- 经常的创建和销毁,会占用特别大的资源,对性能影响很大。
- 思路:提前穿件好多个线程,放入线程池中,使用时直接获取,使用完放回池中,可以避免频繁创建销毁、实现重复利用。
- 好处:
- 提高响应速度(减少创建新线程的时间)
- 降低资源消耗(重复利用线程池中的线程,不需要每次都创建)
- 便于线程管理
- corePoolSize:核心池的大小
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数
- keepAliveTime:线程没有任务时最多保持多长时间后终止
使用线程池
- ExecutorService:真正的线程池接口。
- void execute(Runnable command):执行任务/命令,没有返回值
- Future submit(Callable task):执行任务,有返回值,一般又来执行Callable
- void shutdown():关闭连接池
- Executors:工具类、线程池的工厂类,用于创建并返回不同类型的线程池
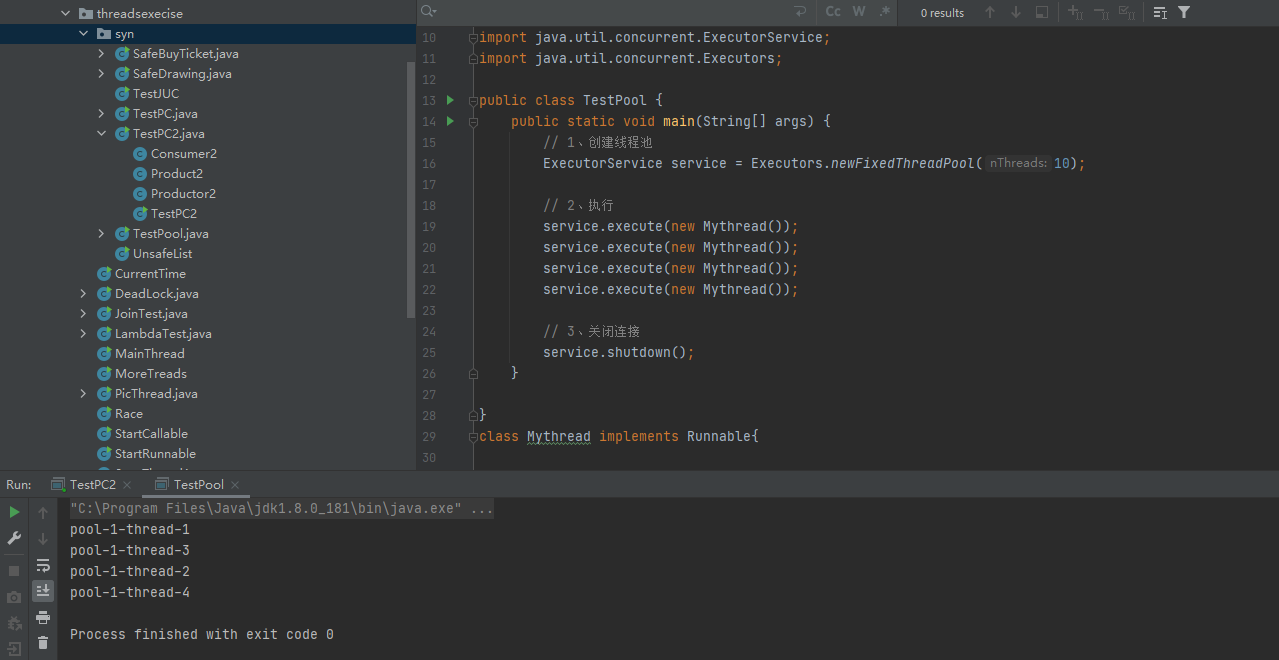
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、创建线程池
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 2、执行
service.execute(new Mythread());
service.execute(new Mythread());
service.execute(new Mythread());
service.execute(new Mythread());
// 3、关闭连接
service.shutdown();
}
}
class Mythread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号