同样环境与 java 做了个对比,差的不是一星半点!先看执行结果,同样环境下读取同一个400M左右数据文件,以下截图是测试结果:
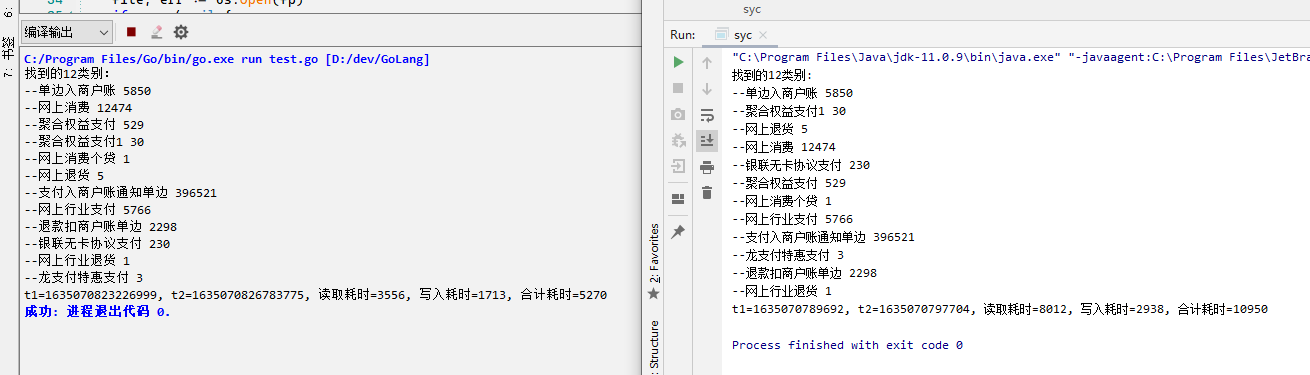
JAVA 代码:
package ccb;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class syc
{
static String fp = "D:\\ccb\\ONL_STLM_JNL_410_20190625.dat";
// static String fp = "D:\\ccb\\ONL.dat";
static File sourceFile = new File(fp);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
long s0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long lnu = get_line_number();
System.out.println(String.format("文件共有:%s行", lnu));
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(String.format("统计文件行数用时:%s", (s1-s0)));
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 读取文件内容,并进行归类
Map<String, List<String>> mapList = read_data();
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 将文件内容写入磁盘
write_data(mapList);
long t3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(String.format("t1=%s, t2=%s, 读取耗时=%s, 写入耗时=%s, 合计耗时=%s",
t1, t2, (t2-t1), (t3-t2), (t3-t1)));
}
/**
* 带缓存读取文件,归类
* @return Map
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public static Map<String, List<String>> read_data() {
Map<String, List<String>> mapList = new HashMap<>();
// 带缓存的输入流读取
BufferedReader buff = null;
try {
buff = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFile));
String line = "";
while ((line = buff.readLine()) != null) {
String[] items = line.split("\\|@\\|");
String type_name = items[1];
if (mapList.containsKey(type_name)) {
List tempList = mapList.get(type_name);
tempList.add(line);
mapList.put(type_name, tempList);
} else {
List lines = new ArrayList<>();
lines.add(line);
mapList.put(type_name, lines);
}
}
buff.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (buff != null) {
try {
buff.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(String.format("找到的%s类别:", mapList.size()));
return mapList;
}
/**
* 带缓存写入文件
* @param mapList
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void write_data(Map<String, List<String>> mapList) throws IOException {
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(sourceFile + ".result");
BufferedWriter buff = new BufferedWriter(fWriter);
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : mapList.entrySet()) {
List<String> lines = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(String.format("--%s %s", entry.getKey(), lines.size()));
for (String line : lines) {
buff.write(line + "\n");
}
}
try {
buff.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 返回文件的总行数
* @return
*/
public static long get_line_number() throws IOException {
File file = new File(fp);
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
LineNumberReader line_num_reader = new LineNumberReader(reader);
long lineNu = 0;
while (line_num_reader.readLine() != null)
lineNu++;
return lineNu;
}
}
Golang 代码:
package main
import (
"bufio"
_ "container/list"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
)
func main() {
file_path := "ONL_STLM_JNL_410_20190625.dat"
new_file_path := file_path + ".result"
t1 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3
// lines := read_file(file_path)
mapList := read_file(file_path)
t2 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3
write_file(mapList, new_file_path)
t3 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3
fmt.Printf("t1=%v, t2=%v, 读取耗时=%v, 写入耗时=%v, 合计耗时=%v\n",
t1, t2, (t2-t1)/1e3, (t3-t2)/1e3, (t3-t1)/1e3)
}
// 逐行读取文件
func read_file(fp string) map[string][]string {
file, err := os.Open(fp)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("读取文件错误: %s\n", err)
return nil
}
defer file.Close()
br := bufio.NewReader(file)
//声明一个切片
// var file_list []string
//声明一个 map
mapList := make(map[string][]string)
for {
b_line, _, err := br.ReadLine()
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
// 向 list 中追加元素
// file_list.PushBack(string(line))
// file_list = append(file_list, string(line)+"\n")
line := string(b_line)
// 使用map
items := strings.Split(line, "|@|")
type_name := items[1]
if mapValue, has_key := mapList[type_name]; has_key {
mapValue := append(mapValue, line)
mapList[type_name] = mapValue
} else {
//创建一个临时切片
tmp_slice := []string{line}
mapList[type_name] = tmp_slice
}
}
// 输出 list 长度
// fmt.Println(file_list)
return mapList
}
func line2map(lines []string) map[string][]string {
/*
_, err := os.Stat(new_file_path)
if err == nil {
//文件存在,删除重建
}
*/
//类别
mapList := make(map[string][]string)
//第一次循环,查找分类
for _, value := range lines {
item := strings.Split(value, "|@|")
//类别名称,作为map主键
key := item[1]
if mapValue, has_key := mapList[key]; has_key {
//包含该类别, map的value继续添加
mapValue := append(mapValue, value)
mapList[key] = mapValue
} else {
//不包含该类别, 新增一个key
lines := []string{value}
mapList[key] = lines
}
/*
//判断类型是否在切片中
_, found := in_array(classes, item[1])
if !found {
classes = append(classes, item[1])
}
*/
}
//找到的类别 共12个类别
fmt.Printf("找到的%d类别:\n", len(mapList))
return mapList
}
/*
Find获取一个切片并在其中查找元素。
如果找到它,它将返回它的密钥,否则它将返回-1和一个错误的bool
*/
//从切片中查找
func in_array(slice []string, val string) (int, bool) {
for i, item := range slice {
if item == val {
return i, true
}
}
return -1, false
}
// 写入文件
func write_file(mapList map[string][]string, new_file_path string) {
file_handle, err := os.OpenFile(new_file_path, os.O_CREATE|os.O_RDWR, 0666)
buf := bufio.NewWriter(file_handle)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("打开新文件错误:", err)
return
}
defer file_handle.Close()
//遍历map
for key, value := range mapList {
fmt.Printf("--%s %v\n", key, len(value))
for nu := range value {
// fmt.Print(value[nu]) //行末带有换行符
buf.WriteString(value[nu])
}
}
//缓存写入文件
/*
fmt.Println(item)
fmt.Printf("%v | %v", key, string(value))
*/
err = buf.Flush()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("写入磁盘错误: ", err)
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号