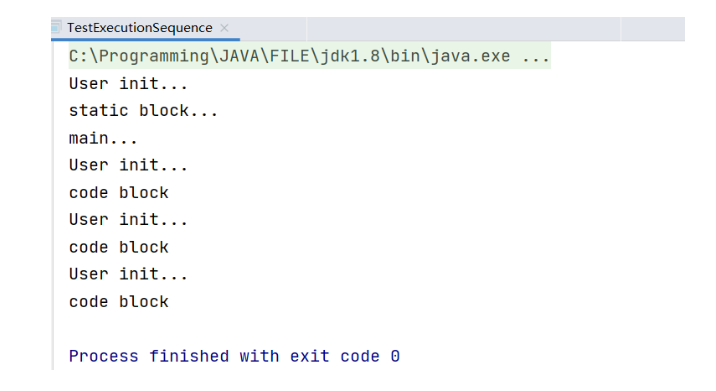
Java代码执行顺序
静态代码的执行一定先于main方法,静态代码块和静态成员变量的执行顺序是由代码位置决定的,谁写前面就先执行谁;
如果是非静态代码块和成员变量,不执行;只有在创建的类的实例对象时,才会执行非静态代码块和非静态成员变量;创建多少个对象,就会执行多少次代码块,创建多少个成员变量。非静态代码和非静态成员变量的执行顺序由位置决定,谁写前面就先执行谁;
如果同时存在非静态代码块和静态代码块,以及非静态成员变量和静态成员变量,先执行静态的东西,并且只执行一次,再执行非静态的东西(创建对象),创建多少个对象就会执行多少次。
package com.jarreet.test;
public class User {
public User(){
System.out.println("User init...");
}
}
package com.jarreet.test;
public class TestExecutionSequence {
// 非静态成员变量
User user = new User();
// 非静态代码块
{
System.out.println("code block");
}
// 静态成员变量
static User staticUser = new User();
// 静态代码块
static {
System.out.println("static block...");
}
// main函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main...");
TestExecutionSequence testExecutionSequence1 = new TestExecutionSequence();
TestExecutionSequence testExecutionSequence2 = new TestExecutionSequence();
TestExecutionSequence testExecutionSequence3 = new TestExecutionSequence();
}
}
加入父子类:
package com.jarreet.test;
public class Stub {
public Stub(String str){
System.out.println(str + "object created");
}
}
package com.jarreet.test;
public class Parent {
static Stub parentStaticStub = new Stub("parent static object-");
static {
System.out.println("parent static code excute");
}
Stub parentStub = new Stub("parent object-");
{
System.out.println("parent code excute");
}
Stub stub;
public Parent(){
System.out.println("parent constructor excute");
stub = new Stub("parent constructor created object-");
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello from parent");
}
}
package com.jarreet.test;
public class Child extends Parent{
static Stub childStaticStub = new Stub("child static object-");
static {
System.out.println("child static code excute");
}
Stub childStub = new Stub("child object-");
{
System.out.println("child code execute");
}
Stub stub;
public Child(){
System.out.println("child constructor excute");
stub = new Stub("child constructor create object-");
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello from child");
}
}
package com.jarreet.test;
public class TestParentChildExSequence {
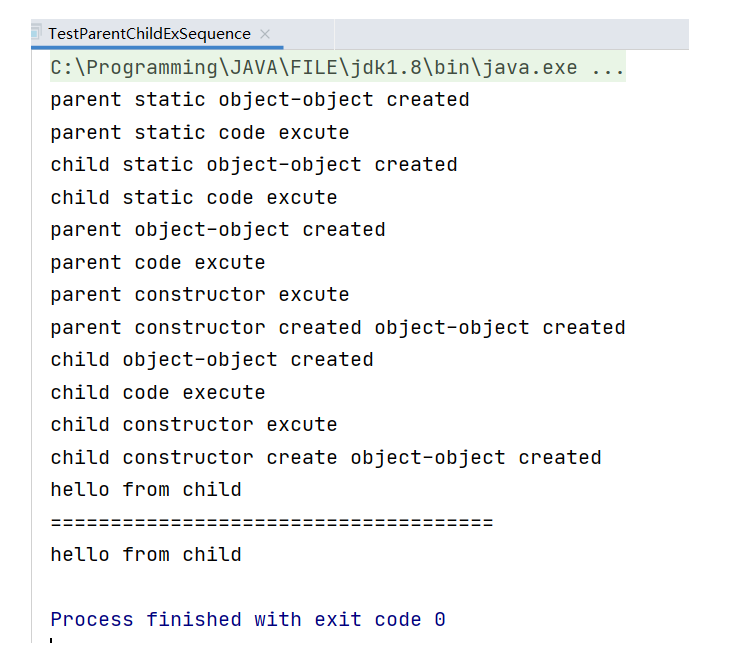
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
child.sayHello();
System.out.println("=====================================");
((Parent)child).sayHello();
}
}
开始分析:
-
首先会加载Parent,则Parent中的静态代码块和静态成员变量会优先执行
![]()
-
加载Child,则Child中的静态代码块和静态成员变量会优先执行
![]()
-
类加载完成之后,创建对象,先创建Parent对象,创建对象之前,先创建对象的资源
![]()
-
执行Parent构造器,完成Parent对象创建
![]()
-
创建Child对象之前,先创建Child的资源
![]()
-
执行Child构造器,完成Child对象创建
![]()
-
执行sayHello方法
![]()
尽管进行强制类型转换,但实际上对象本身还是内存中的子对象,所有hello都是来自于child
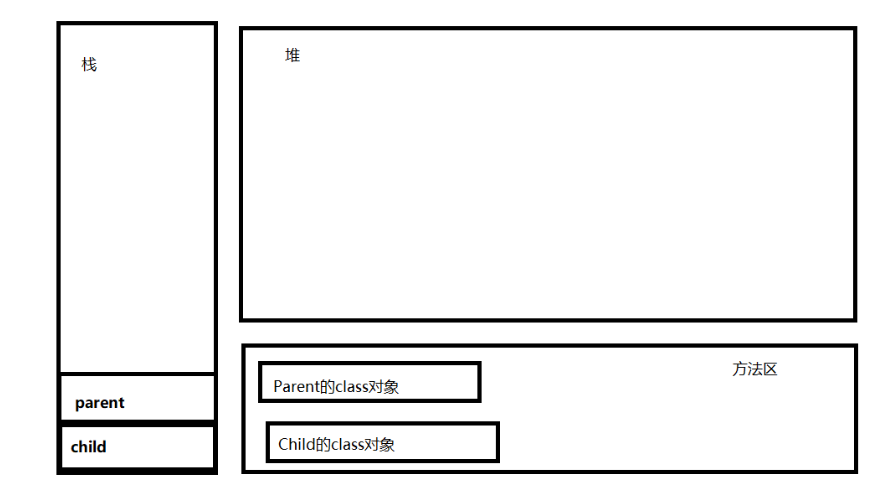
内存分析
-
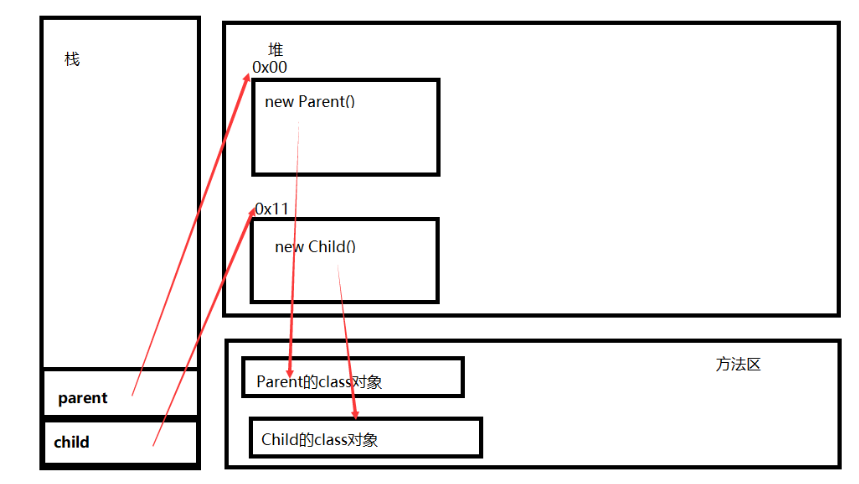
main()方法入栈,由于类Parent是类Child的父类,故先在方法区中加载Parnet的class对象,再加载Child的class对象(类的静态属性和静态方法随着类加载一同加载到内存中)
![]()
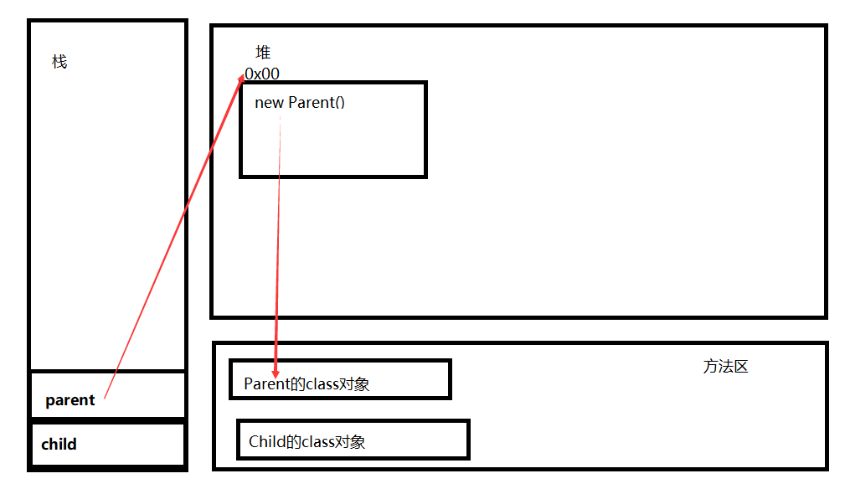
-
类加载完成之后,创建对象,先创建Parent对象,创建对象之前,先创建对象的资源,然后执行Parent构造器,完成Parent对象创建
![]()
-
接着创建Child对象,同样先获取对象的资源,然后再执行Child构造器,完成Child对象创建
![]()
-
执行sayHello()方法









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号