File类的使用
三种文件构造方式
//File file1 = new File("C:\\Users\\Kong\\Desktop\\kong\\xing.txt");
//File file1 = new File("C:\\Users","Kong\\Desktop\\kong\\xing.txt");
File file =new File("C:\\Users");
File file1 = new File(file,"Kong\\Desktop\\kong\\xing.txt");
常用API
bollean es = file.exists();
file.createNewFile();
file.mkdir();
file.mkdirs();
String na = file.getName()
String pa = file.getParent()
boolean cd = file.canRead()
boolean we = file.canWrite()
String gh = file.getPath()
String ah = file.getAbsolutePath()
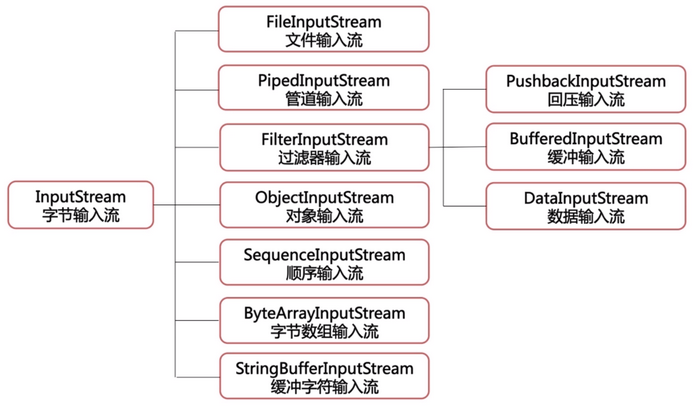
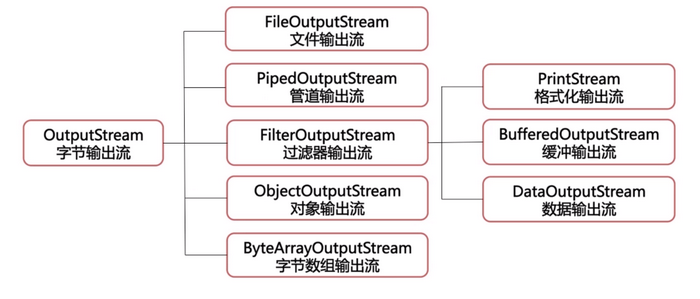
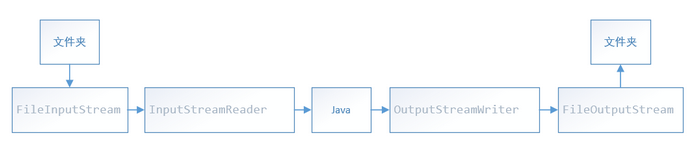
字节流
- 二进制文件传输(图片)
- 注意flush()和close()
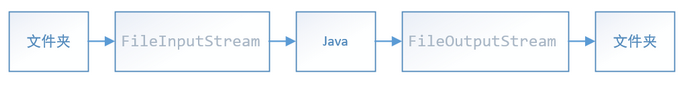
方式一
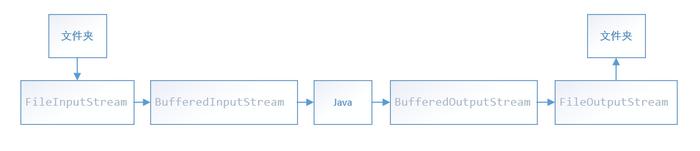
方式二
字符流
- 字符文件传输及字节字符转换
- Reader和Writer
- 注意构造器包装类型
方式一
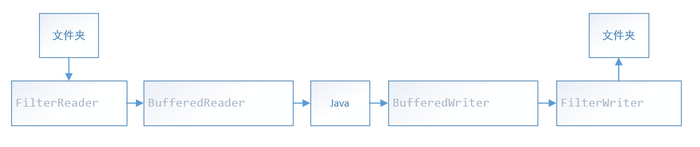
方式二
序列化(Serializable)
public class GoodsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Goods类要实现Serializable
Goods goods1 = new Goods("gd001","电脑",3000);
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("kong.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("kong.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//将对象信息写入文件
oos.writeObject(goods1);
oos.writeBoolean(true);
oos.flush();
//读对象信息
Goods goods = (Goods)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(goods);
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
fis.close();
ois.close();
fos.close();
oos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号