#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class vectorInt {
private:
int n;
int value;
int* arr;
public:
vectorInt(int n0,int value0 = 0 )
{ value = value0;
n = n0;
arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = value;
}
cout << "constructor called. "<<endl;
};
vectorInt(const vectorInt& v)
{
n = v.n;
value = v.value;
arr = new int[v.n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = v.value;
}
cout << "copy constructor called." << endl;
}
~vectorInt()
{
if (arr != NULL)
{
delete[]arr;
arr = NULL;
}
cout << "destructer called." << endl;
}
int &at(int x)
{
return arr[x];
}
int output()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl; return 0;
}
int get_size()
{
return n;
}
};
void output(vectorInt & T) {
for (int i = 0; i < T.get_size(); ++i) {
cout << T.at(i) << ", ";
}
cout << "\b\b \n";
}
#include <iostream>
#include "vectorInt.hpp"
void test() {
using namespace std;
int n;
cin >> n;
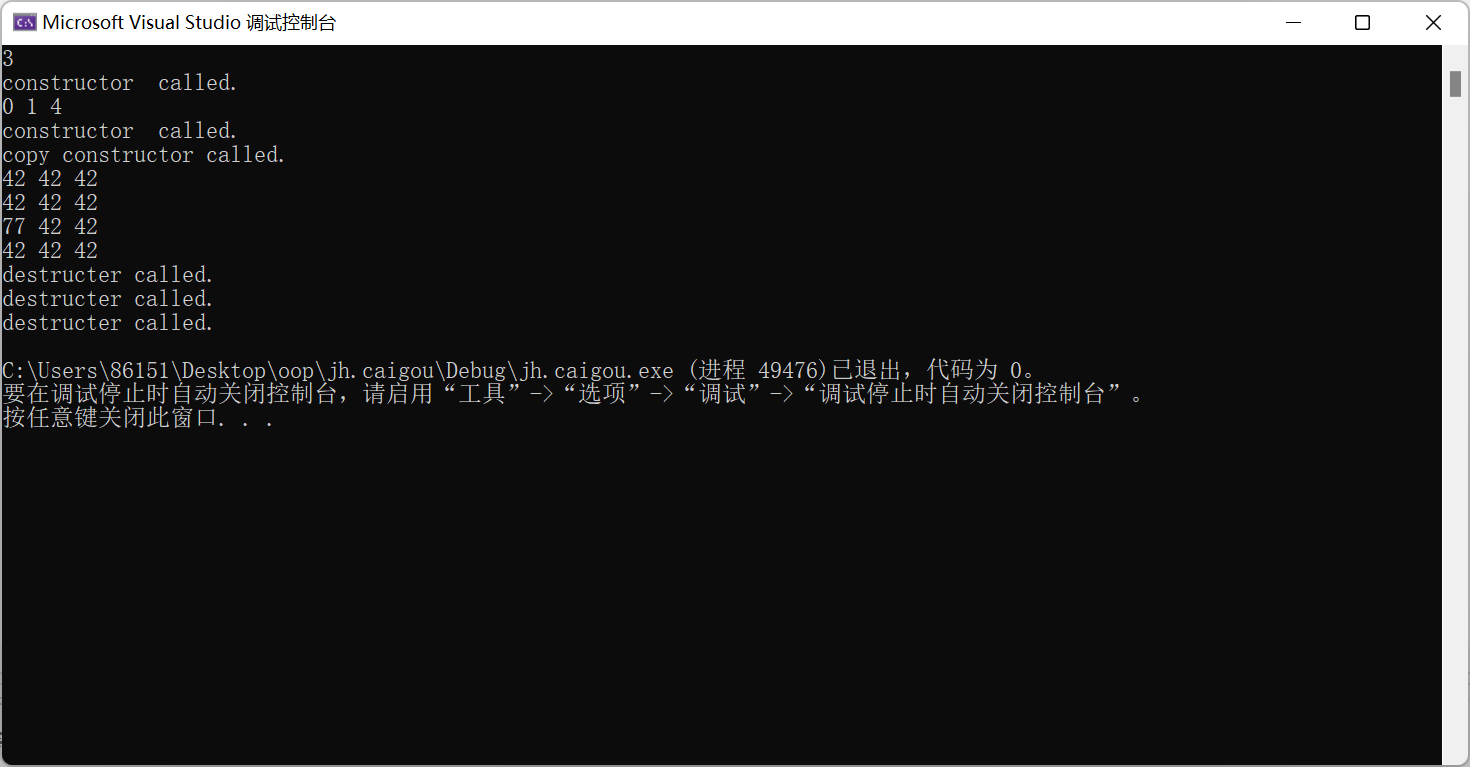
vectorInt x1(n);
for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
x1.at(i) = i * i;
x1.output();
vectorInt x2(n, 42);
vectorInt x3(x2);
output(x2);
output(x3);
x2.at(0) = 77;
output(x2);
output(x3);
}
int main() {
test();
}
![]()
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Matrix {
public:
Matrix(int n); // 构造函数,构造一个n*n的矩阵
Matrix(int n, int m); // 构造函数,构造一个n*m的矩阵
Matrix(const Matrix& X); // 复制构造函数,使用已有的矩阵X构造
~Matrix()//析构函数
{ delete[]p; }
void set(const double* pvalue); // 用pvalue指向的连续内存块数据按行为矩阵
void set(int i, int j, int value); //设置矩阵第i行第j列元素值为value
//返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的引用
double at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的值
int get_lines() const; //返回矩阵行数
int get_cols() const; //返回矩列数
void print() const; // 按行打印输出矩阵
private:
int lines; // 矩阵行数
int cols; // 矩阵列数
double* p; // 指向存放矩阵数据的内存块的首地址
};
Matrix::Matrix(int n)
{
lines = n;
cols = n;
p = new double[n * n];
}
Matrix::Matrix(int n, int m)
{
lines = n;
cols = m;
p = new double[n * m];
}
Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix& X)
{
lines = X.lines;
cols = X.cols;
p = new double[lines * cols];
for (int i = 0; i < lines * cols; i++)
{
p[i ] = X.p[i];
}
}
void Matrix::set(const double* pvalue)
{
int k = 0;
for (k = 0; k < lines * cols; k++)
{
p[k] = pvalue[k];
}
}
void Matrix::set(int i, int j, int value)
{
p [(i * cols) + j] = value;
}
double Matrix::at(int i, int j) const
{
int k = i * cols + j ;
return p[k];
}
int Matrix:: get_lines() const
{
return lines;
}
int Matrix::get_cols() const
{
return cols;
}
void Matrix::print()const {
for (int i = 0; i < lines; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
if (j == cols - 1)
{
cout << p[i * cols + j] << endl;
}
else
{
cout << p[i * cols + j] << ", ";
}
}
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include "matrix.hpp"
void test() {
using namespace std;
double x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,7,8 };
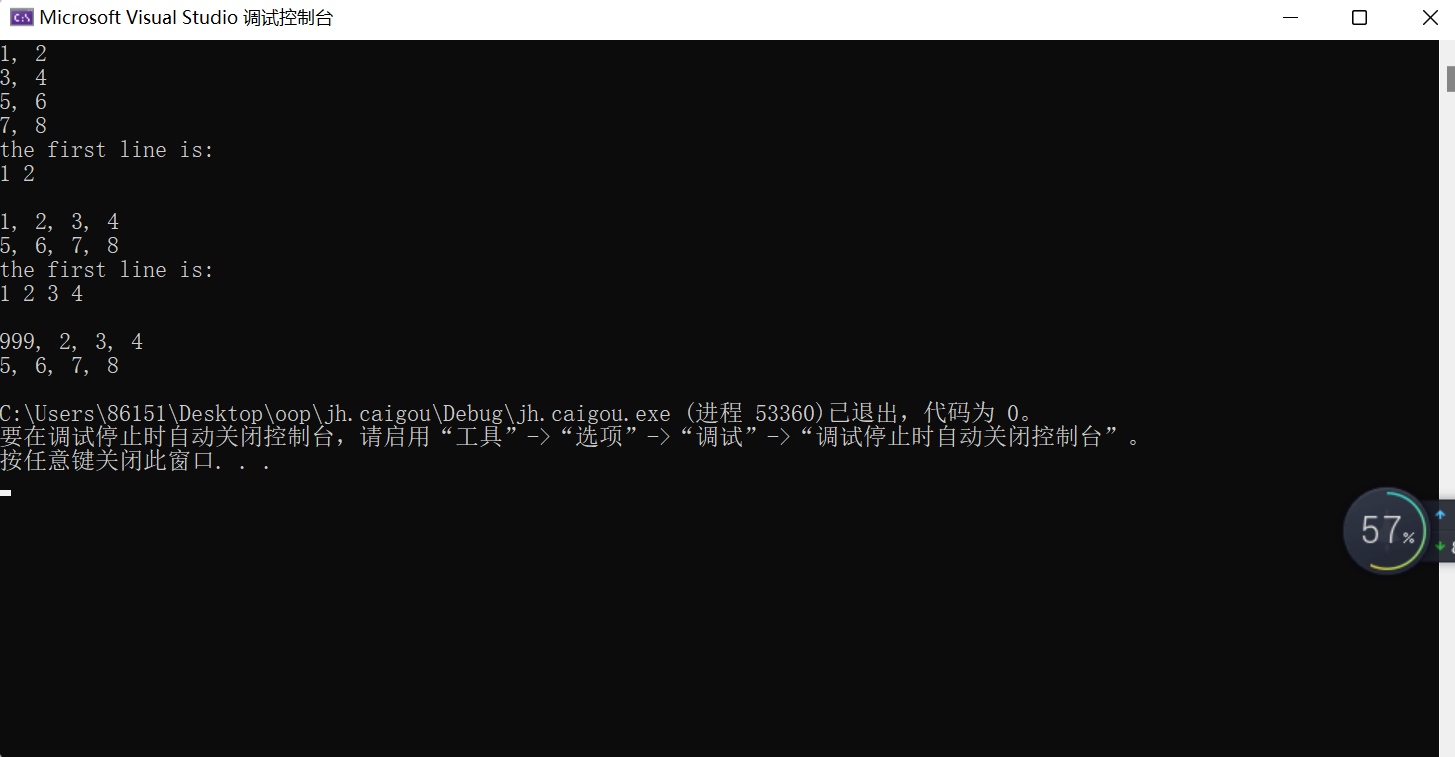
Matrix m1(4, 2); // 创建一个3×2的矩阵
m1.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值
m1.print(); // 打印矩阵m1的值
cout << "the first line is: " << endl;
cout << m1.at(0, 0) << " " << m1.at(0, 1) << endl; // 输出矩阵m1第1行两个元素的值
cout << endl;
Matrix m2(2, 4);
m2.set(x);
m2.print();
cout << "the first line is: " << endl;
cout << m2.at(0, 0) << " " << m2.at(0, 1) << " " << m2.at(0, 2)<<" " << m2.at(0, 3) << " " << endl;
cout << endl;
Matrix m3(m2); // 用矩阵m2构造新的矩阵m3
m3.set(0, 0, 999); // 将矩阵m3第0行第0列元素值设为999
m3.print();
}
int main() {
test();
}
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号