46. 全排列
全排列
第一个字符有三种选择(a,b,c)
第二个字符有两种选择,因为前面选过的字符不能再用
第三个字符只有一种选择
这个也是从左往右尝试的模型
eg:
a b c
排列过程
1:a b c
2:a c b
3:b a c
4:b c a
5:c a b
6:c b a
public static List<String> getAllC(String s){
//准备收集的结果集
List<String> ans =new ArrayList<>();
//把待处理字符串处理成字符集合
List<Character> chs=new ArrayList<>();
for(char cha:s.toCharArray()){
chs.add(cha);
}
//递归处理
process(chs,"",ans);
return ans;
}
/**
*
set中的所有字符都可以选择,
形成的所有全排列放入到ans中
沿途的决定是path
*/
public static void process(List<Character> set,String path,List<String> ans){
//base case
if(set.isEmpty()){
ans.add(path);
}
//set中每个字符都可以作为当前字符,但是一旦当前决定要,后续就不能再使用了
for(int i=0;i<set.size();i++){//1,2,3. 1 ,(2,3)
//分别将i作为当前的决定,
//这里要特别注意,不能用path+=,而要重新申请一个变量来接
String pick=path+set.get(i);
//拷贝一分,再把当前位置的字符去掉,相当于把当前字符排除了考虑
List<Character> nextSet=new ArrayList<>(chs);
//把当前位置的字符移除掉
next.remove(i);
process(nextSet,pick,ans);
}
}
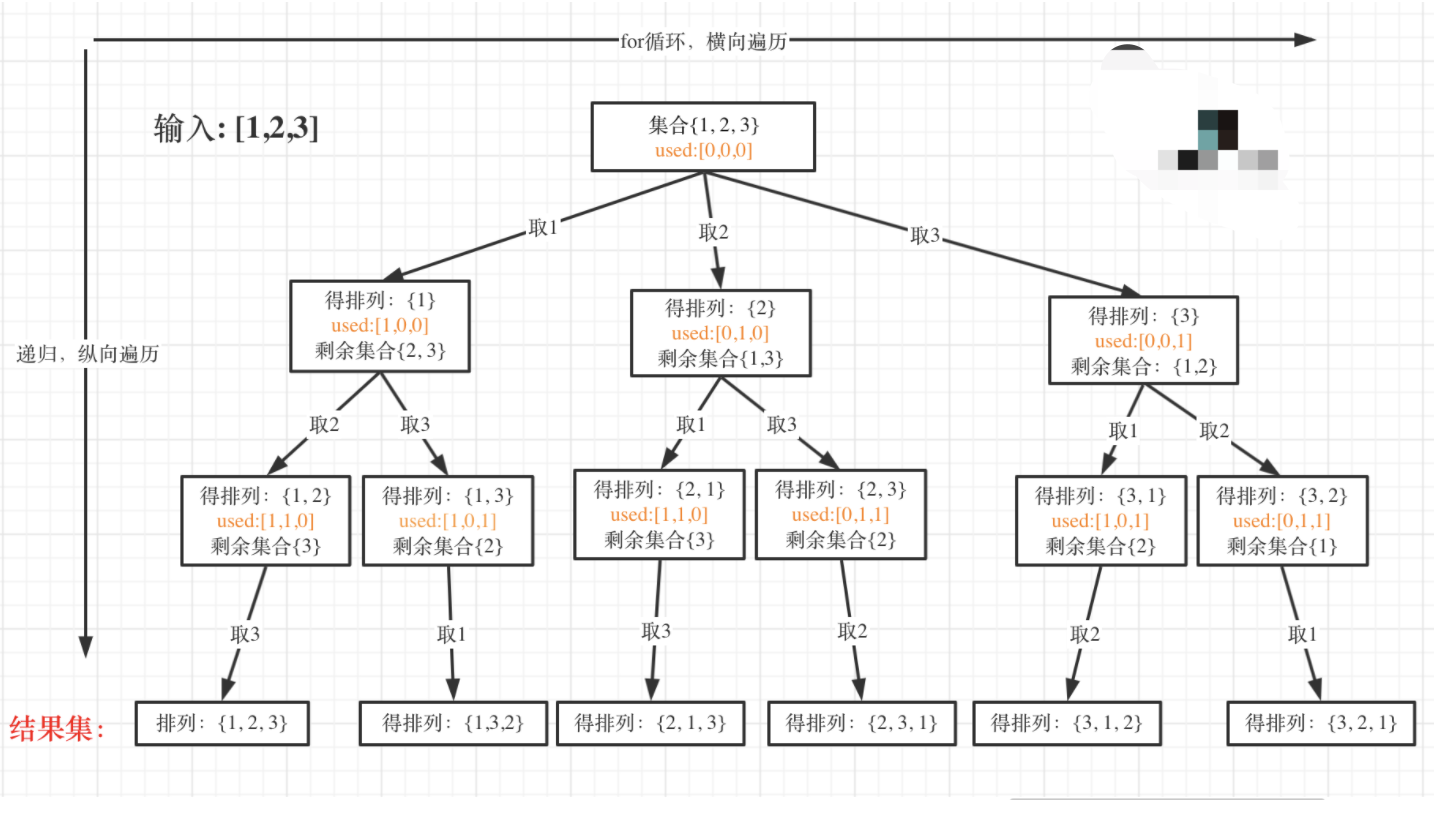
46. 全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6
-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
nums 中的所有整数 互不相同
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> numList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
numList.add(nums[i]);
}
List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();
process(numList,path,ans,numList.size());
return ans;
}
private void process(List<Integer> numList,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> ans,int size){
//base case
if(numList.isEmpty()){
ans.add(path);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<numList.size();i++){
//这里注意不能直接 path.add(numList.get(i)),否则递归后会把所有数字都会收集到path中
//而是要用新的变量来接
List<Integer> pick=new ArrayList<>(path);
pick.add(numList.get(i));
List<Integer> nextList=new ArrayList<>(numList);
nextList.remove(i);
process(nextList,pick,ans,numList.size());
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号