spring-boot-learning-REST风格网站
什么是REST风格:
Representational State Transfer :表现层状态转换,实际上是一种风格。标准,约定
首先需要有资源才能表现, 所以第一个名词是“ 资源”。有了资源也要根
据需要以合适的形式表现资源,这就是第二个名词一一表现层。最后是资源可以被新增、修改、删
除等,也就是第三个名词“状态转换”。
资源: 它可以是系统权限用户、角色和菜单等,也可以是一些媒体类型, 如文本、图片、歌曲,总之它就是一个具体存在的
对象。可以用一个URI ( Unifonn Resource Identifier ,统一资源定位符)指向它, 每个资源对应一个特定的U阳。
要获取这个资源, 访问它的U阳即可,而在REST 中每一个资源都会对应一个独一无二的U阻。在阻ST 中, URI 也可以称
为端点(End Point ) 。
表现层: 有了资源还需要确定如何表现这个资源。例如, 一个用户可以使用JSON 、XML 或者其他的形式表现出来,又如
可能返回的是一幅图片。在现今的互联网开发中, JSON 数据集己经是一种最常用的表现形式
REST风格当中,每一个资源都只是对应一个网址,而一个资源网址应该是一个名词,不存在动词。
URI (Unifonn Resource Identifier)统一资源定位符

REST风格其实就是一种约定问题,不同的http请求对应的不同的资源操作,
@GetMapping
/** * RestController,作用是使返回的结果能够以json数据集的方法进行返回 * 转换为JSTL或者json * 11默认将方法或者类标注为application/json;charset=UTF-8 * 22方法执行结束后,spring会遍历注册号的HttpMessageConverter接口 * 的实现类。 * 33注册好的MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter就会放回true, * 启动转换器将结果转换为JSON数据集 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("annotation") public class RedisUserController { @Autowired private UserService userService =null; /** * http的get请求,获取资源 * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping("/{id}") public User getUser(@PathVariable("id") Long id){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); User user = userService.getUser(id); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); return user; }
请求:
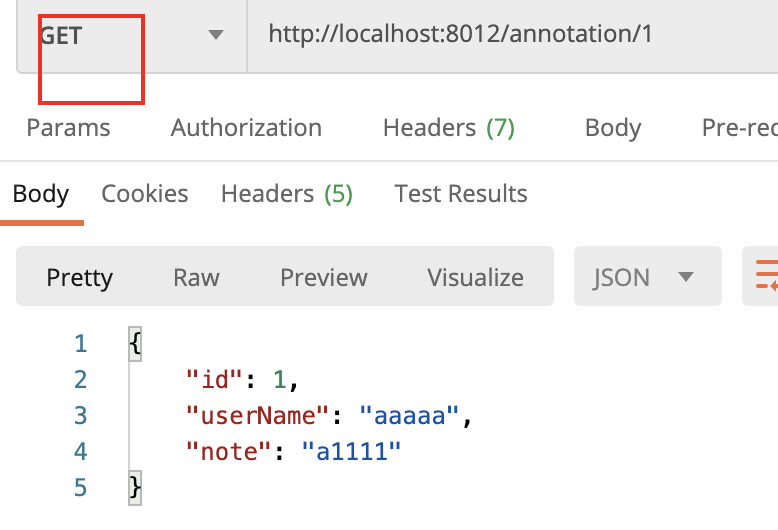
@PostMapping
/** * http的post请求,创建资源 * @param userName * @param note * @return */ @PostMapping() public User insertUser( @RequestParam ("userName") String userName, @RequestParam ("note") String note ){ User user = new User(); user.setUserName(userName); user.setNote(note); userService.insertUser(user); return user; }
请求结果;
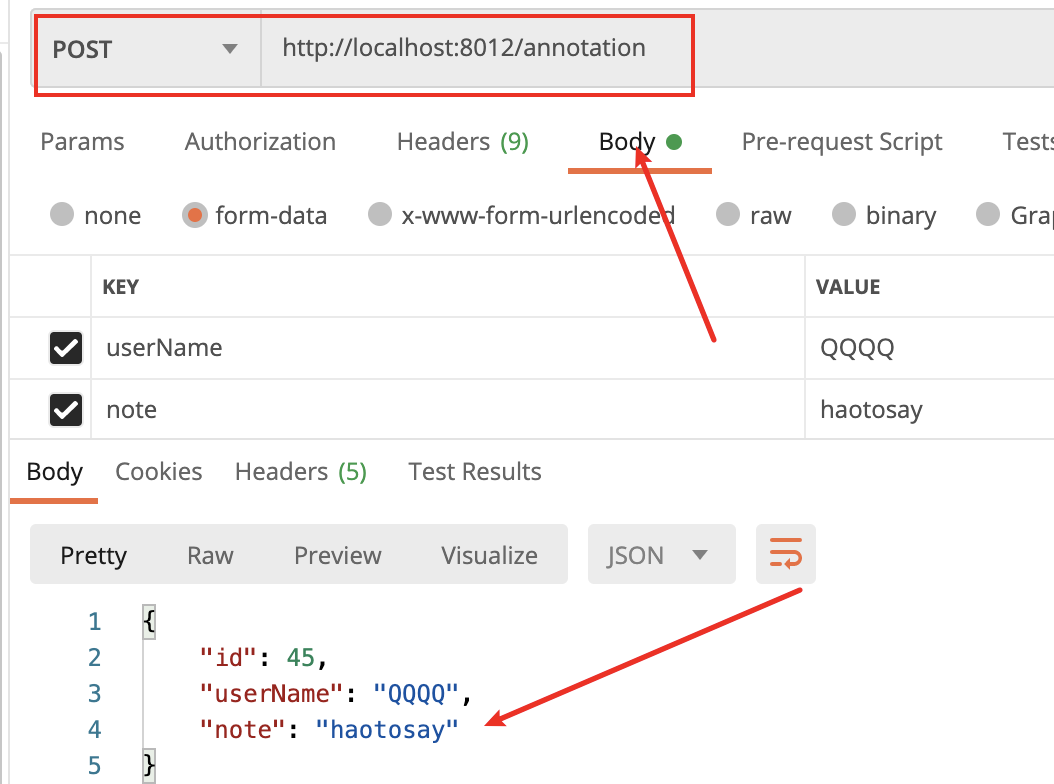
@DeleteMapping
/** * http的Delete请求,删除服务器资源 * @param id * @return */ @DeleteMapping("{id}") public int delUser(@PathVariable("id") Long id){ return userService.deleteUser(id); }
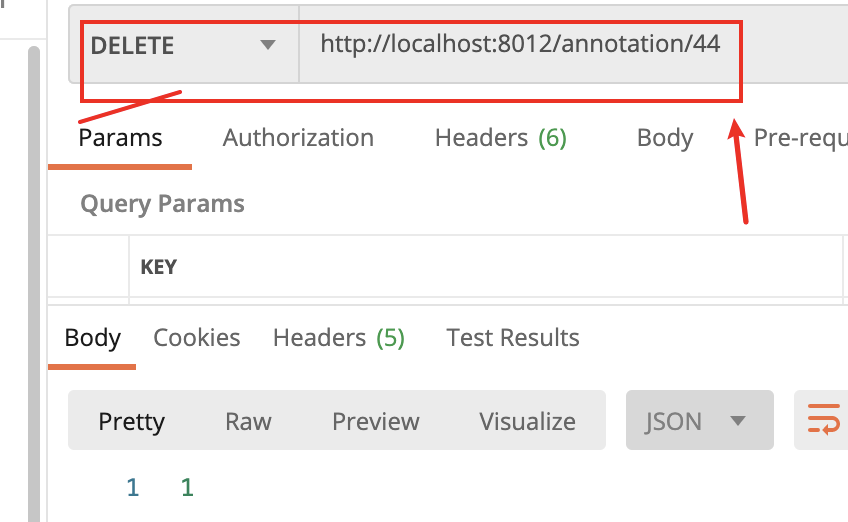
从数据库中删除了id为44员工
@PutMapping
@PatchMapping
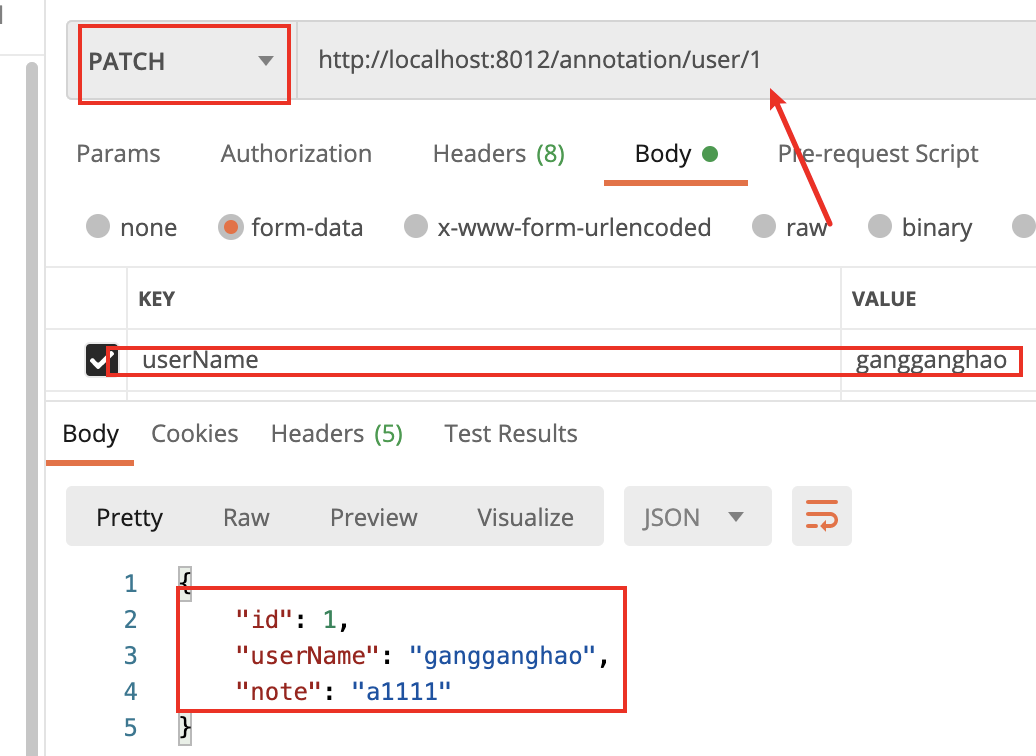
/** * http Put请求,提交所有的资源属性以修改资源, * http patch请求,提交资源的部分修改属性, * 其实他们两个都差不多,只不过是约定的问题而已 * @param id * @param userName * @return */ @PatchMapping("/user/{id}") public User updUser( @PathVariable("id") Long id, @RequestParam("userName") String userName ){ return userService.updateUser(id,userName); }
修改之前的:
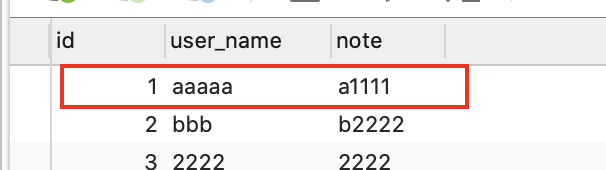
处理HTTP请求状态码,异常和响应头
通过实体类去实现;
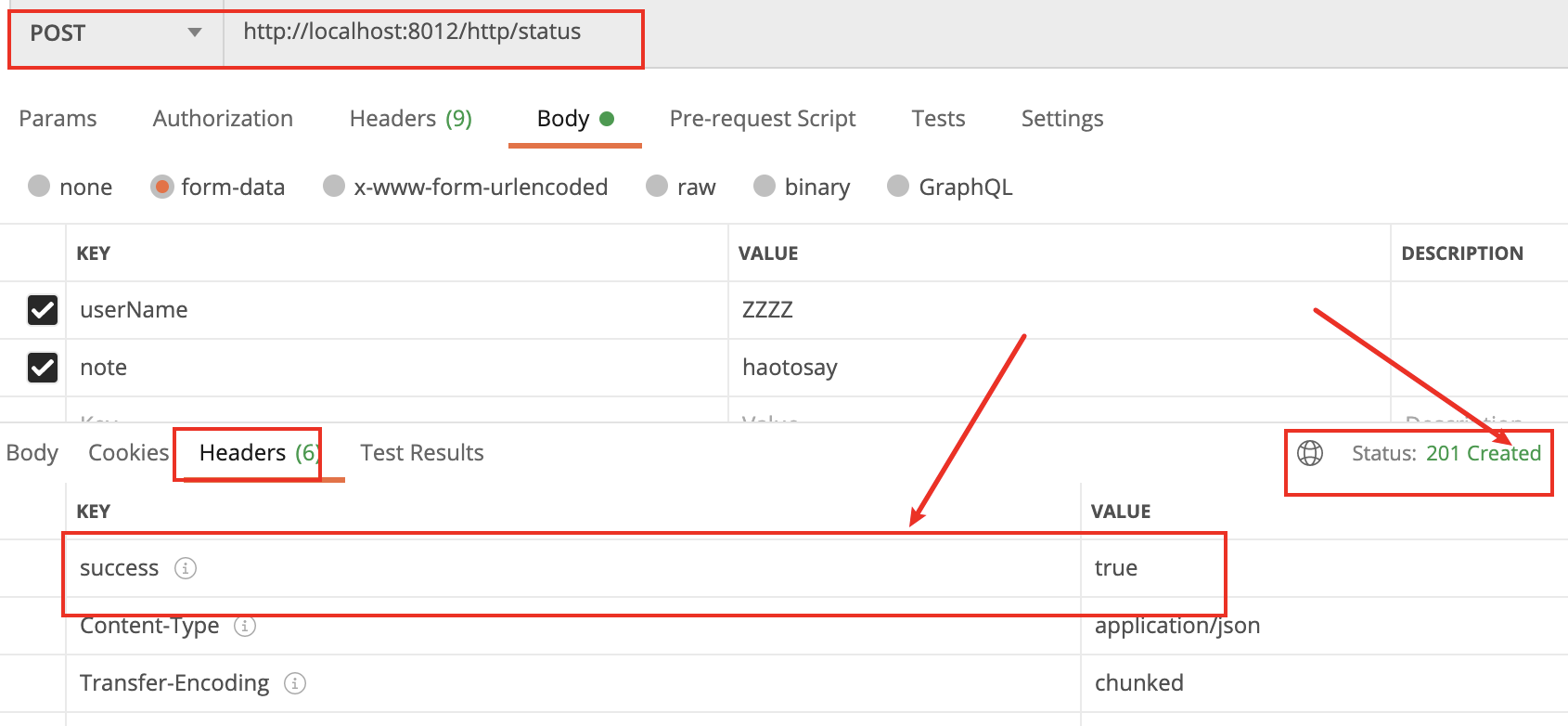
/** * 当发生资源找不到或者处理逻辑发生异常时,需要考虑返回给客户端的http状态码和错误消息 * spring提供实体封装类ResponseEntity:有效的封装错误消息和状态码 * 和注解@ResponseStatus:配置指定的响应码给客户端 */ @RestController public class HttpStatusController { @Autowired UserService userService; /** * 11新建一个请求头对象, * 22向请求头通过add方法进行加入k-v * 33需要建立一个响应实体类,将需要放回的信息,请求头对象,响应http状态码 * 备注:这里使用 HttpStatus.CREATED ,指定状态码为201,标识资源创建成功 * @param userName * @param note * @return */ @PostMapping("/http/status") public ResponseEntity<Integer> insertUser( @RequestParam("userName") String userName, @RequestParam ("note") String note ){ User user = new User(); user.setUserName(userName); user.setNote(note); Integer re = userService.insertUser(user); // 设置http响应头 HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();//新建请求头 String success = (re == 0 ) ? "false" : "true";//如果结果为0,就是false httpHeaders.add("success",success); return new ResponseEntity<Integer>(re,httpHeaders, HttpStatus.CREATED); }
使用注解:
/** * 通过注解@ResponseStatus去指定 * 当方法正常返回的时候,http状态码为201 * @param userName * @param note * @return */ @PostMapping("/http/status/an") @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) public Integer insertUseran( @RequestParam("userName") String userName, @RequestParam ("note") String note ){ User user = new User(); user.setUserName(userName); user.setNote(note); Integer re = userService.insertUser(user); return re; } }
异常处理;
定义一个运行时的异常:
//场景:运行的时候,查询id用户,找不到数据或出现异常,这时候不能以正常返回去处理。 /** * 11自定义异常类:找不到用户的时候抛出异常 * 异常抛出后,可以在控制器通知@ControllerAdvice里面进行处理 * @ControllerAdvice:定义控制器通知 * @ExceptionHandler:指定异常发生的处理方法 *继承的异常RuntimeException是指:运行时的异常,和我们普通的 * Exception:受检查的异常,这种异常是强制我们catch或throw的异常。 * 你遇到这种异常必须进行catch或throw,如果不处理,编译器会报错。 * */ public class NotFoundException extends RuntimeException{ public static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Long code;//异常编码 private String customMsg;//异常自定义消息 public NotFoundException() { } public NotFoundException(Long code, String customMsg) { super(); this.code = code; this.customMsg = customMsg; } public Long getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Long code) { this.code = code; } public String getCustomMsg() { return customMsg; } public void setCustomMsg(String customMsg) { this.customMsg = customMsg; } }
定义一个控制器通知:
/** * 2自定义一个控制器通知 * 在@ControllerAdvice中指定拦截包路径,限定被拦截的注解为@Controller/@RestController * 在@ExceptionHandler注解方法上,通过value属性,指定异常类型进行拦截 * 在@ResponseBody定义响应的信息已json的格式表达 * 在@ResponseStatus定义服务器内部错误500代码 */ @ControllerAdvice( basePackages = {"com.quan.annotationredis.controller.*"}, annotations = {Controller.class, RestController.class} ) public class UserControllerAdvice { @ExceptionHandler(value = NotFoundException.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)//定义服务器错误代码 @ResponseBody public Map<String,Object> exception(HttpServletRequest request, NotFoundException ex){ Map<String,Object> msgMap = new HashMap<>(); msgMap.put("code",ex.getCode()); msgMap.put("message",ex.getCustomMsg()); return msgMap; } }
测试controller:
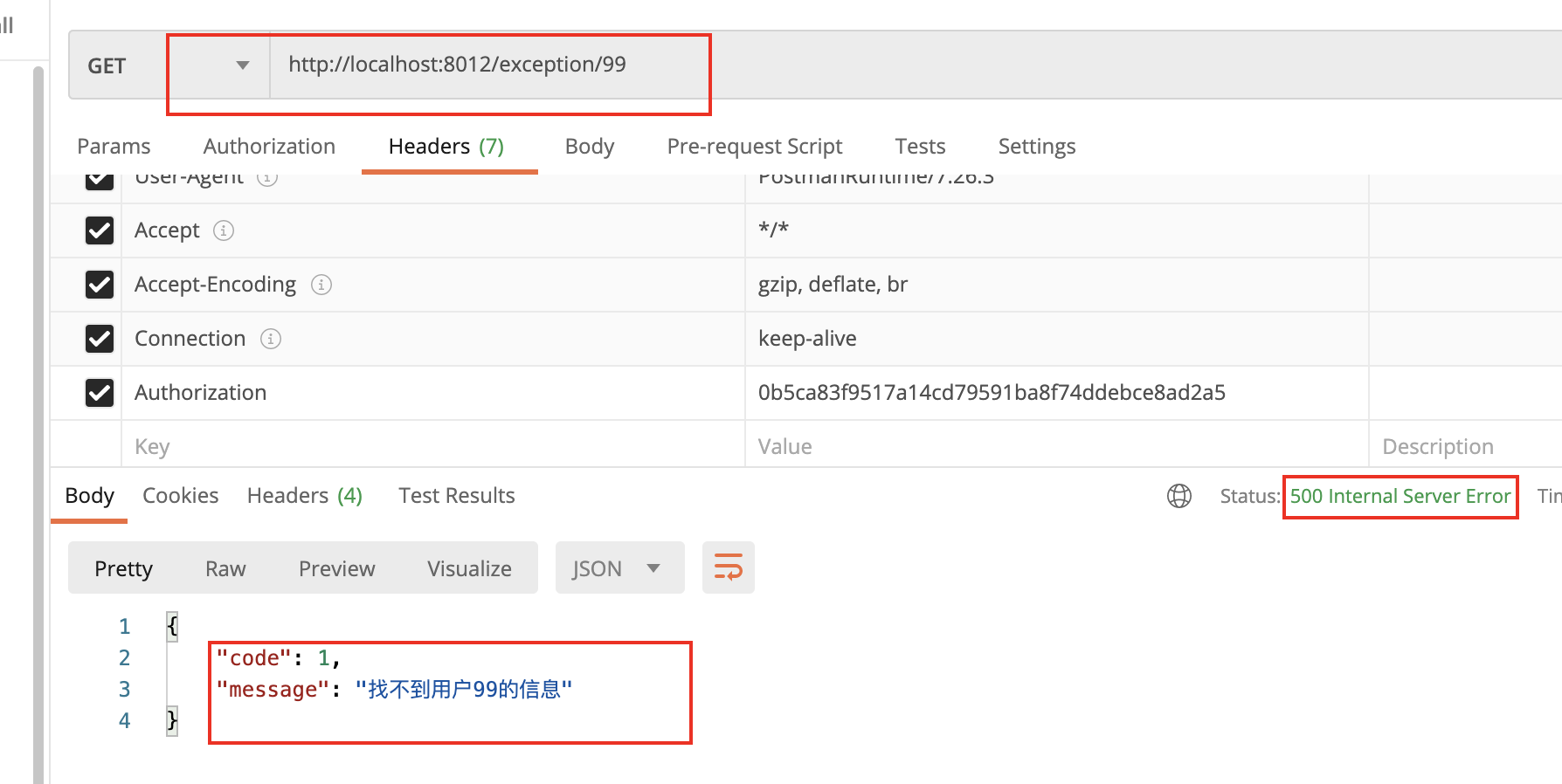
@Controller public class ExceptionController { @Autowired UserService userService; /** * 一旦方法出现异常,就会别控制器通知所拦截,最后经@ExceptionHandler定义 * 的方法进行处理。 * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping("/exception/{id}") @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @ResponseBody public User getUser(@PathVariable("id") Long id){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); User user = userService.getUser(id); if (user == null){ throw new NotFoundException(1L,"找不到用户"+id+"的信息"); } System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); return user; } }
使用RestTemplate请求后端;
底层是通过类HttpURLConnection实现的。
/** * restTemplate.getForObject方法中: * 第一个参数URL:标明请求服务器什么资源,{id}代表参数 * 第二个参数:表示将请求返回User类的结果,实际上服务器只会给回我们json格式数据 * 是因为restTemplate内部将其转化给java对象。 * 第三个参数:就是URL对应的参数。 * @return */ private static User getUser() { int id = 1; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); User user = restTemplate.getForObject( "http://localhost:8012/annotation/{id}", User.class, id ); System.out.println(user.getUserName()); return user; } }
输出的日志结果:
14:10:42.839 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - HTTP GET http://localhost:8012/annotation/1 14:10:42.904 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Accept=[application/json, application/*+json] 14:10:42.921 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK 14:10:42.924 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [com.quan.annotationredis.entity.User] gangganghao
多个参数的时候:
@RestController @RequestMapping("annotation") public class RedisUserController { @Autowired private UserService userService =null; @PostMapping("/{userName}/{note}") public User insertUser( @PathVariable ("userName") String userName, @PathVariable ("note") String note ){ User user = new User(); user.setUserName(userName); user.setNote(note); userService.insertUser(user); return user; }
将参数用一个Map对象封装起来,Map的键名称和URI中所定义的参数时保持一致的。这样子就能将参数统一封装到Map中了
/** *因为我们的Controller层返回的是User类型,所以我们这里也放回User,并使用ResponseEntity<User>接受 * postForEntity ,通过post请求返回一个实体类,需要url,请求类型,返回类型,参数列表 * responseEntity.getBody();通过类的方法从返回体里面拿到返回体的内容。(contorller里面是返回user) * @return */ public static User insertUser(){ RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); String userName = "huolalala"; String note = "huolalanote"; String url = "http://localhost:8012/annotation/{userName}/{note}"; Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<>(); params.put("userName",userName); params.put("note",note); ResponseEntity<User> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url,User.class,User.class,params); User user = responseEntity.getBody(); System.out.println(user); return user; }
运行日志;
14:55:47.888 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - HTTP POST http://localhost:8012/annotation/huolalala/huolalanote 14:55:47.948 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Accept=[application/json, application/*+json] 14:55:47.966 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Writing [class com.quan.annotationredis.entity.User] with org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 14:55:47.987 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK 14:55:47.990 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [com.quan.annotationredis.entity.User] User{id=49, userName='huolalala', note='huolalanote'}
请求体获取参数:
/** * 11先定义请求头HttpHeaders,设置请求体为JSON格式 * 22将请求体实体user和请求头绑定到请求实体对象HttpEntiry * 33restTemplate.postForObject将请求对象传递过去, * @return */ public static User insertUser1(){ User user = new User(); user.setNote("RRRR"); user.setUserName("QQQQ"); HttpHeaders httpheaders = new HttpHeaders(); httpheaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8); HttpEntity<User> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(user,httpheaders); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); restTemplate.postForObject("http://localhost:8012/annotation",httpEntity,User.class); return user; }
删除:
/** * */ public static void delUser(){ Long id = 48L; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); String url = "http://localhost:8012/annotation/{id}"; restTemplate.delete(url,id);//这个方法没有返回值 }
运行日志:
17:09:06.618 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - HTTP DELETE http://localhost:8012/annotation/48 17:09:06.639 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号