Java8新特性之新时间与日期API
Java8新时间与日期API解决了传统的时间API(如SimpleDateFormat)存在线程安全问题。
ISO-8601日历系统是国际标准化组织制定的现代公民的日期和时间的表示法。
-
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime类的实例是不可变的对象,分别表示使用ISO-8601日历系统的日期、时间、日期和时间。它们提供了简单的日期或时间,并不包含当前的时间信息,也不包含与时区相关的信息。
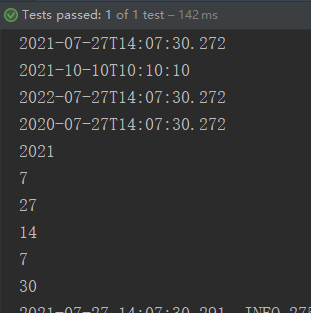
@Test public void test1(){ // 1、LocalDateTime LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(ldt); LocalDateTime ldt2 = LocalDateTime.of(2021, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10); System.out.println(ldt2); LocalDateTime ld3 = ldt.plusYears(1); System.out.println(ld3); LocalDateTime ld4 = ldt.minusYears(1); System.out.println(ld4); System.out.println(ldt.getYear()); System.out.println(ldt.getMonthValue()); System.out.println(ldt.getDayOfMonth()); System.out.println(ldt.getHour()); System.out.println(ldt.getMinute()); System.out.println(ldt.getSecond()); }
- Instant:时间戳(以Unix元年:1970年1月1日 00:00:00 到某个时间之间的毫秒值)
@Test
public void test2(){
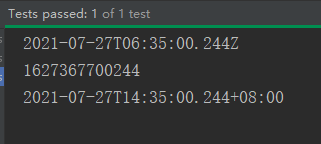
// 2、Instant:时间戳(以Unix元年:1970年1月1日 00:00:00 到某个时间之间的毫秒值)
Instant ins1 = Instant.now(); //默认获取UTC时区
System.out.println(ins1);
System.out.println(ins1.toEpochMilli());
OffsetDateTime odt = ins1.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(odt);
}
- Duration : 计算两个“时间”之间的间隔
@Test
public void test3(){
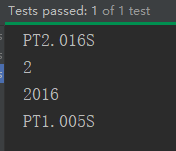
// 3、Duration : 计算两个“时间”之间的间隔
Instant ins1 = Instant.now();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Instant ins2 = Instant.now();
Duration duration = Duration.between(ins1, ins2);
System.out.println(duration);
System.out.println(duration.getSeconds());
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());
LocalTime lt1 = LocalTime.now();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
LocalTime lt2 =LocalTime.now();
Duration duration2 = Duration.between(lt1, lt2);
System.out.println(duration2);
}
- Period:计算两个“日期”之间的间隔
@Test
public void test4(){
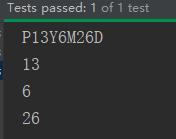
// 4、Period : 计算两个“日期”之间的间隔
LocalDate ld1 = LocalDate.of(2008,1,1);
LocalDate ld2 = LocalDate.now();
Period period = Period.between(ld1, ld2);
System.out.println(period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
}
-
TemporalAdjuster:时间校正器。有时我们可能需要获取例如:将日期调整到“下周一”等操作。
TemporalAdjusters:该类通过静态方法提供了大量的常用TemporalAdjuster实现。
@Test public void test5(){ LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(ldt); LocalDateTime ldt2 = ldt.withDayOfMonth(3); System.out.println(ldt2); LocalDateTime ldt3 = ldt.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.MONDAY)); System.out.println(ldt3); //自定义下一个工作日 LocalDateTime ldt5 = ldt.with((l) -> { LocalDateTime ldt4 = (LocalDateTime) l; DayOfWeek dow = ldt4.getDayOfWeek(); if (dow.equals(DayOfWeek.FRIDAY)) { return ldt4.plusDays(3); } else if (dow.equals(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY)) { return ldt4.plusDays(2); } else { return ldt4.plusDays(1); } }); System.out.println(ldt5); }
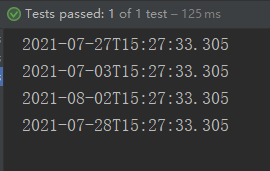
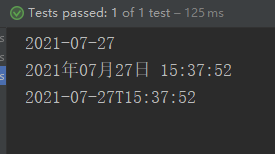
- DateTimeFormatter:格式化时间/日期
@Test
public void test6(){
//DateTimeFormatter:格式化时间/日期
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE;
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
String strDate = dtf.format(ldt);
System.out.println(strDate);
DateTimeFormatter dtf2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String strDate2 = dtf2.format(ldt);
System.out.println(strDate2);
LocalDateTime newDate = ldt.parse(strDate2,dtf2);
System.out.println(newDate);
}
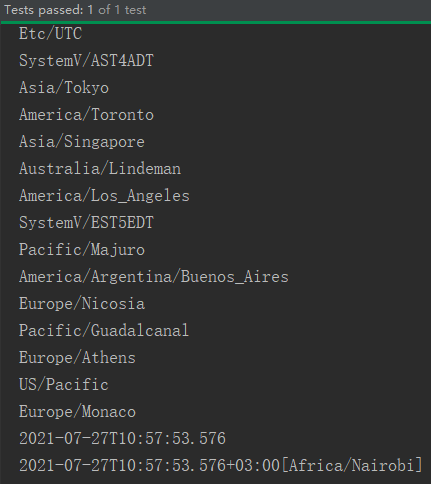
-
时区的处理。Java8中加入了对时区的支持,带时区的时间分别为:ZonedDate、ZonedTime、ZonedDateTime。其中每个时区都对应着ID,地区ID都为“{区域}/{城市}”的格式(eg: Asia/Shanghai)等。
ZoneId:该类中包含了所有的时区信息
getAvailableZoneIds():可以获取所有时区信息。
of(id):用指定的时区信息获取ZoneId对象。
@Test public void test7(){ //ZonedDate、ZonedTime、ZonedDateTime Set<String> set = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds(); set.stream().forEach(System.out::println); LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Africa/Nairobi")); System.out.println(ldt); ZonedDateTime zdt = ldt.atZone(ZoneId.of("Africa/Nairobi")); System.out.println(zdt); }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号