dubbo-spi
ExtensionLoader 获取扩展点原理
ExtensionLoader 容器作为 Dubbo 内部扩展点、成员变量等元素的加载容器。内部含有以下成员变量及其用途:
// dubbo-spi 扫描的文件目录
private static final String SERVICES_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/services/";
private static final String DUBBO_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/dubbo/";
private static final String DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY = DUBBO_DIRECTORY + "internal/";
// class 对象到 ExtensionLoader 的映射
private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> EXTENSION_LOADERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// class 对象到扩展点对象实例的映射
private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Object> EXTENSION_INSTANCES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// class 对象到扩展点名称的映射
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, String> cachedNames = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 扩展点名称到 class 对象的映射
private final Holder<Map<String, Class<?>>> cachedClasses = new Holder<>();
// Holder 用于保存已经实例化的扩展点对象
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Holder<Object>> cachedInstances = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 自适应扩展点对象
private final Holder<Object> cachedAdaptiveInstance = new Holder<>();
// 自适应扩展点 class
private volatile Class<?> cachedAdaptiveClass = null;
核心方法
getExtensionLoader:根据扩展点原始类型初始化ExtensionLoader加载器。
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {
// 校验扩展点类型,检查过滤
if (type == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");
}
if (!type.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type + ") is not an interface!");
}
if (!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type +
") is not an extension, because it is NOT annotated with @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + "!");
}
// 实例化 ExtensionLoader 并保存到全局容器中
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader;
}
getExtension(String name):根据对象名称获取扩展点的入口方法,首先从cachedInstances集合中根据 Name 获取扩展点实现对象;如果为空,通过createExtension(String name)方法创建扩展点对象,方法内会依次调用getExtensionClasses()、loadExtensionClasses()方法来加载扩展点 Class 对象。
public T getExtension(String name) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension name == null");
}
// 获取默认扩展点
if ("true".equals(name)) {
return getDefaultExtension();
}
// 从本地缓存 cachedInstances 中获取扩展点 Holder 对象
final Holder<Object> holder = getOrCreateHolder(name);
Object instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (holder) {
instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
// 缓存扩展点为空,单例模式创建扩展点对象
instance = createExtension(name);
holder.set(instance);
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
// 根据名称创建扩展点实例
private T createExtension(String name) {
// 获取扩展点 Class 对象
Class<?> clazz = getExtensionClasses().get(name);
if (clazz == null) {
throw findException(name);
}
try {
// 从全局容器中获取扩展点对象
T instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
// 反射创建扩展点对象
if (instance == null) {
EXTENSION_INSTANCES.putIfAbsent(clazz, clazz.newInstance());
instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
}
// 依赖注入
injectExtension(instance);
// 如果对象含有包装类,进一步增强
Set<Class<?>> wrapperClasses = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(wrapperClasses)) {
for (Class<?> wrapperClass : wrapperClasses) {
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));
}
}
return instance;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance (name: " + name + ", class: " +
type + ") couldn't be instantiated: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
// 加载扩展点 Class 对象
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
// 根据 @SPI 注解加载默认扩展点名
cacheDefaultExtensionName();
// 加载 META-INF/services/、META-INF/dubbo/、META-INF/dubbo/internal 目录下扩展点的 Class 对象
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<>();
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
return extensionClasses;
}
// 加载指定配置文件,根据实例名解析 Class 对象并存储到 extensionClasses 集合中
private void loadDirectory(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir, String type) {
String fileName = dir + type;
try {
Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls;
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
java.net.URL resourceURL = urls.nextElement();
loadResource(extensionClasses, classLoader, resourceURL);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception occurred when loading extension class (interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}
ExtensionLoader 依赖注入实现原理
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
if (objectFactory == null) {
return instance;
}
try {
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
// 获取目标 setter 方法
if (!isSetter(method)) {
continue;
}
/**
* Check {@link DisableInject} to see if we need auto injection for this property
*/
if (method.getAnnotation(DisableInject.class) != null) {
continue;
}
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (ReflectUtils.isPrimitives(pt)) {
continue;
}
// 获取方法对应属性(首字母小写然后拼接)
try {
String property = getSetterProperty(method);
// 反射调用属性 set 方法
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);
if (object != null) {
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}
自适应扩展点原理
自适应扩展点在框架方法运行时才决定应该调用哪一个扩展点实现,因此不能指定某个扩展点而是依赖一个代理,这个代理就是自适应扩展点。
Dubbo 自适应扩展点的原理如下:
- 定义
@Adaptive注解,标记在类或者方法上,有此标记都支持自适应扩展点; - 通过
ExtensionLoader.getAdaptiveExtension()获取自适应扩展点,获取过程中拼接自适应扩展点 Class 文件,编译为 Class 并实例化。
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
if (createAdaptiveInstanceError != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to create adaptive instance: " +
createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(),
createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
// 加载自适应扩展点对象
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
// 读取配置文件,加载获取扩展点 Class 对象实例
getExtensionClasses();
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
// 创建自适应扩展点对象
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
// 生成 Class 字符串
String code = new AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator(type, cachedDefaultName).generate();
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
// 编译 Class 字符串并返回 Class 对象
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
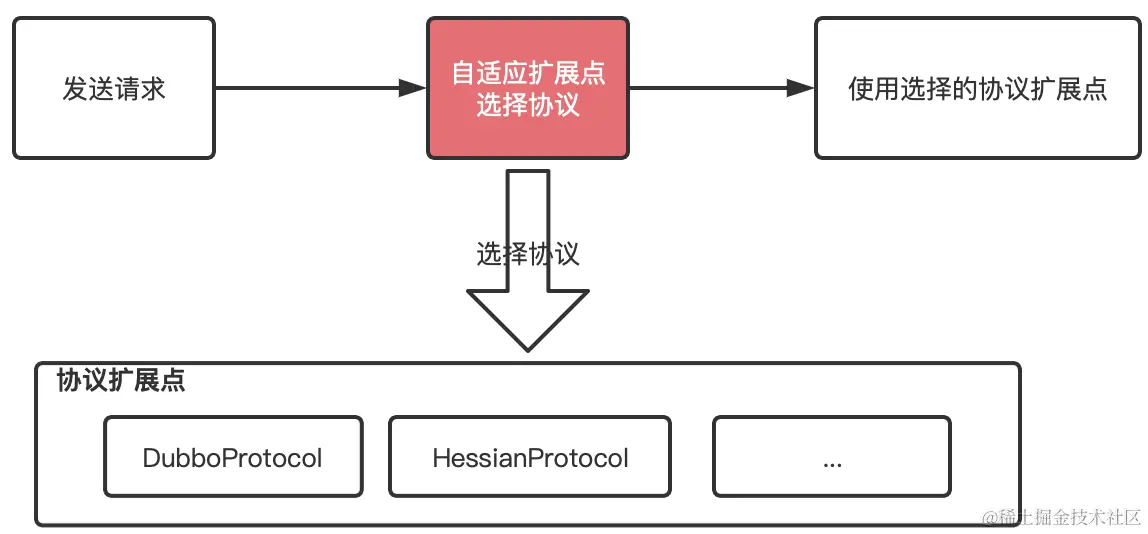
比如 Protocol 这个接口:
@SPI("protocol")
public interface Protocol {
@Adaptive({"protocol"})
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) thorws RpcException;
}
使用时如果想要暂时获取自适应扩展点:
Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
我们跟进 getAdaptiveExtension():
//ExtensionLoader.getAdaptiveExtension()
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//加载扩展点Class
//此处的getExtensionClasses(),包含了解析配置文件、加载类等逻辑。
getExtensionClasses();
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
// 创建自适应扩展点Class,这里有点动态代理的意思了
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
//ExtensionLoader.createAdaptiveExtensionClass()
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//生成Class字符串,里面通过拼接字符串实现。可以跟进去generate()看一看。
String code = new AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator(type, cachedDefaultName).generate();
//将Class字符串编译为Class,并返回
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
接下来就是拼接 Class 字符串,生成后的 Protocol 自适应扩展点 Class 内容为:
package org.apache.dubbo.rpc;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
//类名=扩展点接口名$Adaptive
public class Protocol$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
//生成标记有@Adaptive的方法
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
//核心代码在这里,运行时解析url里的protocol参数
//这里还有个默认值的处理,取的是Protocol接口@SPI注解里的value
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
//根据protocol参数,选择指定的protocol扩展点
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.export(arg0);
}
//没标记@Adaptive的方法,调用时直接抛异常
public void destroy() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The method public abstract void org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
//没标记@Adaptive的方法,调用时直接抛异常
public int getDefaultPort() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The method public abstract int org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
//生成标记有@Adaptive的方法
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, org.apache.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
}
- 自适应扩展点类名为
扩展点接口名 $Adaptive; - 带有
@Adaptive注解的方法会生成代理方法,比如上述例子,在调用export()方法时,实际调用的是Protocol$Adaptive.export(),然后就实现了运行时指定扩展点的目的。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号