sql [not]exists和[not]in的区别
一、数据源:
grade表
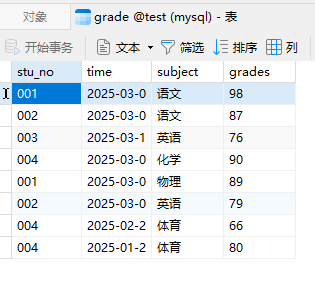
stu_info表
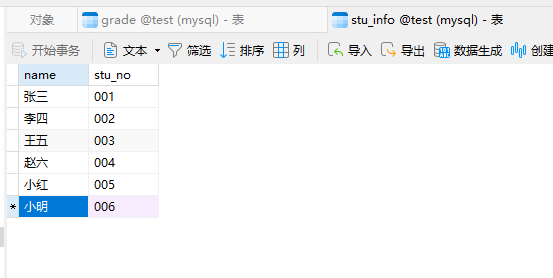
二、exists与in
2.1 in
select name from stu_info where stu_no in ( select distinct stu_no from grade);
执行结果:

执行流程:
- 首先通过子查询查出有成绩的所有学生学号
- 拿到结果后与user表进行比对
in相当于多个or,如果内表即子查询返回m条记录,那么会用外表去遍历匹配内表,查m次。
in是先查内表,在查外表。
2.2 exists
select name from stu_info where exists (select * from grade where stu_info.stu_no = grade.stu_no);
执行结果:

执行流程:
- 首先查询外表,及执行 select name from stu_info
- 然后根据每条记录执行内表,判断内表中where条件是否成立,成立返回true,该行记录保留;不成立返回false,该行记录舍弃,得到最终结果。
exists是先查外表,再查内表,根据外表行数去逐条查询。
2.3 区别:
内表m条,外表n条
in:循环比对n次
exists:循环比对m次
2.4 什么时候用in什么时候用exists?
- 当内表大外表小,即m>n时,使用in
- 当内表小外表大,即m<n时,使用exists
- 当内表外表数据量差距很小时,用哪个都可以
三、not in 与 not exists:
比对结果与上述相反,但执行流程与上述相同
select name from stu_info where stu_no not in ( select distinct stu_no from grade);
select name from stu_info where not exists (select * from grade where stu_info.stu_no = grade.stu_no);
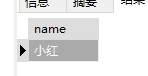
结果均为:
四、注意事项
- exists子句中返回结果只为true或false,因此无论select后面时*或者某些字段效果都一样,mysql在子查询中忽略这些字段。
如select name from stu_info where exists (select * from grade where stu_info.stu_no = grade.stu_no);与select name from stu_info where exists (select 1 from grade where stu_info.stu_no = grade.stu_no);执行结果是相同的。 - exists子句中返回任意行即为true,即便是包含null值的行,若不返回任何行则为false。
如:select name from stu_info where exists (select null);等同于select name from stu_info;,因为select null返回含null的行,exists子句返回true。
select name from stu_info where exists (select * from grade where stu_no = '100');等同于select name from stu_info where false;,不返回任意行,因为exists子查询中的结果不返回任意行,exists返回false。 - 以上可参考文档:Subqueries with EXISTS or NOT EXISTS






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号