spring-boot-learning-配置文件相关
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-configuration-processor --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
•application.yml
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值;SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
YML文件的语法:
server:
port: 8081
<server> <port>8081</port> </server>
yaml基本的语法:
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;
只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
注意:属性和值也是大小写敏感;
server: port: 8080 error: path: /error
值的写法:
字面量:普通的数,布尔值,字符串字面直接来写; 字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号; "":双引号===不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符; 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思 name: "zhangsan \n lisi" 输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi '':单引号===会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据 name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’ 输出;zhangsan \n lisi
user:
name: quan
age: 20
就是user.name = quan
user.age = 20
注意:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
用-来表示数组或者集合的元素:
names: - quan - zhi - qiang
上面表达的就是
names[quan,zhi,qiang]
配置文件的注入方式
@ConfigurationProperties 定义类中的属性和配置文件的那些配置相关prefix指定前缀
@Component 将组建加入都容器当中
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定; 默认在全局配置文件中获取值的 * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能; @Component * */
配置文件内容:
person:
lastName: hello
age: 18
boss: false
birth: 2017/12/12
maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12}
lists:
- lisi
- zhaoliu
映射:
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class QuanTestConfig { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String, Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Boolean getBoss() { return boss; } public void setBoss(Boolean boss) { this.boss = boss; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } public Map<String, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public List<Object> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Object> lists) { this.lists = lists; } @Override public String toString() { return "QuanTestConfig{" + "lastName='" + lastName + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", boss=" + boss + ", birth=" + birth + ", maps=" + maps + ", lists=" + lists + '}'; } }
这里类的属性名字需要和配置文件里面的变量名字一样
test:
@SpringBootTest class HuolalaApplicationTests { @Autowired QuanTestConfig quanTestConfig; @Test public void setQua(){ System.out.println(quanTestConfig); } }
结果:
QuanTestConfig{lastName='hello', age=18, boss=false, birth=Tue Dec 12 00:00:00 CST 2017, maps={k1=v1, k2=12}, lists=[lisi, zhaoliu]}
注意:可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就有提示了
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
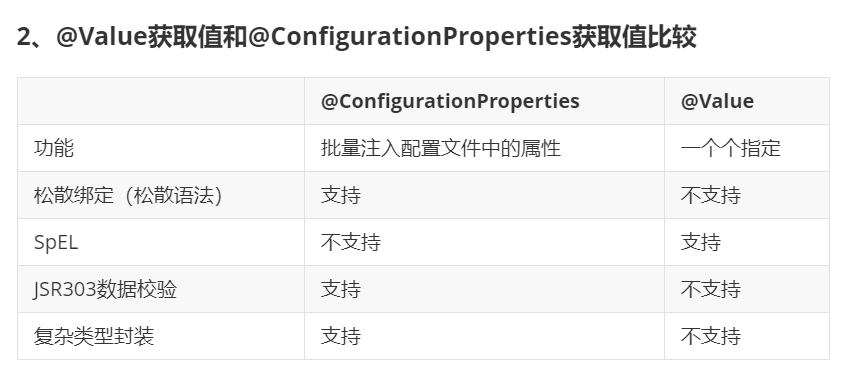
除了使用 @ConfigurationProperties进行配置值获取
之前使用bean标签添加到容器中的时候,对应现在的就是@Component
value标签对应的就是现在注解@Value
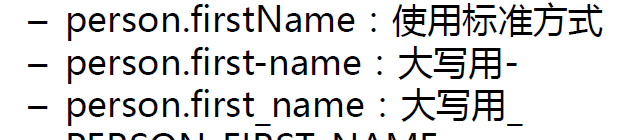
什么是松散语法:
@Value 和@ConfigurationProperties的区别是什么
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值; 如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value; 如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties
@Component
@Validated//表示里面的value需要进行JSR303数据校验,就是下面的@Email
public class Person {
/**
* <bean class="Person">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//lastName必须是邮箱格式
@Email
//@Value("${person.last-name}")
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{11*2}")
private Integer age;
//@Value("true")
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
上面就是配置文件注入的数据校验
关于数据校验:
什么是数据校验
数据校验就是在应用程序中,对输入进来得数据做语义分析判断,阻挡不符合规则得数据,放行符合规则得数据
一种是 Spring 自带的验证框架
一种是利用 JSR 实现。JSR 是一个规范,提供了完整得一套 API,通过标注给对象属性添加约束,例如Hibernate Validator
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
Hibernate Validator 定义的校验包括:
注解 作用目标 检查规则 @Length(min=, max=) 属性(String) 检查字符串长度是否符合范围 @Max(value=) 属性(以 numeric 或者 string 类型来表示一个数字) 检查值是否小于或等于最大值 @Min(value=) 属性(以 numeric 或者 string 类型来表示一个数字) 检查值是否大于或等于最小值 @NotNull 属性 检查值是否非空(not null) @Future 属性(date 或 calendar) 检查日期是否是未来 @Pattern(regex="regexp", flag=) 属性(string) 检查属性是否与给定匹配标志的正则表达式相匹配 @Range(min=, max=) 属性(以 numeric 或者 string 类型来表示一个数字) 检查值是否在最小和最大值之间(包括临界值) @Size(min=, max=) 属性(array,collection,map) 检查元素大小是否在最小和最大值之间(包括临界值) @AssertFalse 属性 检查方法的演算结果是否为 false(对以代码方式而不是注解表示的约束很有用) @AssertTrue 属性 检查方法的演算结果是否为 true(对以代码方式而不是注解表示的约束很有用) @Valid 属性(object) 对关联对象递归进行验证。如果对象是集合或数组,就递归地验证其元素;如果对象是 Map,则递归验证其值元素 @Email 属性(String) 检查字符串是否符合有效的 email 地址规范 @Past 属性(date 或 calendar) 检查日期是否是过去
@PropertySource& @ImportResource& @Bean三个注解
当我们将所有配置都配置到一个文件application.properties,显然这个文件太多内容,所以我们
可能会使用新的属性文件,例如数据库的配置可以在jdbc.properties中,加入下面注解指定就行。
@PropertySource加载指定的配置文件;
例子:
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})//classpath表示的是main路径下的,就是类路径下的。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//@Validated
public class Person {
。。。。。。
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:jdbc.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
igoreResourceNotFound可以忽略找不到配置文件,不报错
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
导入Spring的配置文件让其生效
以前我们每加入一个bean则需要编写spring配置文件:即bean的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloService" class="com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean>
</beans>
现在:
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、@Configuration放在配置类------>等同于我们之前的Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
*
* 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件
*
*/
@Configuration
public class MyAppConfig {
//将一个类的实例返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名
//下面就是加入bean HelloService ,并且id为helloService02
@Bean
public HelloService helloService02(){
System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器中添加组件了...");
return new HelloService();
}
}

使用占位符的时候是可以设置好默认值的:如果没有可以是用:指定默认值
多Profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
编写不同环境的配置文件: application-dev.properties 在默认的全局配置文件当中 即application.properties中配置: 在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
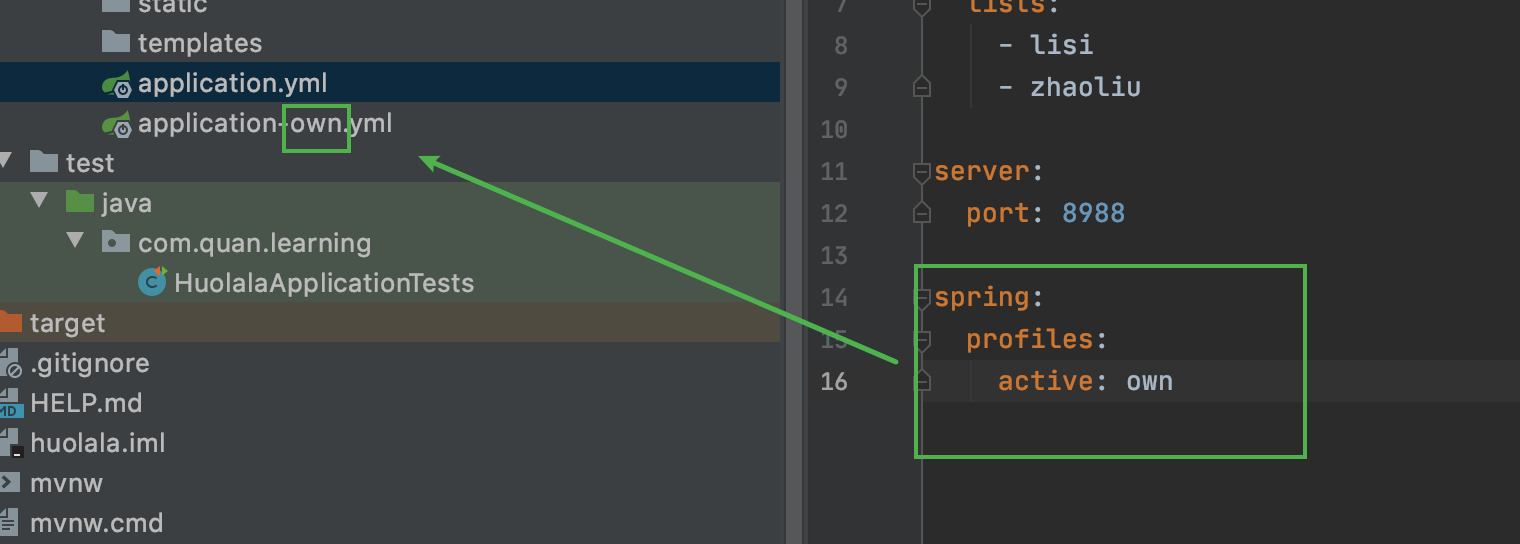
要在默认的配置文件中加入激活的配置文件才能进行知道。
也可以使用yml的多文档块模式,不用写多个配置文件
yml支持多文档块方式
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境
---三个横线就是代表不同的配置内容分块,active:就是要激活的配置块

JVM参数的设置如下 VM options

1、config/application.properties(项目根目录中config目录下) 2、config/application.yml 3、application.properties(项目根目录下) 4、application.yml 5、resources/config/application.properties(项目resources目录中config目录下) 6、resources/config/application.yml 7、resources/application.properties(项目的resources目录下) 8、resources/application.yml
配置文件的生效顺序,会对值进行覆盖
注意:
**项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;
指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;** java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
--spring.config.location=G:/application.properties

直接在命令行去配置端口
jar --jfijeifjie --server.port= 8089 命令行
SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 ==@EnableAutoConfiguration==
@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
导入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector的selectImports()方法通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()扫描所有具有META-INF/spring.factories的jar包
通过selectImport方法进行选择加载
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 扫描所有jar包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
==将 类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;==

# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Error Reporters org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor # Failure Analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer # FailureAnalysisReporters org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
#############################
每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
//表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和ServerProperties绑定起来;
//并把ServerProperties加入到ioc容器中
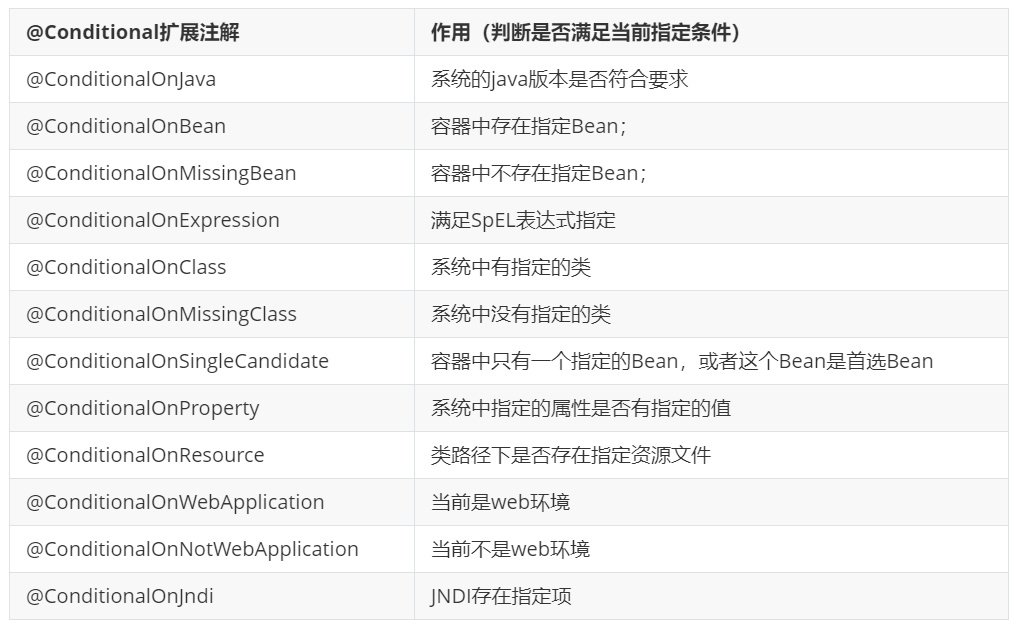
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class}) /Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置
就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器; @ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class}) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.servlet.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置spring.servlet.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的; @ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "server.servlet.encoding", value = {"enabled"}, matchIfMissing = true ) public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final Encoding properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties properties) { this.properties = properties.getServlet().getEncoding(); } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件filter,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 //@ConditionnalOnMissingBean判断容器没有这个组件? @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Encoding.Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个
功能对应的这个属性类

作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
注意:自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
怎么才能知道呢
============================
CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT
============================
Positive matches: //自动加载启用的配置累
-----------------
AopAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号