JDBC
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是一个独立于特定数据库管理系统、通用的SQL数据库存取和操作的公共接口(一组API)。
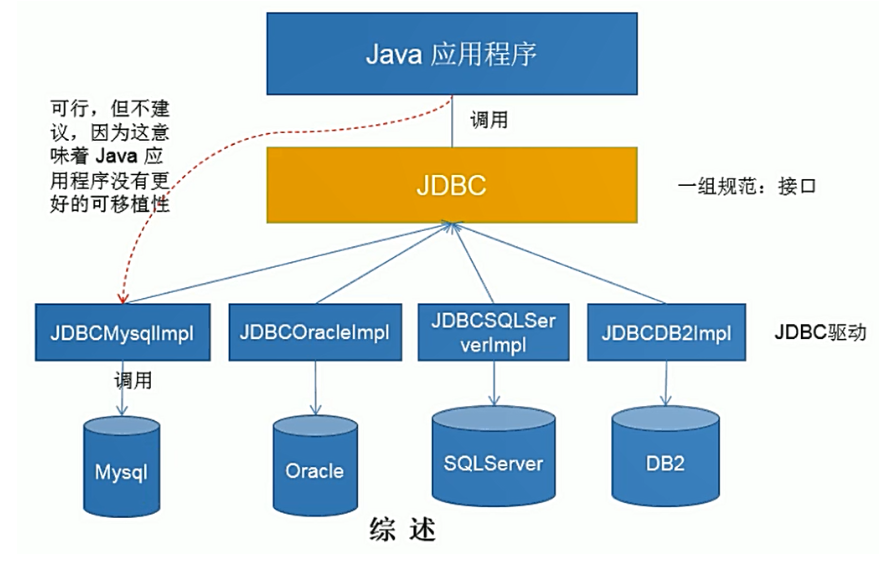
JDBC接口(API)包括两个层次:
-
面向应用的API:java API,抽象接口,供应用程序开发人员使用(连接数据库,执行SQL语句,获得结果)
-
面向数据库的API:Java Driver API,供开发商开发数据库驱动程序用
JDBC程序编写步骤:
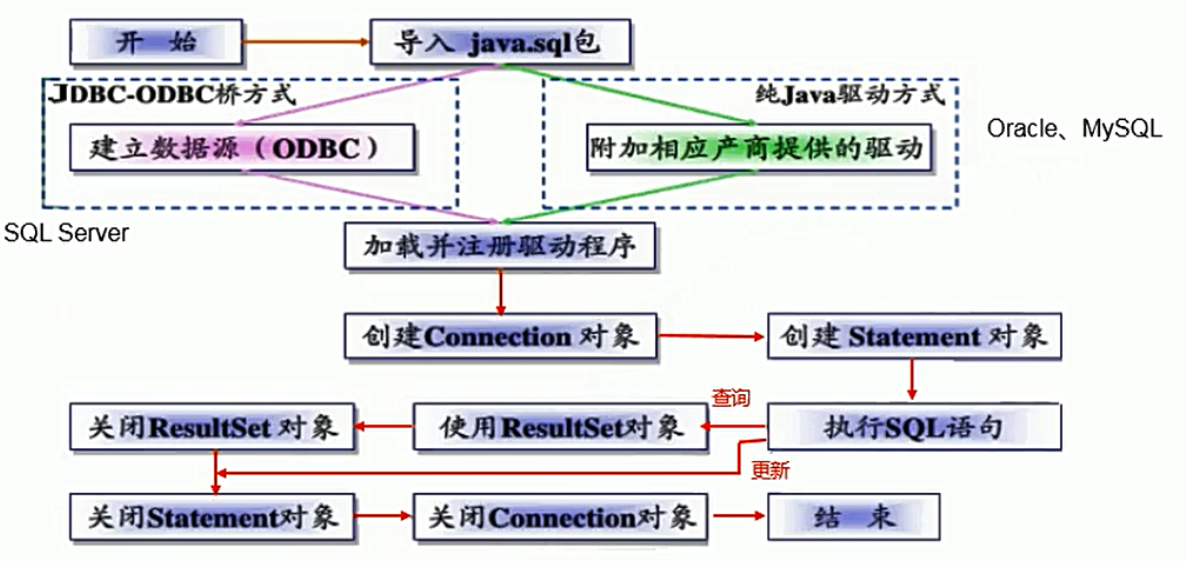
获取数据库连接
配置文件jdbc.properties:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
user=root
password=123456
jdbc程序:
使用PreparedStatement实现CRUD操作
JDBCUtils工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
/**
* 获取数据库连接
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
// 1. 读取配置文件的4个基本信息
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String driver = pros.getProperty("driver");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
// 2. 加载驱动
Class.forName(driver);
// 3. 获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps, ResultSet rs){
try{
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch(SQLEXception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch(SQLEXception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
if(rs != null)
rs.close();
} catch(SQLEXception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
插入数据
-
删除一条数据
-
更新一条数据
-
查询一条数据
考虑事务的JDBC
-
模拟转账过程中出现异常导致有一部分SQL执行失败后让数据库自动回滚事务
-
模拟转账过程中出现异常导致有一部分SQL执行失败时手动通知数据库回滚事务
@Test
public void testTransaction2() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);//通知数据库开启事务(start transaction)
String sql1 = "update account set money=money-100 where name='A'";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps.executeUpdate();
//用这句代码模拟执行完SQL1之后程序出现了异常而导致后面的SQL无法正常执行,事 务也无法正常提交
int x = 1/0;
String sql2 = "update account set money=money+100 where name='B'";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ps.executeUpdate();
conn.commit();//上面的两条SQL执行Update语句成功之后就通知数据库提交事务 (commit)
System.out.println("成功!!!");
}catch (Exception e) {
try{
//捕获到异常之后手动通知数据库执行回滚事务的操作
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JdbcUtils.closeResource(conn, st, rs);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号