【狂神说Java】线程同步机制
多个线程操作同一个资源
处理多线程问题,多个线程访问同一个对象,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象。这时候我们就要线程同步。线程同步其实是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等待前面的线程使用完毕,下一个线程再使用。
队列和锁
- 由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突问题,为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制【synchronized】
- 当一个线程获得对象耳朵排他锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用完毕后释放锁即可,存在以下问题:
- 一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起
- 在多线程竞争下,加锁,释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,CPU压力上升,引发性能问题
- 如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁,会导致优先级倒置,引发性能问题
不安全的例子
- 银行取钱
public class SafeDrawing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(200,"1123");
Drawing a = new Drawing(account,100,0,"aaa");
Drawing b = new Drawing(account,200,0,"bbb");
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
class Account{
public Account(int money, String id) {
this.money = money;
this.id = id;
}
// 银行账户
int money;// 余额
String id;// 账号
}
class Drawing extends Thread{
Account account; // 账户
int drawingMoney; //取钱
int nowMoney; // 手上的钱
public Drawing(Account id,int drawingMoney,int nowMoney,String name){
super(name);
this.account = id;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
this.nowMoney = nowMoney;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 判断有没有钱
if (account.money < drawingMoney){
System.out.println("钱不够");
return;
}
// 加延时,先不更新数据
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 账户上的钱
account.money -= drawingMoney;
// 你手里的钱
nowMoney += drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.id+ "账户余额为:"+ account.money);
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱为:"+ nowMoney);
}
}
- 10000个线程同时跑添加list,结果如下:
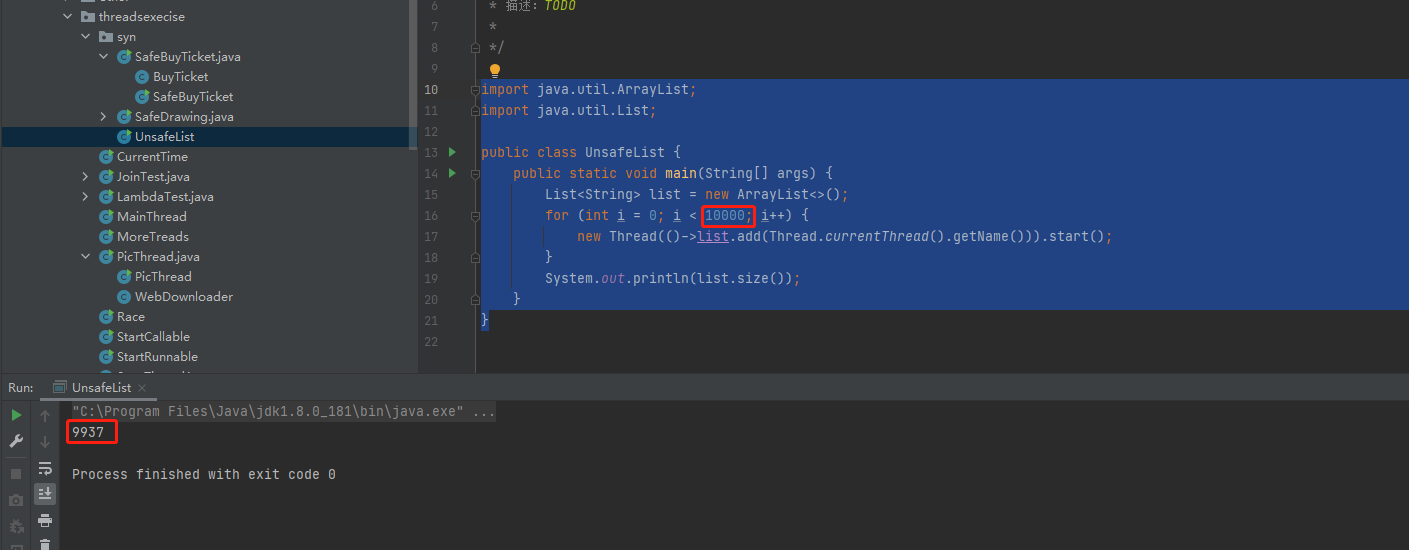
代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName())).start();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号