重载与多态
一、概念
重载:函数名相同,但是函数参数不同。调用时根据参数的不同决定调用哪一个函数
多态:函数名相同,函数形参也相同。调用时根据函数类型是虚函数还是普通成员函数决定调用哪一个
重写:若子类和父类的某个函数具有相同的函数名,相同的形参列表,且父类中的函数被定义为虚函数,则子类对该函数的实现被称为函数的重写
二、重载
1.函数重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
class chongZ
{
public:
void print(int i) {
cout << "重载1" << i << endl;
}
{
public:
void print(int i) {
cout << "重载1" << i << endl;
}
void print(double j) {
cout << "重载2 " << j << endl;
}
cout << "重载2 " << j << endl;
}
void print(char c[]) {
cout << "重载3 " << c << endl;
}
};
cout << "重载3 " << c << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
chongZ CZ;
CZ.print(5);
CZ.print(123.456);
char c[] = "CHONGZZAI";
CZ.print(c);
return 0;
}
{
chongZ CZ;
CZ.print(5);
CZ.print(123.456);
char c[] = "CHONGZZAI";
CZ.print(c);
return 0;
}
运行结果: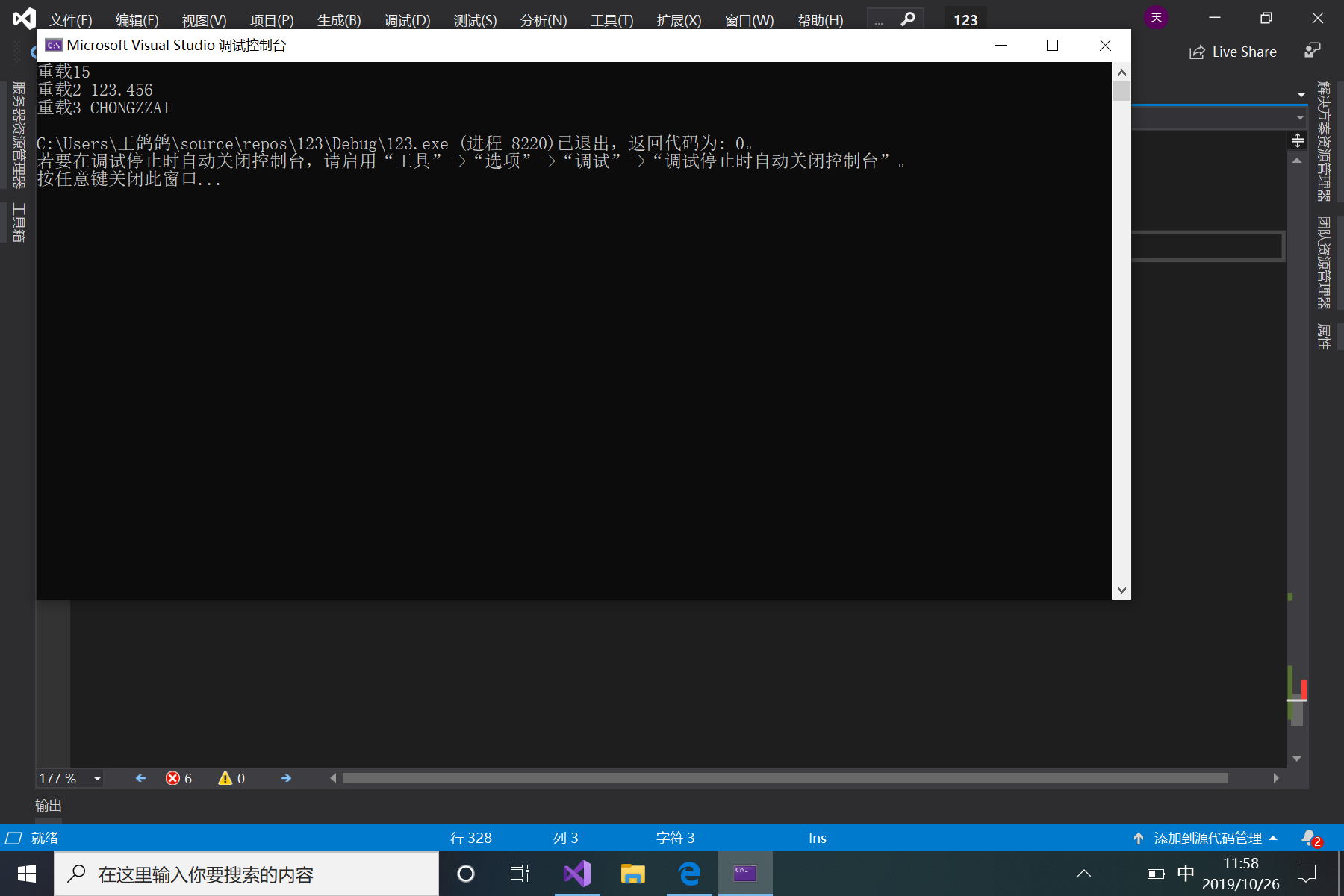
2.运算符重载
其语法形式为:
返回类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体
}
仿照该语法形式重载“++”运算符
1 Point operator +(const Point& A ,const Point& B) { 2 return Point(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); 3 }
该重载运算符的作用是让A,B中的x,y相加,放入程序中运行:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct Point { 5 int x, y; 6 Point(int x = 0, int y = 0) :x(x), y(y) {}; 7 }; 8 9 Point operator +(const Point& A ,const Point& B) { 10 return Point(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); 11 } 12 ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Point& p) { 13 out << "(" << p.x << "," << p.y << ")"; 14 return out; 15 } 16 int main() 17 { 18 Point a, b(1, 2); 19 a.x = 3; 20 cout << a + b << "\n"; 21 return 0; 22 }
运行结果:

实现了(1,2)和(3,0)相加。
对于前置单目运算符,重载函数没有形参,对于后置单目运算符,重载函数有一个int型形参,如以下程序中:
#include <iostream> using namespce std; class Point { public: Point& operator++(); Point operator++(int); Point& operator--(); Point operator--(int); Point() { _x = _y = 0; } int x() { return _x; } int y() { return _y; } private: int _x, _y; }; Point& Point::operator++() { _x++; _y++; return *this; } Point Point::operator++(int) { Point temp = *this; ++*this; return temp; } Point& Point::operator--() { _x--; _y--; return *this; } Point Point::operator--(int) { Point temp = *this; --*this; return temp; } void main() { Point A; cout << "A 的值为:" << A.x() << " , " << A.y() << endl; A++; cout << "A 的值为:" << A.x() << " , " << A.y() << endl; ++A; cout << "A 的值为:" << A.x() << " , " << A.y() << endl; A--; cout << "A 的值为:" << A.x() << " , " << A.y() << endl; --A; cout << "A 的值为:" << A.x() << " , " << A.y() << endl; }
以同时重载前缀和后缀的形式对Point类“++”,“--”运算符进行重载
三、多态
相较于重载来说,函数名相同,函数形参也相同的叫多态。在基类的函数前加上virtual关键字,在派生类中重写该函数,运行时将会根据对象的实际类型来调用相应的函数。即对象类型是派生类,就调用派生类的函数;对象类型是基类,就调用基类的函数。
如课后题8-6
编写一个抽象类Shape,在此基础上派生出类Rectangle和Circle,二者都有计算对象面积的函数getArea()、计算对象周长的函数getPerim()
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Shape 5 { 6 public: 7 Shape(){} 8 ~Shape(){} 9 virtual float GetArea() =0 ; //纯虚函数,抽象类就是具有纯虚函数的类 10 virtual float GetPerim () =0 ; 11 }; 12 class Circle : public Shape 13 { 14 public: 15 Circle(float radius):itsRadius(radius){} 16 ~Circle(){} 17 float GetArea() { 18 return 3.14 * itsRadius * itsRadius; 19 } 20 float GetPerim () { 21 return 6.28 * itsRadius; 22 } 23 private: 24 float itsRadius; 25 }; 26 class Rectangle : public Shape 27 { 28 public: 29 Rectangle(float len, float width): itsLength(len), itsWidth(width){}; 30 ~Rectangle(){}; 31 virtual float GetArea() { //虚函数 32 return itsLength * itsWidth; 33 } 34 float GetPerim () { 35 return 2 * itsLength + 2 * itsWidth; 36 } 37 virtual float GetLength() { 38 return itsLength; 39 } 40 virtual float GetWidth() { 41 return itsWidth; 42 } 43 private: 44 float itsWidth; 45 float itsLength; 46 }; 47 void main() 48 { 49 Shape * sp; 50 sp = new Circle(5); 51 cout << "The area of the Circle is " << sp->GetArea () << endl; 52 cout << "The perimeter of the Circle is " << sp->GetPerim () << endl; 53 delete sp; 54 sp = new Rectangle(4,6); 55 cout << "The area of the Rectangle is " << sp->GetArea() << endl; 56 cout << "The perimeter of the Rectangle is " << sp->GetPerim () << endl; 57 delete sp; 58 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号