标签平滑实战 mnist手写字体识别
全部代码如下

# https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42325947/article/details/108318673 # mnist import torch import torchvision import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch import optim from matplotlib import pyplot as plt def plot_curve(data): fig = plt.figure() plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue') plt.legend(['value'], loc='upper right') plt.xlabel('step') plt.ylabel('value') plt.show() def plot_image(img, label, name): fig = plt.figure() for i in range(6): plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1) plt.tight_layout() plt.imshow(img[i][0] * 0.3081 + 0.1307, cmap='gray', interpolation='none') plt.title("{}: {}".format(name, label[i].item())) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.show() # 加载数据集 batch_size = 512 train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( torchvision.datasets.MNIST('mnist_data', train=True, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose( [ torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # 这里的两个数字分别是数据集的均值是0.1307,标准差是0.3081 ] ) ), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True ) test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( torchvision.datasets.MNIST('mnist_data/', train=False, download=True, # 是验证集所以train=False transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose( [ torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), torchvision.transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) ] ) ), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False # 是验证集所以无需打乱,shuffle=False ) # 创建网络模型 class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() #wx+b self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28*28,256)#256是自己根据经验随机设定的 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256,64) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64,10)#注意这里的10是最后识别的类别数(最后一层的输出往往是识别的类别数) def forward(self, x): #x : [ b 1 28 28]有batch_size张图片,通道是1维灰度图像 图片大小是28*28 #h1=relu(wx+b) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))#使用relu非线性激活函数包裹 x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) #x = F.softmax(self.fc3(x))#由于是多类别识别,所以使用softmax函数 x = F.relu(self.fc3(x)) #x = self.fc3(x) return x # 训练 net = Net() optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.1,momentum=0.9) train_loss = [] for epoch in range(5): for batch_idx,(x,y) in enumerate(train_loader):#enumerate表示在数据前面加上序号组成元组,默认序号从0开始 # x :[512 1 28 28] y : [512] #由于这里的x维度为[512 1 28 28],但是在网络中第一层就是一个全连接层,维度只能是[b,feature(784)],所以要把x打平 #将前面多维度的tensor展平成一维 # 卷积或者池化之后的tensor的维度为(batchsize,channels,x,y),其中x.size(0) # 指batchsize的值,最后通过x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 将tensor的结构转换为了(batchsize, channels * x * y),即将(channels,x,y)拉直,然后就可以和fc层连接了 x = x.view(x.size(0),28*28) #输出之后的维度变为[512,10] out=net(x) #使用交叉熵损失 # loss = F.cross_entropy(out,y) # ************************************************************************************************************* # 使用LabelSmoothing LS = LabelSmoothing(smoothing=0.1) loss = LS(out, y) # ************************************************************************************************************* #清零梯度——计算梯度——更新梯度 #要进行梯度的清零 optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() #功能是: w` = w-lr*grad optimizer.step() train_loss.append(loss.item())#将loss保存在trainloss中,而loss.item()表示将tensor 的类型转换为数值类型 #打印loss if batch_idx % 10 == 0: print(epoch,batch_idx,loss.item()) # 验证 plot_curve(train_loss) total_correct = 0 for x, y in test_loader: x = x.view(x.size(0),28*28) out = net(x) #out :[512,10] pred = out.argmax(dim = 1) correct = pred.eq(y).sum().float().item()#当前批次识别对的个数 total_correct+= correct total_number = len(test_loader.dataset) acc = total_correct / total_number print('test acc',acc) x,y = next(iter(test_loader)) out = net(x.view(x.size(0),28*28)) pred = out.argmax(dim=1) plot_image(x,pred,'test')
这个main.py要调用我前面文章(https://www.cnblogs.com/jie-74/p/15686416.html)提到的LabelSmoothing类

import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.autograd import Variable # Wangleiofficial # https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/7455#issuecomment-720100742 class LabelSmoothingLoss(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, smoothing: float = 0.1, reduction="mean", weight=None): super(LabelSmoothingLoss, self).__init__() self.smoothing = smoothing self.reduction = reduction self.weight = weight def reduce_loss(self, loss): return loss.mean() if self.reduction == 'mean' else loss.sum() \ if self.reduction == 'sum' else loss def linear_combination(self, x, y): return self.smoothing * x + (1 - self.smoothing) * y def forward(self, preds, target): assert 0 <= self.smoothing < 1 if self.weight is not None: self.weight = self.weight.to(preds.device) n = preds.size(-1) log_preds = F.log_softmax(preds, dim=-1) loss = self.reduce_loss(-log_preds.sum(dim=-1)) nll = F.nll_loss( log_preds, target, reduction=self.reduction, weight=self.weight ) return self.linear_combination(loss / n, nll) # NVIDIA # https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples/blob/8d8b21a933fff3defb692e0527fca15532da5dc6/PyTorch/Classification/ConvNets/image_classification/smoothing.py#L18 class LabelSmoothing(nn.Module): """NLL loss with label smoothing. """ def __init__(self, smoothing=0.0): # 平滑因子 """Constructor for the LabelSmoothing module. :param smoothing: label smoothing factor """ super(LabelSmoothing, self).__init__() self.confidence = 1.0 - smoothing self.smoothing = smoothing def forward(self, x, target): logprobs = torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(x, dim=-1) # x: (batch size * class数量),即log(p(k)) nll_loss = -logprobs.gather(dim=-1, index=target.unsqueeze(1)) # target: (batch size) 数字标签 # 相当于取出logprobs中的真实标签的那个位置的logit的负值 nll_loss = nll_loss.squeeze(1) # (batch size * 1)再squeeze成batch size,即log(p(k))δk,y,δk,y表示除了k=y时该值为1,其余为0 smooth_loss = -logprobs.mean(dim=-1) # 在class维度取均值,就是对每个样本x的所有类的logprobs取了平均值。 # smooth_loss = -log(p(k))u(k) = -log(p(k))∗ 1/k loss = self.confidence * nll_loss + self.smoothing * smooth_loss # (batch size) # loss = (1−ϵ)log(p(k))δk,y + ϵlog(p(k))u(k) return loss.mean() # −∑ k=1~K [(1−ϵ)log(p(k))δk,y+ϵlog(p(k))u(k)] if __name__=="__main__": # Wangleiofficial crit = LabelSmoothingLoss(smoothing=0.3, reduction="mean") predict = torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0.2, 0.7, 0.1, 0], [0, 0.9, 0.2, 0.2, 1], [1, 0.2, 0.7, 0.9, 1]]) v = crit(Variable(predict), Variable(torch.LongTensor([2, 1, 0]))) print(v) # NVIDIA crit = LabelSmoothing(smoothing=0.3) predict = torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0.2, 0.7, 0.1, 0], [0, 0.9, 0.2, 0.2, 1], [1, 0.2, 0.7, 0.9, 1]]) v = crit(Variable(predict), Variable(torch.LongTensor([2, 1, 0]))) print(v) # tensor(1.3883) # tensor(1.3883)
两个文件放在同一文件夹下即可,单独运行main.py是手写数字识别,单独运行LabelSmoothing.py是一个小demo

参考自 pytorch实现mnist识别实战
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42325947/article/details/108318673
有评论提到

果断百度,确实如评论所说
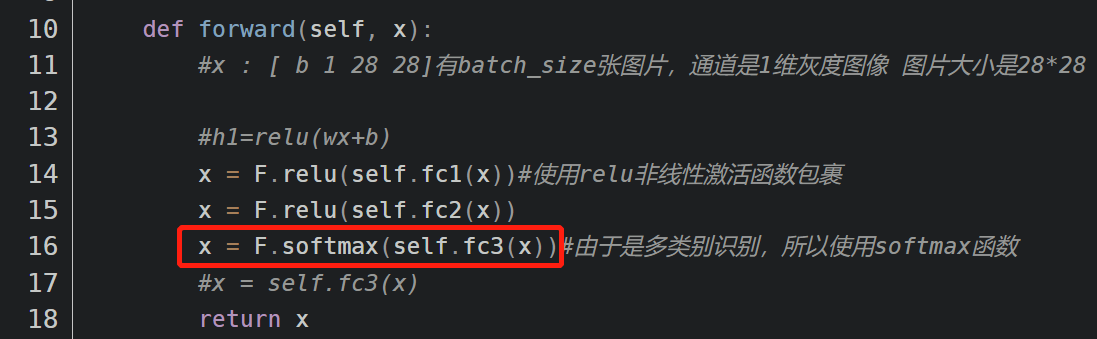
可以把上图红框注释,如下图所示换成x = F.relu(self.fc3(x))

不过我们今天的重点不是用普通的loss,是用Label Smoothing

调用我们前一篇文章使用的LabelSmoothing类
最后得到使用LabelSmoothing的前后准确率,左图使用LS前0.974,右图后0.982
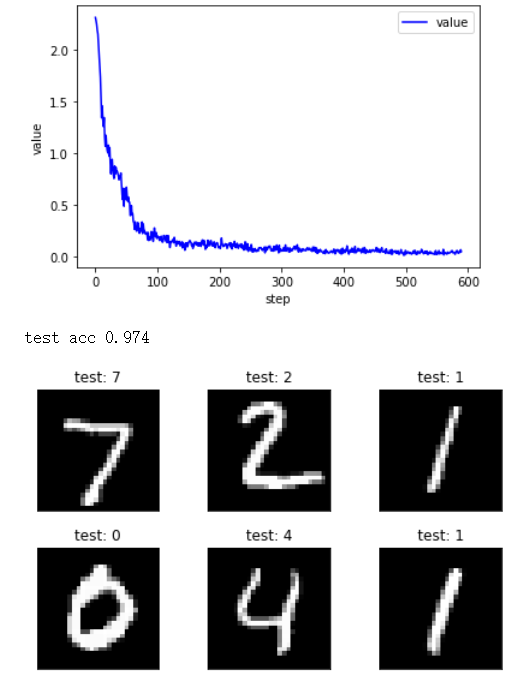
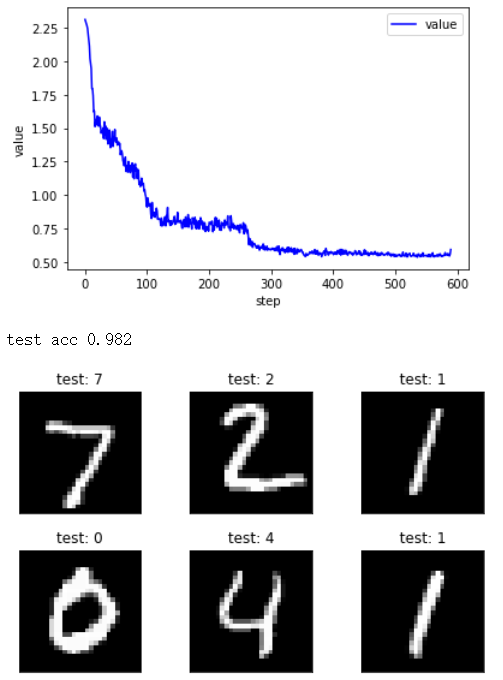
先了解LabelSmoothing,可以跳转到https://www.cnblogs.com/jie-74/p/15686416.html
摸鱼失败




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号