RT-Thread - rtservice.h分析
本笔记作为自己的学习记录,纯属个人理解。
rtservice.h是 RT_Thread中关于双向链表和单相链表的相关定义。
双向链表主要实现了节点插入、删除、是否为空、计算链表长度的功能。这里主要分析一下是否为空、计算链表长度的功能。
是否为空:
1 rt_inline int rt_list_isempty(const rt_list_t *l) 2 { 3 return l->next == l; 4 }
计算链表长度:
1 rt_inline unsigned int rt_list_len(const rt_list_t *l) 2 { 3 unsigned int len = 0; 4 const rt_list_t *p = l; 5 while (p->next != l) 6 { 7 p = p->next; 8 len ++; 9 } 10 11 return len; 12 }
这里输入的变量 const rt_list_t *l 其实是一个链表节点,这个节点作为链表头节点在使用时候创建,并初始化为指向本身,这个节点是一直存在的,也即链表至少有一个头节点存在。理解了这一点上边两个函数就好理解了。
下面在看一个重要的宏 rt_list_entry,这个宏本质是 rt_container_of,获取list的拥有者的入口地址。
1 #define rt_list_entry(node, type, member) \ 2 rt_container_of(node, type, member)
1 #define rt_container_of(ptr, type, member) \ 2 ((type *)((char *)(ptr) - (unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)))
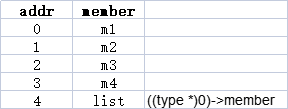
例如如下一个结构体
1 struct obj { 2 uint8_t m1; 3 uint8_t m2; 4 uint8_t m3; 5 uint8_t m4; 6 rt_list_t list; 7 ... 8 };
(char *)(ptr):ptr 是一个指向list的指针,转换为一个char 类型的指针;
(type *)0:等价于将0转换为一个指向 obj 类型变量的指针,且变量存储地址为0;
(type *)0)->member:获取 obj 类型的member元素,即 list 元素;
&((type *)0)->member:获取 obj 类型的 list 元素的地址,由于首地址为0,所以这个地址也是 list 元素相对于结构体变量的存储地址的偏移地址
(char *)(ptr) - (unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)):指向list的指针 减去 偏移地址,就指向了 list 元素所在结构体的存储地址,也即得到了结构体变量指针
其内存地址空间如下:
单相链表的内容相对好理解一些,就不再赘述了。下面是rtservice.h的部分代码,仅供参考
1 #define rt_container_of(ptr, type, member) \ 2 ((type *)((char *)(ptr) - (unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member))) 3 4 #define RT_LIST_OBJECT_INIT(object) { &(object), &(object) } 5 6 rt_inline void rt_list_init(rt_list_t *l) 7 { 8 l->next = l->prev = l; 9 } 10 11 rt_inline void rt_list_insert_after(rt_list_t *l, rt_list_t *n) 12 { 13 l->next->prev = n; 14 n->next = l->next; 15 16 l->next = n; 17 n->prev = l; 18 } 19 20 rt_inline void rt_list_insert_before(rt_list_t *l, rt_list_t *n) 21 { 22 l->prev->next = n; 23 n->prev = l->prev; 24 25 l->prev = n; 26 n->next = l; 27 } 28 29 rt_inline void rt_list_remove(rt_list_t *n) 30 { 31 n->next->prev = n->prev; 32 n->prev->next = n->next; 33 34 n->next = n->prev = n; 35 } 36 37 rt_inline int rt_list_isempty(const rt_list_t *l) 38 { 39 return l->next == l; 40 } 41 42 rt_inline unsigned int rt_list_len(const rt_list_t *l) 43 { 44 unsigned int len = 0; 45 const rt_list_t *p = l; 46 while (p->next != l) 47 { 48 p = p->next; 49 len ++; 50 } 51 52 return len; 53 } 54 55 #define rt_list_entry(node, type, member) \ 56 rt_container_of(node, type, member) 57 58 #define rt_list_for_each(pos, head) \ 59 for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) 60 61 rt_inline void rt_slist_init(rt_slist_t *l) 62 { 63 l->next = RT_NULL; 64 } 65 66 rt_inline void rt_slist_append(rt_slist_t *l, rt_slist_t *n) 67 { 68 struct rt_slist_node *node; 69 70 node = l; 71 while (node->next) node = node->next; 72 73 /* append the node to the tail */ 74 node->next = n; 75 n->next = RT_NULL; 76 } 77 78 rt_inline void rt_slist_insert(rt_slist_t *l, rt_slist_t *n) 79 { 80 n->next = l->next; 81 l->next = n; 82 } 83 84 rt_inline unsigned int rt_slist_len(const rt_slist_t *l) 85 { 86 unsigned int len = 0; 87 const rt_slist_t *list = l->next; 88 while (list != RT_NULL) 89 { 90 list = list->next; 91 len ++; 92 } 93 94 return len; 95 } 96 97 rt_inline rt_slist_t *rt_slist_remove(rt_slist_t *l, rt_slist_t *n) 98 { 99 /* remove slist head */ 100 struct rt_slist_node *node = l; 101 while (node->next && node->next != n) node = node->next; 102 103 /* remove node */ 104 if (node->next != (rt_slist_t *)0) node->next = node->next->next; 105 106 return l; 107 } 108 109 rt_inline rt_slist_t *rt_slist_first(rt_slist_t *l) 110 { 111 return l->next; 112 } 113 114 rt_inline rt_slist_t *rt_slist_tail(rt_slist_t *l) 115 { 116 while (l->next) l = l->next; 117 118 return l; 119 } 120 121 rt_inline rt_slist_t *rt_slist_next(rt_slist_t *n) 122 { 123 return n->next; 124 } 125 126 rt_inline int rt_slist_isempty(rt_slist_t *l) 127 { 128 return l->next == RT_NULL; 129 } 130 131 #define rt_slist_entry(node, type, member) \ 132 rt_container_of(node, type, member)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号