三个线程创建方式
Thread
class MyThread extends Thread
{
public MyThread(String name)
{
super(name);
}
public void run()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.out.println(getName() + "正在运行" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt1 = new MyThread("线程1");
MyThread mt2 = new MyThread("线程2");
mt1.start();
mt2.start();
}
}
Runnable
class PrintRunnable implements Runnable
{
int i = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
while (i <= 10)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在运行!" + (i++));
}
}
}
public class RunnableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintRunnable pr = new PrintRunnable();
Thread t1 = new Thread(pr);
t1.start();
PrintRunnable pr1 = new PrintRunnable();
Thread t2 = new Thread(pr1);
// Thread t2 = new Thread(pr); //多线程共享资源
t2.start();
}
}
Callable
class ThirdThread implements Callable<String>
{
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
String str = "多线程的第三种创建方式";
return str;
}
}
public class ThirdThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable<String> call = new ThirdThread();
FutureTask<String> ft = new FutureTask<>(call);
Thread t3 = new Thread(ft);
t3.start();
try {
System.out.println(ft.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
线程的生命周期
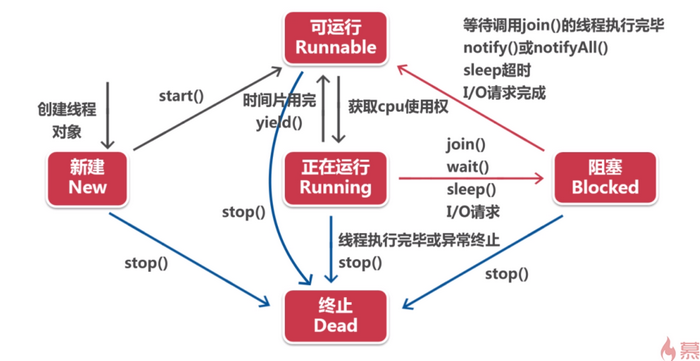
sleep()和join()
- sleep()让出CPU资源
- join()抢占CPU资源(一般抢占主线程)
线程优先级
线程同步(synchronized)

线程间通信(wait())
public class Queue {
private int n;
boolean flag = false;
public synchronized int getN(){
if (!flag) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("消费:" + n);
flag = false;
notifyAll();
return n;
}
public synchronized void setN(int n) {
if (flag)
{
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("生产:" + n);
this.n = n;
flag = true;
notifyAll();
}
}
public class Producer implements Runnable {
Queue queue;
Producer(Queue queue)
{
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
queue.setN(i++);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
Queue queue;
Consumer(Queue queue)
{
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
queue.getN();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
new Thread(new Producer(queue)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(queue)).start();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号