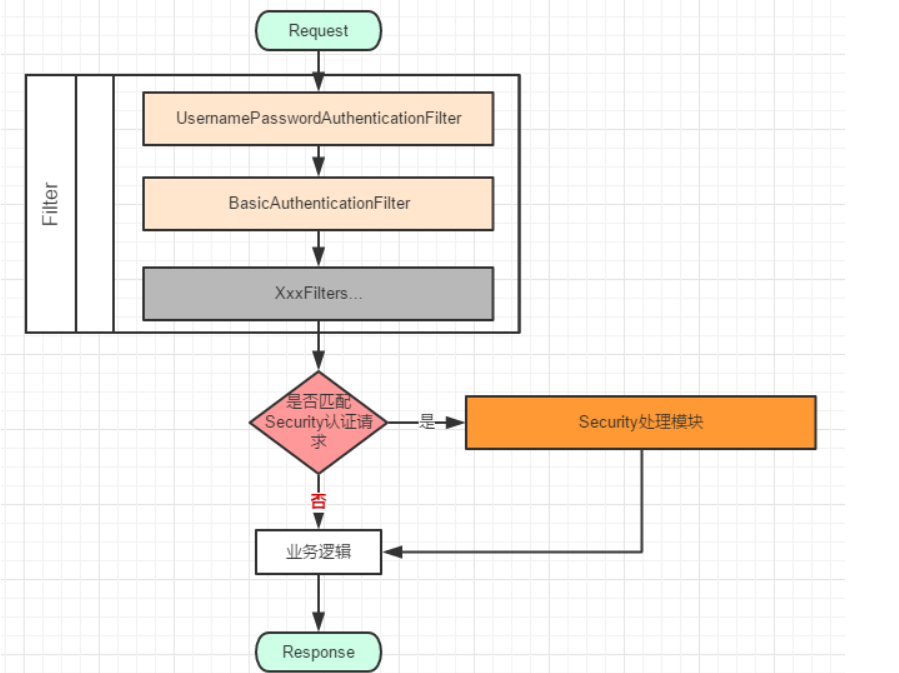
根据JavaEE的流程,本质就是Filter过滤请求,转发到不同处理模块处理,最后经过业务逻辑处理,返回Response的过程。
当请求匹配了我们定义的Security Filter的时候,就会导向Security 模块进行处理,例如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(这里是精简了的代码)
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password";
private String usernameParameter = "username";
private String passwordParameter = "password";
private boolean postOnly = true;
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
//1.匹配URL和Method
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
//啥?你没有用POST方法,给你一个异常,自己反思去
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
//从请求中获取参数
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
//我不知道用户名密码是不是对的,所以构造一个未认证的Token先
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
//顺便把请求和Token存起来
this.setDetails(request, token);
//Token给谁处理呢?当然是给当前的AuthenticationManager喽
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(token);
}
}
}
那怎么区别token 是否认证了呢?
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 510L;
//未认证是是用户名密码
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
//这个构造方法用来初始化一个没有认证的Token实例
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super((Collection)null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
this.setAuthenticated(false);
}
//这个构造方法用来初始化一个已经认证的Token实例,为啥要多此一举,不能直接Set状态么,不着急,往后看
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true);
}
//便于理解无视他
public Object getCredentials() {
return this.credentials;
}
//便于理解无视他
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (isAuthenticated) {
//如果是Set认证状态,就无情的给一个异常,意思是:
//不要在这里设置已认证,不要在这里设置已认证,不要在这里设置已认证
//应该从构造方法里创建,别忘了要带上用户信息和权限列表哦
//原来如此,是避免犯错吧
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
} else {
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
}
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
this.credentials = null;
}
}
AuthenticationManager会注册多种AuthenticationProvider,例如UsernamePassword对应的DaoAuthenticationProvider,既然有多种选择,那怎么确定使用哪个Provider呢?以DaoAuthenticationProvider为例
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
//熟悉的supports,需要UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
//取出Token里保存的值
String username = authentication.getPrincipal() == null ? "NONE_PROVIDED" : authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
//从缓存取
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
//啥,没缓存?使用retrieveUser方法获取呀
user = this.retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)authentication);
}
//...删减了一大部分,这样更简洁
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (this.forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
return this.createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
try {
//熟悉的loadUserByUsername
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
} else {
return loadedUser;
}
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException var4) {
this.mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw var4;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var5) {
throw var5;
} catch (Exception var6) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
}
//检验密码
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
} else {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
}
}
所以整体的流程是:
Filter->构造Token->AuthenticationManager->转给Provider处理->认证处理成功后续操作或者不通过抛异常




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号