多线层相关
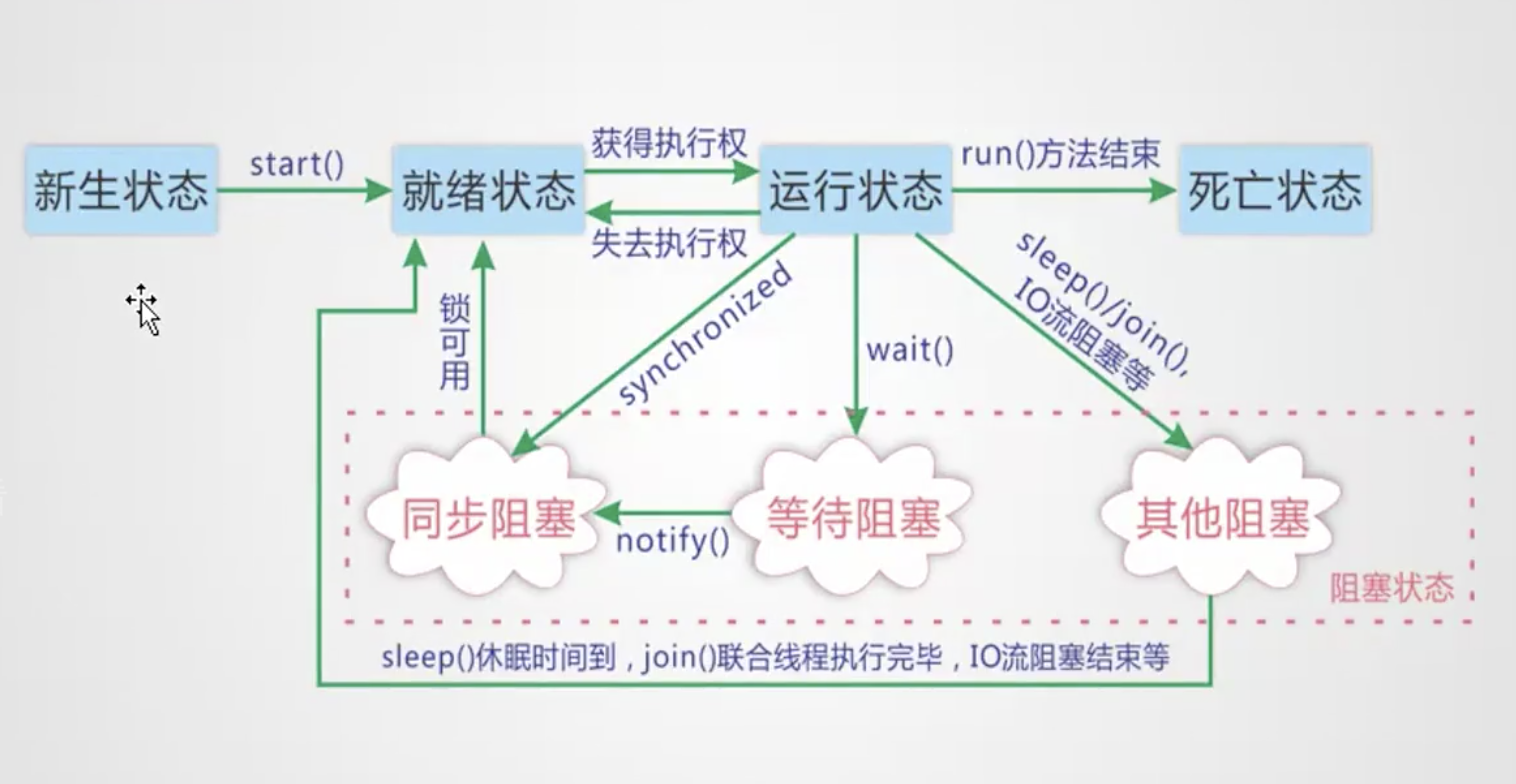
创建线程的方式:
1: 继承Thread

package com.sxt.thread; /** * 创建线程方式一: * 1、创建:继承Thread+重写run * 2、启动: 创建子类对象 + start * @author * */ public class StartThread extends Thread{ /** * 线程入口点 */ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //创建子类对象 StartThread st =new StartThread(); //启动 st.start(); //不保证立即运行 cpu调用 //st.run(); //普通方法调用 for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { System.out.println("一边coding"); } } }
2: 实现Runnable接口

package com.sxt.thread; /** * 创建线程方式二: * 1、创建:实现Runnable+重写run * 2、启动: 创建实现类对象 +Thread对象+ start * * 推荐: 避免单继承的局限性,优先使用接口 * 方便共享资源 * @author * */ public class StartRun implements Runnable{ /** * 线程入口点 */ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { /*//创建实现类对象 StartRun sr =new StartRun(); //创建代理类对象 Thread t =new Thread(sr); //启动 t.start(); //不保证立即运行 cpu调用 */ new Thread(new StartRun()).start(); //st.run(); //普通方法调用 for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { System.out.println("一边coding"); } } }
3:实现Callable接口(线程安全)

package com.sxt.thread; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /** * 了解创建线程的方式三: * * @author * */ public class CDownloader implements Callable<Boolean>{ private String url; //远程路径 private String name; //存储名字 public CDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { WebDownloader wd =new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); return true; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CDownloader cd1 =new CDownloader("http://upload.news.cecb2b.com/2014/0511/1399775432250.jpg","phone.jpg"); CDownloader cd2 =new CDownloader("http://p1.pstatp.com/large/403c00037462ae2eee13","spl.jpg"); CDownloader cd3 =new CDownloader("http://5b0988e595225.cdn.sohucs.com/images/20170830/d8b57e0dce0d4fa29bd5ef014be663d5.jpeg","success.jpg"); //创建执行服务: ExecutorService ser=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //提交执行: Future<Boolean> result1 =ser.submit(cd1) ; Future<Boolean> result2 =ser.submit(cd2) ; Future<Boolean> result3 =ser.submit(cd3) ; //获取结果: boolean r1 =result1.get(); boolean r2 =result1.get(); boolean r3 =result1.get(); System.out.println(r3); //关闭服务: ser.shutdownNow(); } }
lamda表达式

new Thread(()->{ //run方法 }).start();
线程控制方法:
sleep
暂停: 当前线程被阻塞,任务回到待添加状态;
如果调用了sleep方法之后,没有其他等待执行的线程,这个时候当前线程不会马上恢复执行
yield
礼让: 让当前正在执行的线程暂停,不是阻塞线程,而是将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态,让CPU调度器重新调用.
如果调用了yield方法之后,没有其他等待执行的线程,这个时候当前线程就会马上恢复执行
join
插队: 阻塞指定线程等到另一个线程完成以后再继续执行
设置优先级:

package com.test.thread; public class PriorityTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority(); Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程一"); Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程二"); Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程三"); Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程四"); Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程五"); Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority, "线程六"); //设置优先级在启动前 t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t3.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); t4.setPriority(8); t5.setPriority(7); t6.setPriority(1); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); t4.start(); t5.start(); t6.start(); /** 线程一===>10 线程三===>5 线程二===>1 线程四===>8 线程五===>7 线程六===>1 */ } } class MyPriority implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===>" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); } }
守护线程:
setDatmon(false),默认为false
守护线程是为用户线程服务的,jvm停止不用等待守护线程执行完毕
默认:jvm等待用户线程执行完毕才会停止
isAlive: 线程是否还活着
setName: 设置名称(代理角色的名称,如果是真实角色的名称,向真实角色对象设置name属性)
getName:
Thread.currentThread():
线程安全:
如果只是对数据进行读取,不需要考虑线程安全;如果是读取后需要改动数据,则需要考虑线程安全问题
并发:
同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
synchronized:
synchronized方法: 锁this
synchronized块: 锁具体对象,一般就是要修改的对象

package com.test.thread; public class CinemaTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Cinema2 c2 = new Cinema2(3, "官网"); Customer2 ct1 = new Customer2(c2, "张三", 2); Customer2 ct2 = new Customer2(c2, "李四", 1); ct1.start(); ct2.start(); } } class Customer2 extends Thread { int seats; public Customer2 (Runnable target, String nameString, int seats) { super(target, nameString); this.seats = seats; } } class Cinema2 implements Runnable { int available; String nameString; public Cinema2(int available, String nameString) { this.available = available; this.nameString = nameString; } @Override public void run() { Customer2 ct = (Customer2)Thread.currentThread(); boolean flag = getTickets(ct.seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("购票成功" + "===>" + "剩余票数" + available); }else { System.err.println("出票失败"); } } public synchronized boolean getTickets(int tiketsNum) { if (available - tiketsNum >= 0) { available -= tiketsNum; return true; }else { return false; } } }
模拟售票:

package com.test.thread; public class BuyTicketTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //同一份资源 SaleTickets sale = new SaleTickets(); //被多个线程同时调用 new Thread(sale, "张三").start(); new Thread(sale, "李四").start(); new Thread(sale, "王五").start(); } } class SaleTickets implements Runnable { private int ticketsNumber = 5; private boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { while (flag) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } sale(); } } /* * synchronized块,锁住具体对象 */ public void sale() { //如果没有票了,线程不进行等待,提高效率 if (ticketsNumber <= 0) { flag = false; return; } //flag,ticketsNumber都需要进行修改,锁住this synchronized (this) { if (ticketsNumber <= 0) { flag = false; return; } System.out.println("当前剩余票数--->" + ticketsNumber-- + "---->" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } /** * synchronized 方法, 锁住this * 线程安全 同步 */ public synchronized void sale2() { if(ticketsNumber<=0) { flag = false; return ; } //模拟延时 try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("当前剩余票数--->" + ticketsNumber-- + "---->" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
容器:

package com.sxt.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 线程安全:操作容器 * * @author * */ public class SynBlockTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { new Thread(()->{ //同步块 synchronized(list) { list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }) .start(); } Thread.sleep(10000); System.out.println(list.size()); } }
CopyOnWriteArrayList 并发容器:

package com.sxt.syn; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 线程安全:操作并发容器 * * @author * */ public class SynContainer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { new Thread(()->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }) .start(); } Thread.sleep(10000); System.out.println(list.size()); } }
synchronized块模拟影院售票:

package com.test.thread; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class CinemaTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list1.add(1); list1.add(2); list1.add(3); list1.add(4); list1.add(5); list1.add(6); list1.add(7); List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list2.add(1); list2.add(2); list2.add(3); List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list3.add(1); list3.add(6); list3.add(7); Cinema cinema = new Cinema(list1, "百老汇"); Customer c1Customer = new Customer(list2, cinema); Customer c2Customer = new Customer(list3, cinema); new Thread(c1Customer).start(); new Thread(c2Customer).start(); } } class Customer implements Runnable { List<Integer> seats; Cinema cinema; public Customer(List<Integer> seats, Cinema cinema) { this.seats = seats; this.cinema = cinema; } public Customer() { } @Override public void run() { synchronized (cinema) { boolean flag = cinema.getTickets(seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("欢迎光临" + cinema.name + "===>" + "购票成功" + "===>" + "购票位置为" + seats + "===>" + "剩余票数" + cinema.available); }else { System.out.println("购票失败"); } } } } class Cinema { List<Integer> available; String name; public Cinema(List<Integer> available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } public boolean getTickets(List<Integer> ticktesNums) { List<Integer> copyList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); copyList.addAll(available); copyList.removeAll(ticktesNums); System.out.println("ticktesNums: " + ticktesNums); System.out.println("copyList剩座位" + copyList); if (available.size() == ticktesNums.size() + copyList.size() ) { available = copyList; return true; }else { return false; } } }
synchronized方法模拟影院售票:

package com.test.thread; public class CinemaTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Cinema2 c2 = new Cinema2(3, "官网"); Customer2 ct1 = new Customer2(c2, "张三", 2); Customer2 ct2 = new Customer2(c2, "李四", 1); ct1.start(); ct2.start(); } } class Customer2 extends Thread { int seats; public Customer2 (Runnable target, String nameString, int seats) { super(target, nameString); this.seats = seats; } } class Cinema2 implements Runnable { int available; String nameString; public Cinema2(int available, String nameString) { this.available = available; this.nameString = nameString; } @Override public void run() { Customer2 ct = (Customer2)Thread.currentThread(); boolean flag = getTickets(ct.seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("购票成功" + "===>" + "剩余票数" + available); }else { System.err.println("出票失败"); } } public synchronized boolean getTickets(int tiketsNum) { if (available - tiketsNum >= 0) { available -= tiketsNum; return true; }else { return false; } } }
Timer

package com.sxt.others; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; /** * 任务调度: Timer 和TimerTask类 * * @author * */ public class TimerTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer(); //执行安排 //timer.schedule(new MyTask(), 1000); //执行任务一次 //timer.schedule(new MyTask(), 1000,200); //执行多次 Calendar cal = new GregorianCalendar(2099999,12,31,21,53,54); timer.schedule(new MyTask(), cal.getTime(),200); //指定时间 } } //任务类 class MyTask extends TimerTask{ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { System.out.println("放空大脑休息一会"); } System.out.println("------end-------"); } }
Volatile
volatile保证线程间变量的可见性,简单地说就是当线程A对变量X进行了修改,在线程A后面执行的其他线程能看到变量X的变动,更详细的说是要符合以下两个规则:
1: 线程对变量进行修改之后,要立刻回写到主内存
2: 线程对变量读取的时候,要从主内存中读,而不是缓存
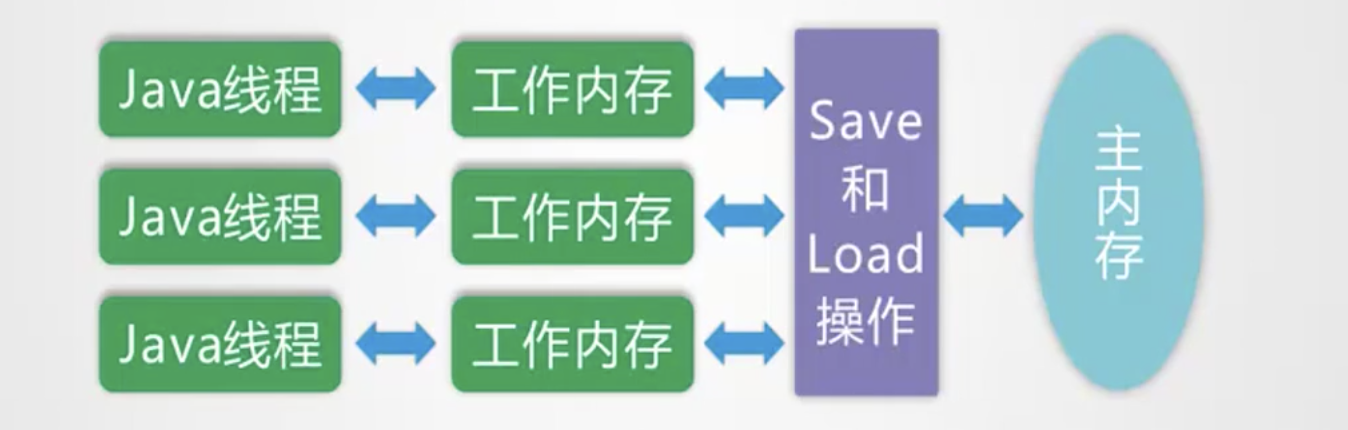
各线程的工作内存间彼此独立,互不可见,在线程启动的时候,虚拟机为每个内存分配一块工作内存,不仅包含了线程内部定义的局部变量,也包含了线程所需要使用的(非线程内构造的对象)的副本,即为了提高执行效率
volatile是不错的机制,但volatile不能保证原子性
现在机器性能比较强大,很少出现线程忙不过的情况,所以volatile在开发中较少使用

package com.sxt.others; /** * volatile用于保证数据的同步,也就是可见性 * * @author * */ public class VolatileTest { private volatile static int num = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(()->{ while(num==0) { //此处不要编写代码 // 不加volatile,此处死循环 } }) .start(); Thread.sleep(1000); num = 1; } }
DCL单例模式:

package com.sxt.others; /** * DCL单例模式: 懒汉式套路基础上加入并发控制,保证在多线程环境下,对外存在一个对象 * 1、构造器私有化 -->避免外部new构造器 * 2、提供私有的静态属性 -->存储对象的地址 * 3、提供公共的静态方法 --> 获取属性 * * * */ public class DoubleCheckedLocking { //2、提供私有的静态属性 //没有volatile其他线程可能访问一个没有初始化的对象 private static volatile DoubleCheckedLocking instance; //1、构造器私有化 private DoubleCheckedLocking() { } //3、提供公共的静态方法 --> 获取属性 public static DoubleCheckedLocking getInstance() { //再次检测 if(null!=instance) { //避免不必要的同步 ,已经存在对象 return instance; } synchronized(DoubleCheckedLocking.class) { if(null == instance) { instance = new DoubleCheckedLocking(); //1、开辟空间 //2、初始化对象信息 //3、返回对象的地址给引用 } } return instance; } public static DoubleCheckedLocking getInstance1(long time) { if(null == instance) { try { Thread.sleep(time); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } instance = new DoubleCheckedLocking(); //1、开辟空间 //2、初始化对象信息 //3、返回对象的地址给引用 } return instance; } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(DoubleCheckedLocking.getInstance()); }) ; t.start(); System.out.println(DoubleCheckedLocking.getInstance()); } }
ThreadLocal:

package com.sxt.others; /** * ThreadLocal:每个线程自身的存储本地、局部区域 * get/set/initialValue * @author 裴新 QQ:3401997271 * */ public class ThreadLocalTest01 { //private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<> (); //更改初始化值 /*private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<> () { protected Integer initialValue() { return 200; }; };*/ private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> 200); public static void main(String[] args) { //获取值 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get());//main-->200 //设置值 threadLocal.set(99); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get());//main-->99 new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } public static class MyRun implements Runnable{ public void run() { threadLocal.set((int)(Math.random()*99));//Thread-1-->28; Thread-0-->65 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); } } }

package com.sxt.others; /** * ThreadLocal:每个线程自身的数据,更改不会影响其他线程 * Thread-0得到了-->1 Thread-0还剩下-->0 Thread-1得到了-->1 Thread-2得到了-->1 Thread-1还剩下-->0 Thread-3得到了-->1 Thread-4得到了-->1 Thread-2还剩下-->0 Thread-4还剩下-->0 Thread-3还剩下-->0 * */ public class ThreadLocalTest02 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> 1); public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } } public static class MyRun implements Runnable{ public void run() { Integer left =threadLocal.get(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"得到了-->"+left); threadLocal.set(left -1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"还剩下-->"+threadLocal.get()); } } }

package com.sxt.others; /** * ThreadLocal:分析上下文 环境 起点 * 1、构造器: 哪里调用 就属于哪里 找线程体 * 2、run方法:本线程自身的 * * */ public class ThreadLocalTest03 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> 1); public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } public static class MyRun implements Runnable{ public MyRun() { threadLocal.set(-100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); } public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); //new Thread(new MyRunxxx()).start(); } } } /* * main-->-100 main-->-100 Thread-0-->1 Thread-1-->1 * */

package com.sxt.others; /** * InheritableThreadLocal:继承上下文 环境的数据 ,拷贝一份给子线程 * * main-->2 Thread-0-->2 Thread-0-->200 * */ public class ThreadLocalTest04 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { threadLocal.set(2); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); //线程由main线程开辟 new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); threadLocal.set(200); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get()); }) .start(); } }
posted on 2019-08-16 09:51 JieFangZhe 阅读(187) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号