Stanford_CS224W----Graph Neural Networks
Stanford_CS224W----Graph Neural Networks
这节课讲解了GNN中的一些普遍概念,为后面讲特定的GCN GraphSage等奠定基础
Deep learning for Graphs
在对图做深度学习时,主要的思想是,使用节点序无关的函数对图进行处理(当然有也有特例)。在这个思想上,其他的CNN,RNN甚至MLPs不能作用到图上。
解决思想:Node's neighborhood defines a computation graph---节点的领域构成了一个计算图,基于本地网络邻域生成节点嵌入
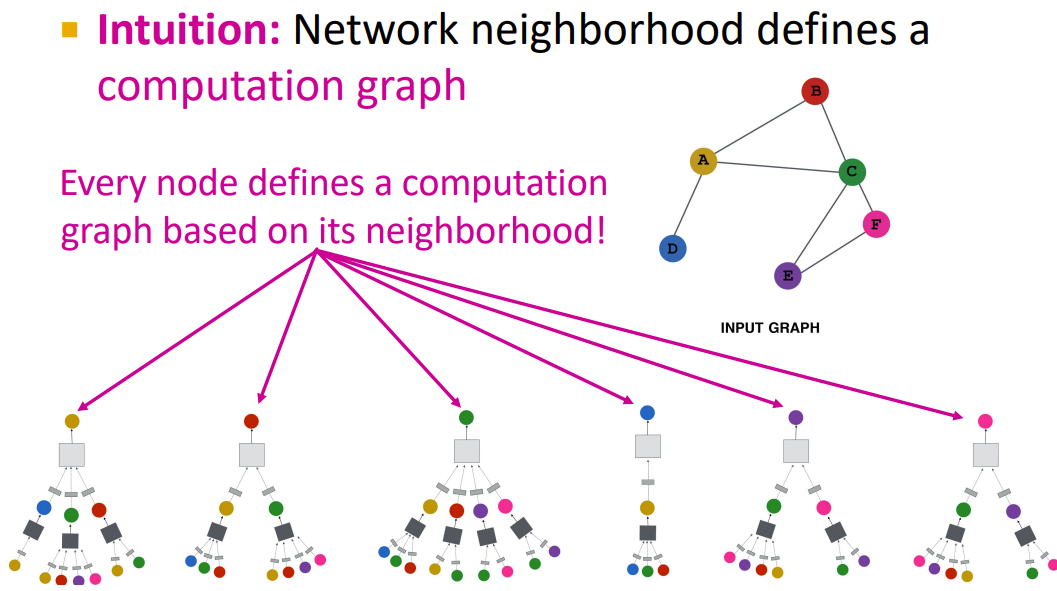
可以看到上午的矩形是灰色的,那里体现出了每种GNN方法的差异。
A Single GNN Layer
分为message计算和message聚合
- Message: each node computes a message
- Aggregation: aggregate messages from neighbors
GCN
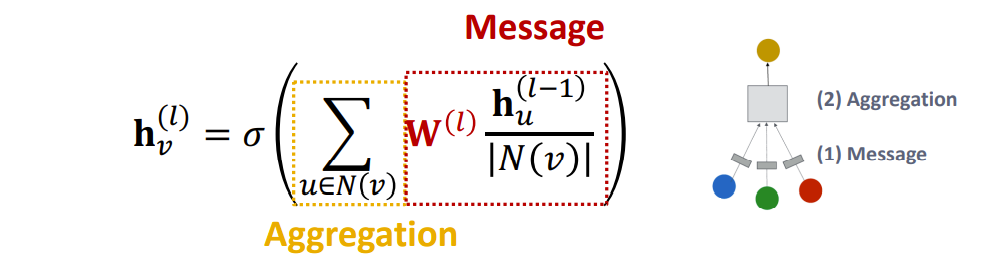
- Message
- Aggregation
GraphSAGE
其中AGG代表了许多种计算message的方法,以下都是可用的
- Mean
- Pool: Transform neighbor vectors and apply symmetric vector function Mean(⋅) or Max(⋅)
- LSTM
- ℓ2 Normalization 可选的正则化
GAT
其中的\(\alpha_{v u}\)代表了u->v的消息的权重大小,注意这些权重是训练过程中的副产物
- Multi-head attention 稳定了注意力机制的学习过程,初始化不同的注意力权重,它们落到不同的优化区域中
benefit:
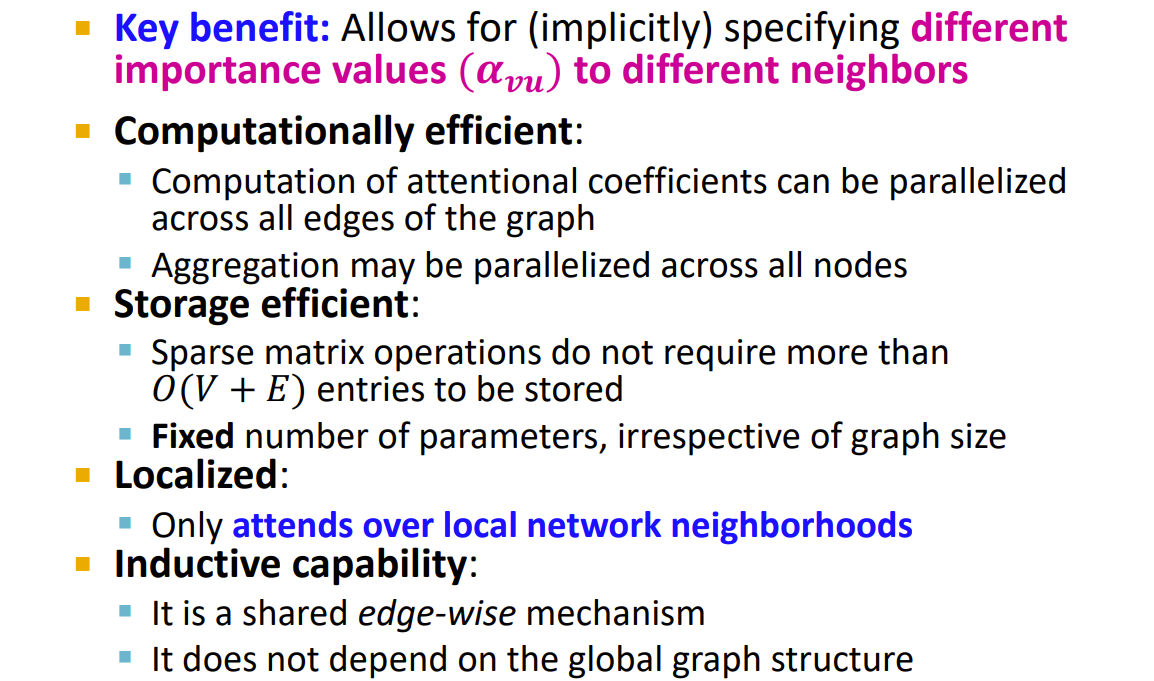
practice in GNN
How to make a shallow GNN more expressive?
Solution 1: Increase the expressive power within each GNN layer
在每一层的内部添加一些多层感知机进行计算
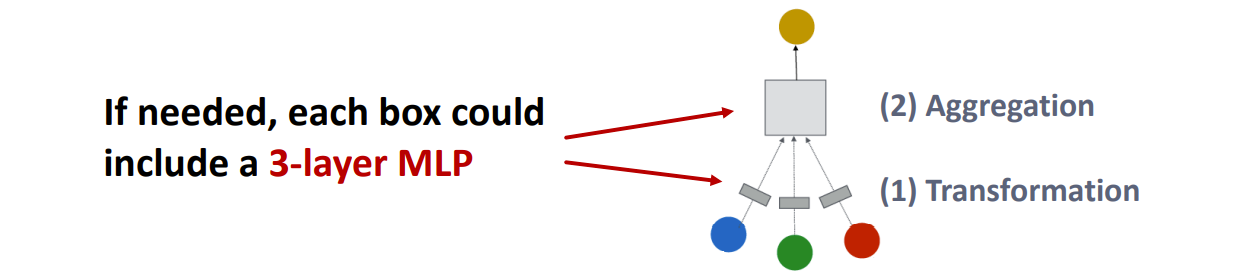
Solution 2: Add layers that do not pass messages
添加一些多层感知机的层
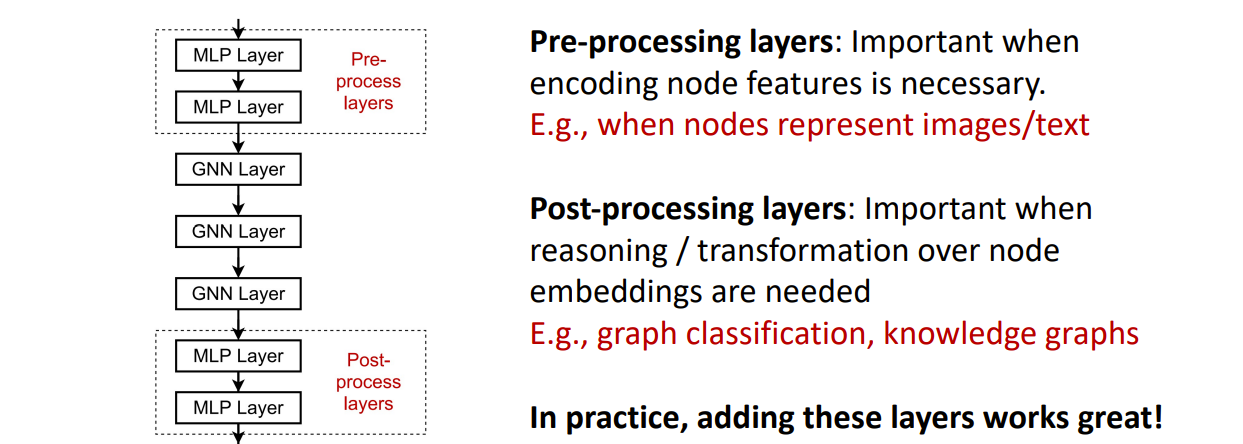
What if my problem still requires many GNN layers
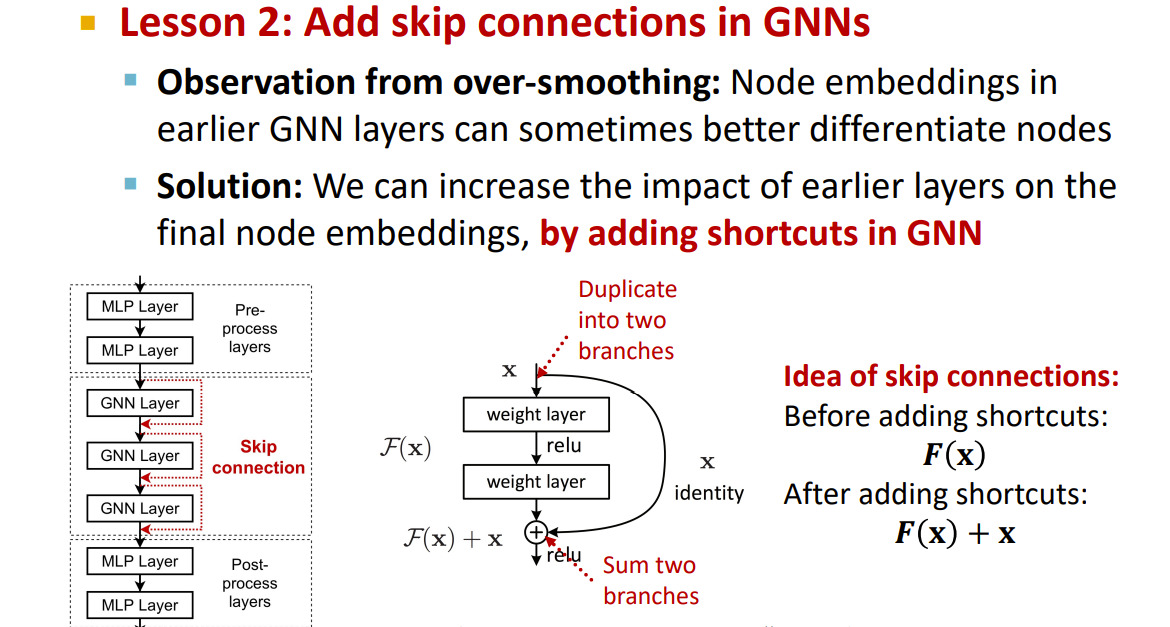
The Over-smoothing Problem
Stack many GNN layers -》 nodes will have highly-overlapped receptive fields -》 node embeddings will be highly similar -》 suffer from the over-smoothing problem
危害:所有的节点嵌入都收敛到相同的值。
Solution 1

Solution 2
Augment Graphs
有些时候输入的图需要进行处理,并不是可计算的图。会碰到以下这些情况:
- Features
- 输入的图缺少特征 -> 自定义特征
- Graph tructure
- 图稀疏->消息传递十分低效->添加虚拟节点或者边
- 图稠密->消息传递花费多->进行邻居采样
- 图巨大->难以使用GPU计算->对子图进行采样
解决方法
feature augmentation
-
图没有特征
- 两种方法及对比
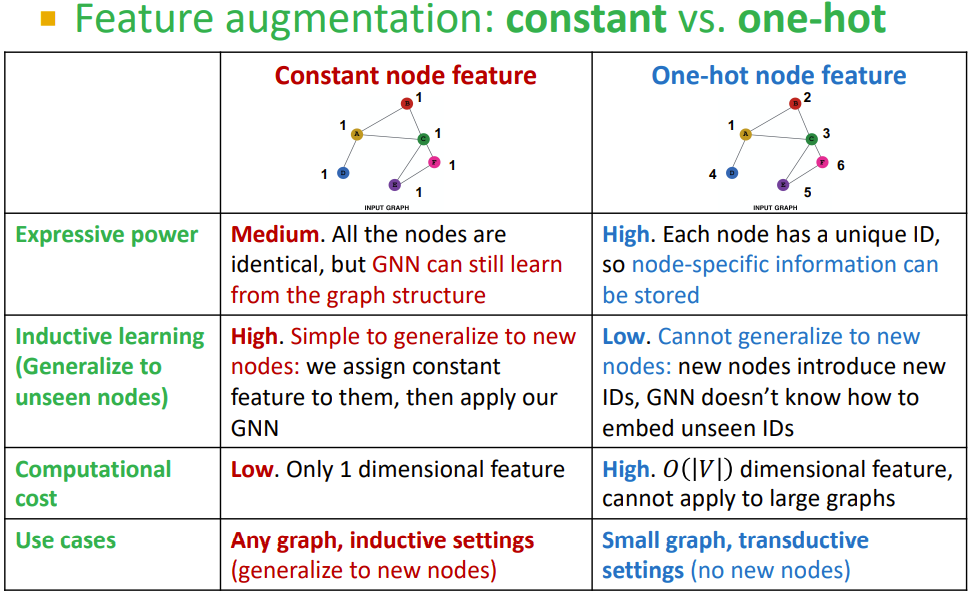
- 两种方法及对比
-
部分特定的结构难以被GNN学习:比如在环中的点,因为计算树结构相同(如果没有点的特定特征),无法得出3环形图和4环形图的区别。
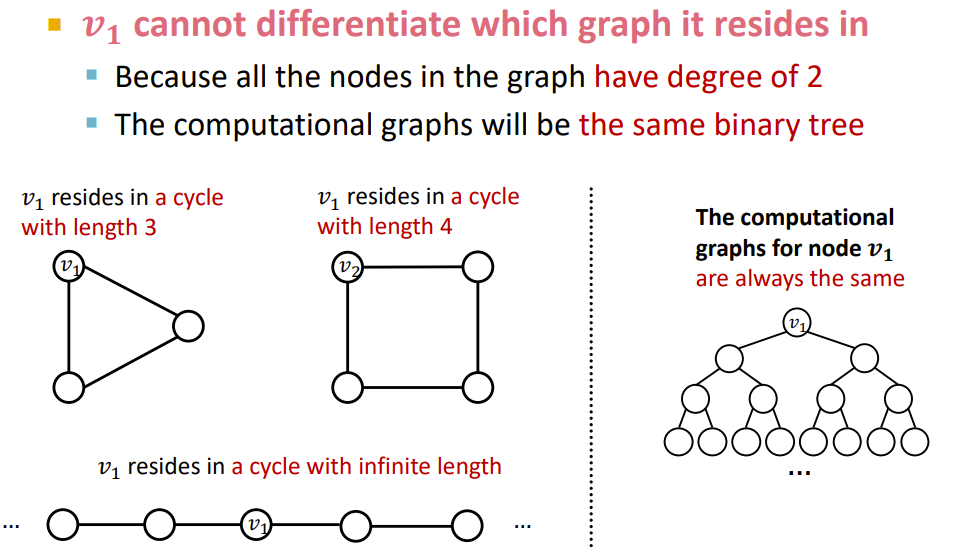
一些可以用的方法
- Node degree
- Clustering coefficient
- PageRank
- Centrality
- 其他传统机器学习的特点
Add Virual Nodes or edges
-
添加虚拟边
- 通常的方法是连接2-hop的点(在二分图类具有解释作用)
- 在邻接矩阵中为\(A+A^2\)
-
添加虚拟点
- 添加一些能连接所有点的虚拟点,因为在某些情况下,相聚很远的两个点也会产生联系。
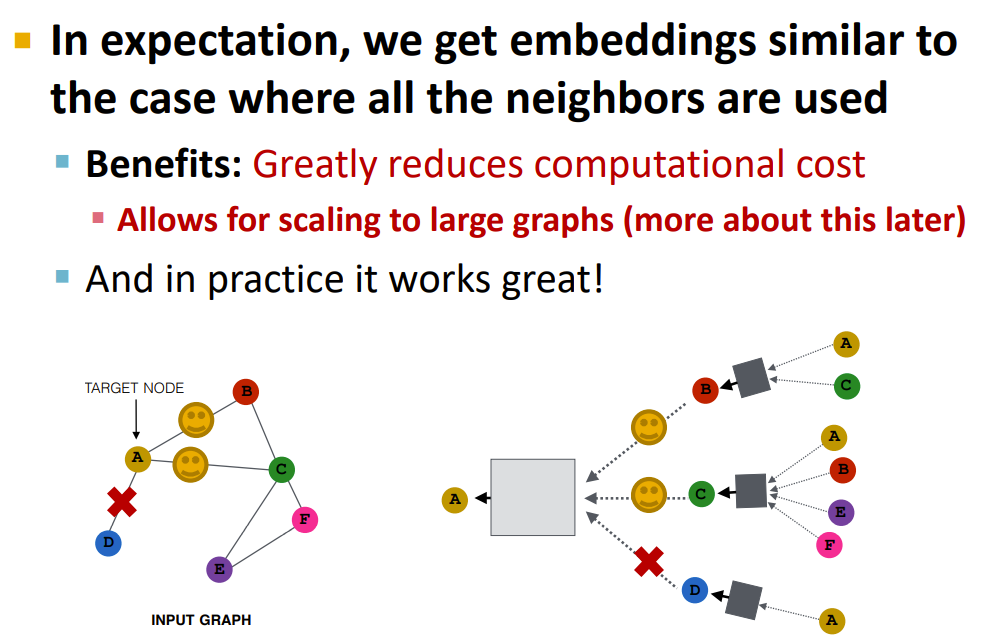
Neighborhood Samping
希望采样的邻居,在后续的聚合时,能使用所有的节点
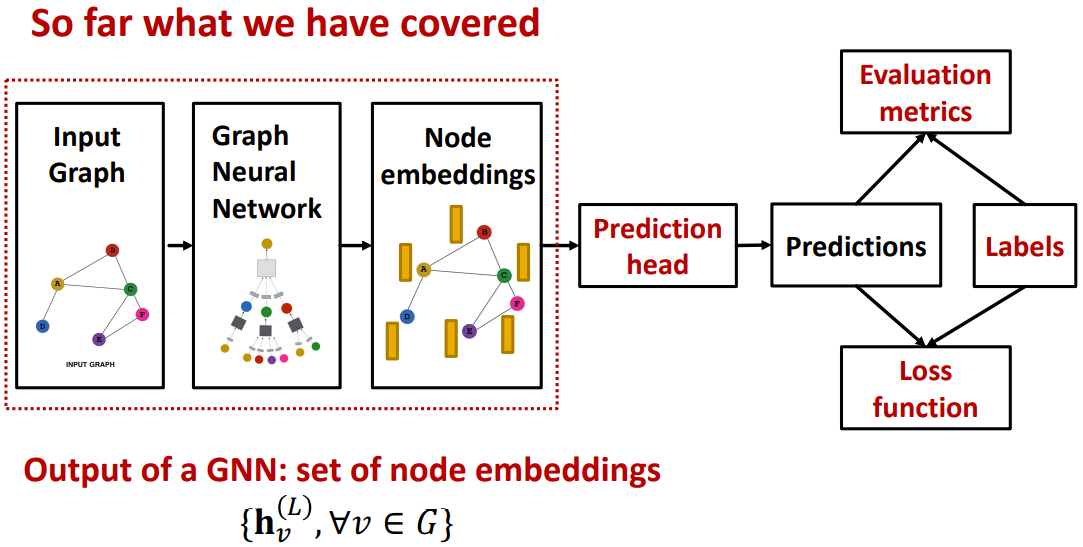
GNN Training Pipeline
目前学习了节点的嵌入,接下来会对点,边,整图的应用进行分类讲解。
Prediction heads
- Node-level tasks
- Edge-level tasks
- Graph-level tasks
Node-level tasks
可以直接使用节点嵌入进行计算
其中\(W\)为学习的参数,讲节点嵌入参数变成需要的预测值,当然这只是一个简单的例子。
Edge-level tasks
假设做一个k-way多分类。
- Concatenation + Linear
- \(\widehat{y}_{uv}=\operatorname{Linear}\left(\operatorname{Concat}\left(\mathbf{h}_{u}^{(L)},\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(L)}\right)\right)\)
- Dot product
- \(\widehat{y}_{\boldsymbol{u} v}=\left(\mathbf{h}_{u}^{(L)}\right)^{T} \mathbf{h}_{v}^{(L)}\)
- Applying to k-way prediction

Graph-level tasks
对所有的节点的嵌入向量进行处理,不同的方法对应不同的函数。
- Global mean pooling
- \(\widehat{y}_{G}=\operatorname{Mean}\left(\left\{\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(L)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}, \forall v \in G\right\}\right)\)
- Global max pooling
- \(\widehat{y}_{G}=\operatorname{Max}\left(\left\{\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(L)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}, \forall v \in G\right\}\right)\)
- Global sum pooling
- \(\widehat{y}_{G}=\operatorname{Sum}\left(\left\{\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(L)} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}, \forall v \in G\right\}\right)\)
根据不同的应用和图需要的特点,选择不同的方法
Issue:在pooling中会存在信息的丢失
A solution: hierarchical--DiffPool
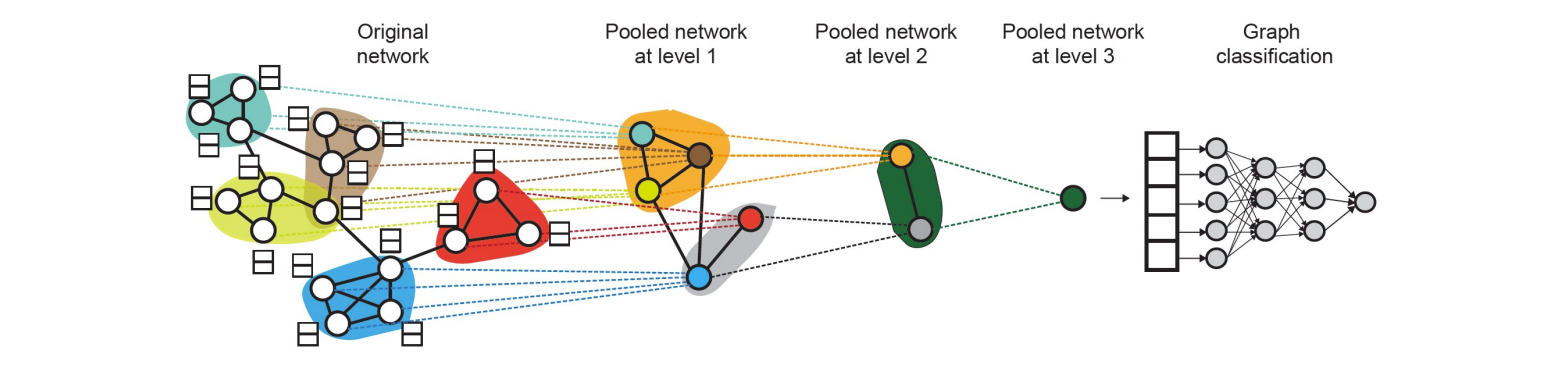
每层都有两个神经网络
- GNN A: Compute node embeddings
- GNN B: Compute the cluster that a node belongs to
process
- Use clustering assignments from GNN B to aggregate node embeddings generated by GNN A
- Create a single new node for each cluster, maintaining edges between clusters to generated a new pooled network
Prediction & Label
Supervised Labels On Graphs

Training Loss
对于不同的任务有不同的损失
Classification Loss
Regression Loss
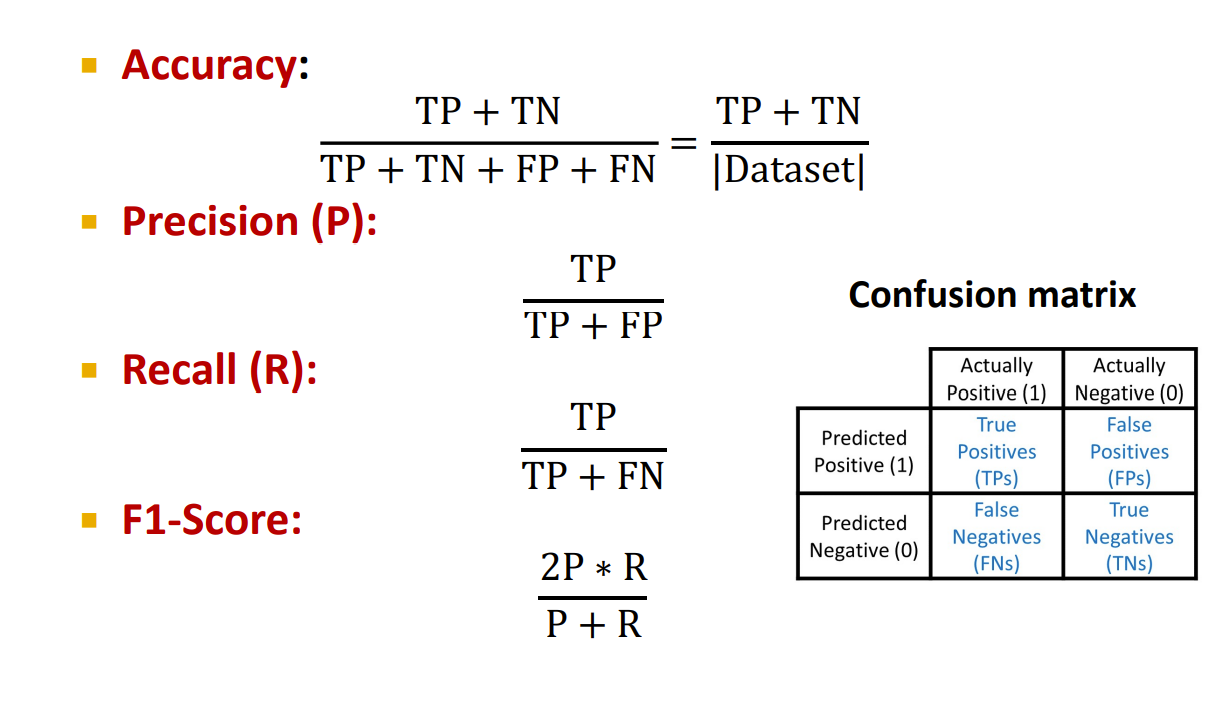
Evaluation Metrics
和常规的评估矩阵一样
Dataset Split
对于图级别的训练集和验证集的分裂和其他神经网络一样,不再赘述。
Transductive and Inductive
直推式和归纳式,
node
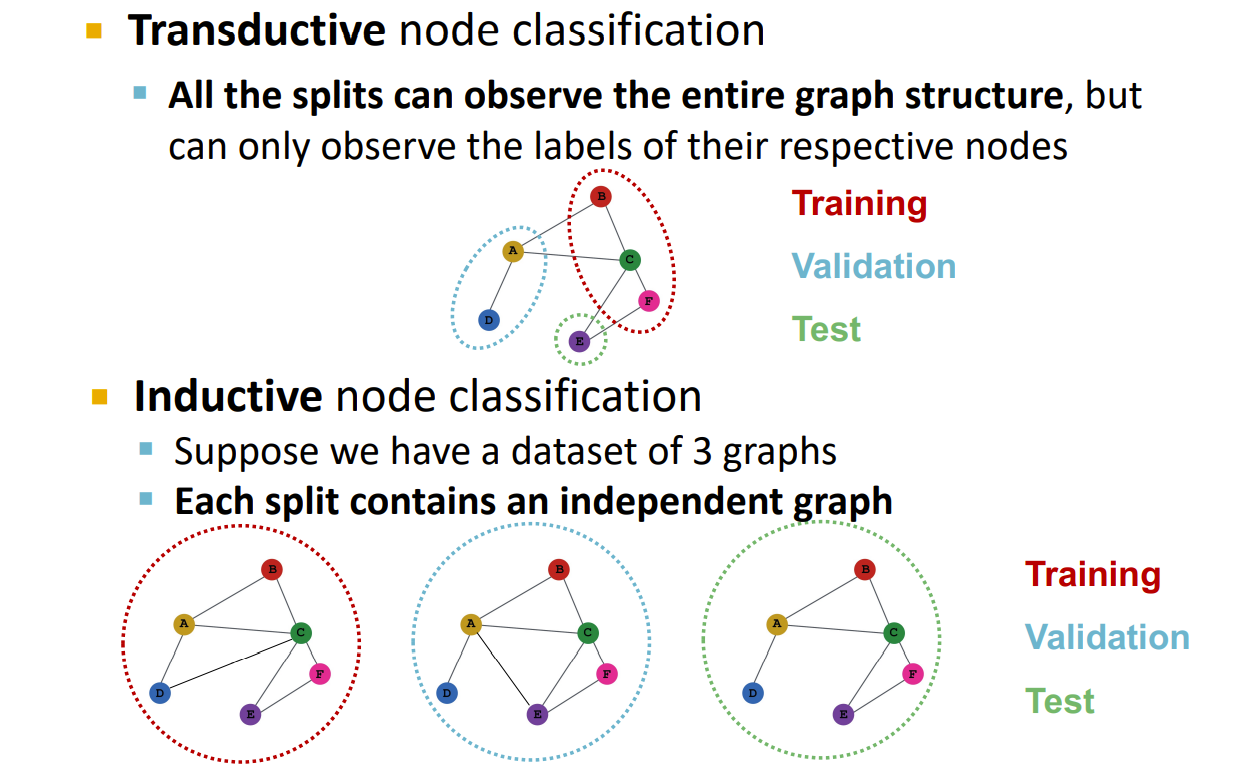
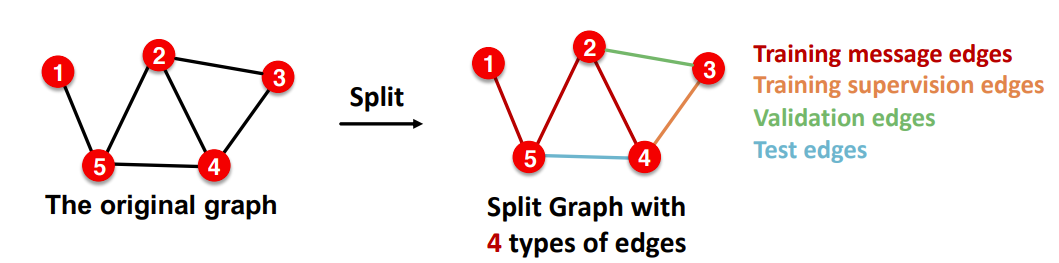
Link
Pytorch yyds。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号