C++(26)-多线程-POSIX(4)-一个主线程+多个工作线程
一般情况下,我们会有一个主线程和多个工作线程。
如下图所示: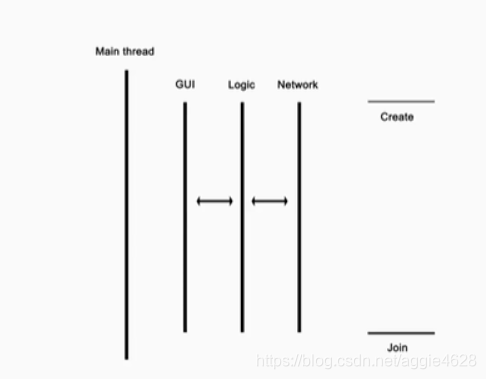
把众多的子线程分成工作队列和非工作队列进行管理。
1.工作节点,工作队列;非工作节点,非工作队列结构体定义。
2.main函数运行流程。
3.调用过程中的5个函数:
线程运行函数threadfunc(),
添加线程函数 join_threads(),
创建线程函数 create_threads(),
初始化结构函数initialize_structs(),
销毁结构化函数cleanup_structs()。
1.工作节点,工作队列;非工作节点,非工作队列结构体定义。
//工作线程队列
struct work_queue {
data_control control;
queue work;
} wq;
//工作线程node
typedef struct work_node {
struct node *next;
int jobnum;
} wnode;
//未工作队列
struct cleanup_queue {
data_control control;
queue cleanup;
} cq;
//非工作的线程node
typedef struct cleanup_node {
struct node *next;
int threadnum;
pthread_t tid;
} cnode;2.main函数运行流程
int main(void) {
//1.初始化
int x;
wnode *mywork;
initialize_structs();
//2.创建
if (create_threads()) {
printf("Error starting threads... cleaning up.\n");
join_threads();
dabort();
}
//3.工作队列添加互斥变量
pthread_mutex_lock(&wq.control.mutex);
for (x=0; x<16000; x++)
{
mywork=malloc(sizeof(wnode));
if (!mywork)
{
printf("ouch! can't malloc!\n");
break;
}
mywork->jobnum=x;
queue_put(&wq.work,(node *) mywork);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&wq.control.mutex);
//4.工作线程广播
pthread_cond_broadcast(&wq.control.cond);
printf("sleeping...\n");
sleep(2);
//5.监管工作线程
printf("deactivating work queue...\n");
control_deactivate(&wq.control);
//6.添加线程
join_threads();
//7.清理
cleanup_structs();
}
3.调用过程中的5个函数:
//1.线程函数 处理工作线程+清理线程
void *threadfunc(void *myarg) {
wnode *mywork; //工作的线程node
cnode *mynode; //非工作的线程node
mynode=(cnode *) myarg;
//1.1工作队列加互斥
pthread_mutex_lock(&wq.control.mutex);
//工作队列是激活状态
while (wq.control.active)
{
while (wq.work.head==NULL && wq.control.active) //工作队里中无线程+是激活状态
{
pthread_cond_wait(&wq.control.cond, &wq.control.mutex);//等待线程
}
if (!wq.control.active)
break;
mywork=(wnode *) queue_get(&wq.work); //得到工作线程
pthread_mutex_unlock(&wq.control.mutex);//去掉互斥量
printf("Thread number %d processing job %d\n",mynode->threadnum,mywork->jobnum);
free(mywork);
pthread_mutex_lock(&wq.control.mutex);
}
// 1.2工作队列解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&wq.control.mutex);
//2.1非工作队列加互斥
pthread_mutex_lock(&cq.control.mutex);
queue_put(&cq.cleanup,(node *) mynode);
//2.2非工作队列加互斥
pthread_mutex_unlock(&cq.control.mutex);
//等待条件
pthread_cond_signal(&cq.control.cond);
printf("thread %d shutting down...\n",mynode->threadnum);
return NULL;
}
#define NUM_WORKERS 4
int numthreads;
//2.添加线程 把线程添加到线程链表中
void join_threads(void) {
cnode *curnode; //非工作线程节点
printf("joining threads...\n");
while (numthreads)
{
//添加互斥量
pthread_mutex_lock(&cq.control.mutex);
while (cq.cleanup.head==NULL)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cq.control.cond,&cq.control.mutex);
}
//添加到队列中
curnode = (cnode *) queue_get(&cq.cleanup);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&cq.control.mutex);
//解除互斥量
pthread_join(curnode->tid,NULL);
printf("joined with thread %d\n",curnode->threadnum);
free(curnode);
numthreads--;
}
}
//3.创建线程 创建了一个线程Id,并把Id放入工作队列中
int create_threads(void)
{
int x;
cnode *curnode; //非工作线程节点
for (x=0; x<NUM_WORKERS; x++)
{
curnode=malloc(sizeof(cnode));
if (!curnode)
return 1;
curnode->threadnum=x;
if (pthread_create(&curnode->tid, NULL, threadfunc, (void *) curnode))
return 1;
printf("created thread %d\n",x);
numthreads++;
}
return 0;
}
//4.初始化 工作队列+非工作队列
void initialize_structs(void) {
numthreads=0;
if (control_init(&wq.control))
dabort();
queue_init(&wq.work);
if (control_init(&cq.control)) {
control_destroy(&wq.control);
dabort();
}
queue_init(&wq.work);
control_activate(&wq.control);
}
//5.销毁结构函数
void cleanup_structs(void) {
control_destroy(&cq.control);
control_destroy(&wq.control);
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号